
What is a repeating unit of protein?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: Proteins are large molecules having high molecular weight. These molecules are of high importance in many fields. Within the organisms, proteins perform a vast variety of functions. Some of these include performing DNA replication, acting as catalysts during biological reactions.
Complete answer:
Proteins are known as polymers, that is they are molecules of greater molecular weight composed of repeating units of smaller structural and functional units. These repeating units present in a protein molecule are known as amino acids. It is also known as the monomers in a protein polymer. These are organic compounds that contain an amino group, that is –NH2 and a carboxylic acid group –COOH, along with an R side chain group, which can be either an H atom or an alkane chain of any length. The nature of the amino acid depends on the composition of the R group. The major atoms that constitute amino acids are C, H, O, S and N. There exist about 500 naturally occurring amino acids.
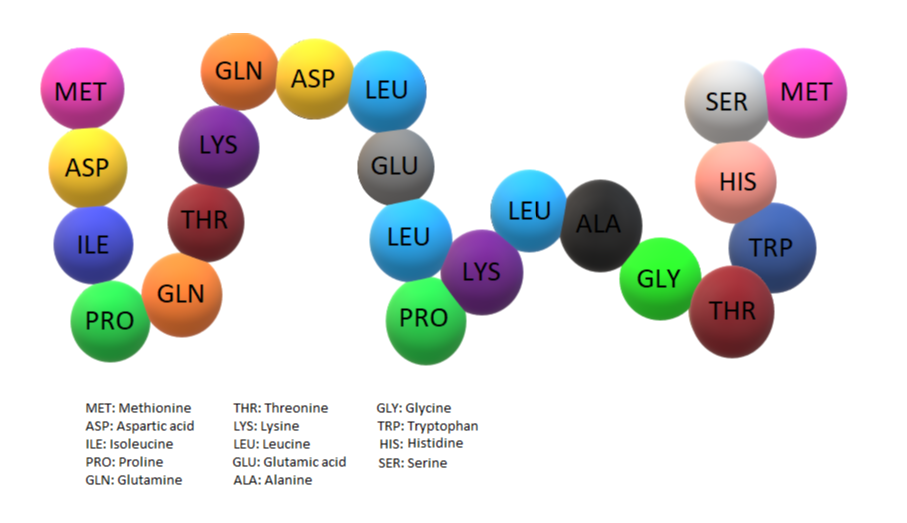
Figure: An amino acid chain making up a peptide or a protein molecule
These chains of amino acids make up a peptide chain and multiple peptide chains aligned together in various conformations make up a protein molecule.
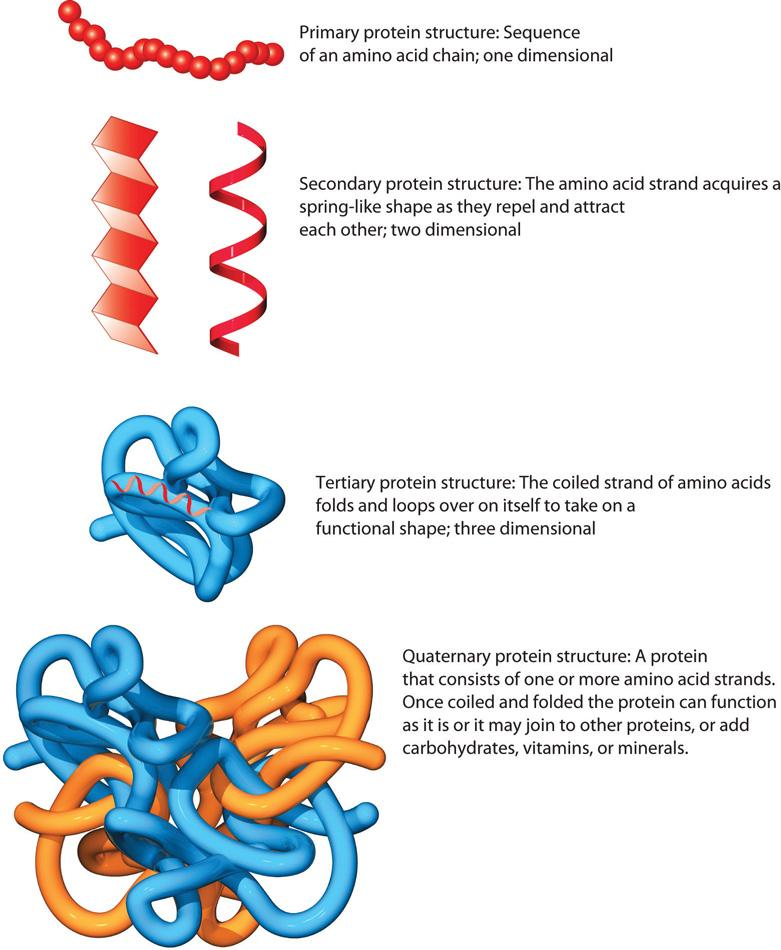
Figure: The different structures of a protein molecule.
Note:
A protein molecule has different structures. That is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. The primary structure includes the arrangement of amino acids one after the other connected by peptide bonds. The secondary structure involves the further folding of the primary structure; there are two types of secondary structures, known as the alpha helix and the beta pleated structures. The tertiary structure involves further forming a loop and forming a three dimensional structure. Quaternary structure involves looping of further more amino acid strands.
Complete answer:
Proteins are known as polymers, that is they are molecules of greater molecular weight composed of repeating units of smaller structural and functional units. These repeating units present in a protein molecule are known as amino acids. It is also known as the monomers in a protein polymer. These are organic compounds that contain an amino group, that is –NH2 and a carboxylic acid group –COOH, along with an R side chain group, which can be either an H atom or an alkane chain of any length. The nature of the amino acid depends on the composition of the R group. The major atoms that constitute amino acids are C, H, O, S and N. There exist about 500 naturally occurring amino acids.

Figure: An amino acid chain making up a peptide or a protein molecule
These chains of amino acids make up a peptide chain and multiple peptide chains aligned together in various conformations make up a protein molecule.

Figure: The different structures of a protein molecule.
Note:
A protein molecule has different structures. That is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. The primary structure includes the arrangement of amino acids one after the other connected by peptide bonds. The secondary structure involves the further folding of the primary structure; there are two types of secondary structures, known as the alpha helix and the beta pleated structures. The tertiary structure involves further forming a loop and forming a three dimensional structure. Quaternary structure involves looping of further more amino acid strands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




