
A rocket has been fired upwards to launch a satellite in its orbit. Name the two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad.
Answer
529.9k+ views
Hint: When a rocket is fired upwards, two forces act on the rocket at that instant. The first force is responsible to pull the rocket downwards towards the Earth, and the second force is due to the ejecting fuel responsible for the rocket’s upward motion.
Complete step by step solution:
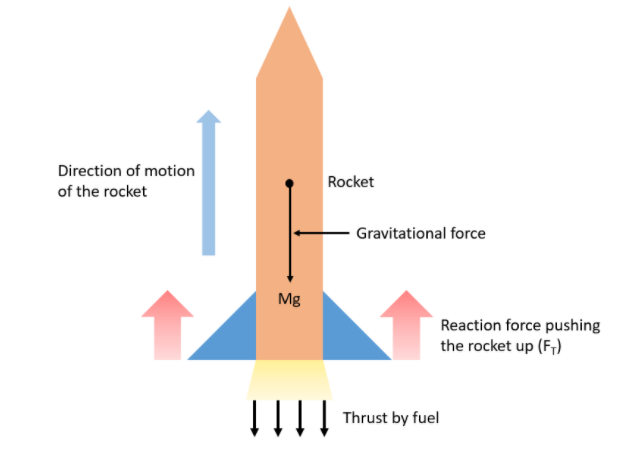
The above figure shows a rocket of mass M that has been fired up to launch a satellite in its orbit. Immediately after leaving the launching pad, the primary force acting on the rocket is the gravitational force Mg, which is acting in the downwards direction. This force opposes the motion of the rocket as the Earth tries to pull the rocket down with an acceleration equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g). As the rocket starts to take off, the fuel inside the rocket rushes down and imparts a force on the launching pad. This force by the fuel is called thrust, which is acting in a downwards direction. According to Newton’s third law of motion, the rocket, as a result, experiences a backward reaction force due to the thrust. This reactional force is much greater than the gravitational pull Mg, thereby this force is responsible for the upward motion of the rocket.
$\therefore$ The two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad are the downward gravitational force (Mg) and the upward reaction force due to the thrust by the fuel (${{F}_{T}}$).
Note:
In this question, the most common mistake done by the students is that the second force acting on the rocket is considered the frictional force due to the air present in the atmosphere. In the case of rocket propulsion, the frictional force due to atmospheric air or air drag is almost negligible as the head of the rocket is pointed. The pointy-head makes the rocket aerodynamic and reduces the frictional force due to air.
Complete step by step solution:

The above figure shows a rocket of mass M that has been fired up to launch a satellite in its orbit. Immediately after leaving the launching pad, the primary force acting on the rocket is the gravitational force Mg, which is acting in the downwards direction. This force opposes the motion of the rocket as the Earth tries to pull the rocket down with an acceleration equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g). As the rocket starts to take off, the fuel inside the rocket rushes down and imparts a force on the launching pad. This force by the fuel is called thrust, which is acting in a downwards direction. According to Newton’s third law of motion, the rocket, as a result, experiences a backward reaction force due to the thrust. This reactional force is much greater than the gravitational pull Mg, thereby this force is responsible for the upward motion of the rocket.
$\therefore$ The two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad are the downward gravitational force (Mg) and the upward reaction force due to the thrust by the fuel (${{F}_{T}}$).
Note:
In this question, the most common mistake done by the students is that the second force acting on the rocket is considered the frictional force due to the air present in the atmosphere. In the case of rocket propulsion, the frictional force due to atmospheric air or air drag is almost negligible as the head of the rocket is pointed. The pointy-head makes the rocket aerodynamic and reduces the frictional force due to air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




