
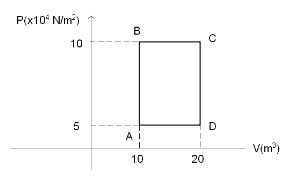
A sample of 2kg of monatomic Helium (assume ideal) is taken through the process ABC and another sample of 2 kg of the same gas is taken through the process ADC. Given, the relative molecular mass of Helium =4. What is the temperature of Helium in each of the states A, B, C, and D?
A) $ {T_A} = 220.33\,K;\,{T_B} = {T_D} = 2{T_A};{T_C} = 5{T_A} $
B) $ {T_A} = 320.33\,K;\,{T_B} = {T_D} = 3{T_A};{T_C} = 4{T_A} $
C) $ {T_A} = 120.33\,K;\,{T_B} = {T_D} = 2{T_A};{T_C} = 4{T_A} $
D) $ {T_A} = 520.33\,K;\,{T_B} = {T_D} = 2{T_A};{T_C} = 4{T_A} $

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint We need to use the graph of the pressure and volume to find the temperature of the gas at various points using the ideal gas law. The number of moles of a gas is the ratio of its mass in grams to its relative molecular mass.
Formula used: In this solution, we’ll use the following formulae,
Ideal gas law: $ PV = nRT $ where $ P $ is the pressure of the gas, $ V $ is the volume, $ n $ is the number of moles, $ R $ is the gas constant, and $ T $ is the temperature of the gas.
Complete step by step answer
To find the temperature at a given point using the ideal gas law, we must find the number of moles of gas from the mass of the gas given. The number of moles $ n $ can then be calculated as the ratio of the mass of the gas in grams to its relative molecular mass. So,
$ n = \dfrac{{2 \times 1000}}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow n = 500 $
Let us now find the temperature of the gas at point A using the ideal gas law. So, substituting $ {P_A} = 5 \times {10^4} $ and $ {V_A} = 10 $ in
$ {P_A}{V_A} = nR{T_A} $ , we get
$ 5 \times {10^4} \times 10 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_A} $
Solving for the temperature, we get
$ {T_A} = 120.33K $
Similarly, at point B, we can use the ideal gas law and write
$ {P_B}{V_B} = nR{T_B} $
$ 10 \times {10^4} \times 10 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_B} $
Solving for the temperature, we get
$ {T_B} = 240.66K $
For point D,
$ 5 \times {10^4} \times 20 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_D} $
$ \Rightarrow {T_D} = 240.66\;K $
And for point C,
$ 10 \times {10^4} \times 20 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_C} $
$ \Rightarrow {T_C} = 481.33\;K $
These values of temperature correspond to option (C).
Note
Since the temperatures for point A are different in all the options, just finding the temperature at point A is sufficient to select one choice from the options. Here, the process of the gas taken by the gas is inconsequential to the temperature of the gas since the temperature of the gas only depends on the pressure and volume at a given point and not on the path taken by the gas.
Formula used: In this solution, we’ll use the following formulae,
Ideal gas law: $ PV = nRT $ where $ P $ is the pressure of the gas, $ V $ is the volume, $ n $ is the number of moles, $ R $ is the gas constant, and $ T $ is the temperature of the gas.
Complete step by step answer
To find the temperature at a given point using the ideal gas law, we must find the number of moles of gas from the mass of the gas given. The number of moles $ n $ can then be calculated as the ratio of the mass of the gas in grams to its relative molecular mass. So,
$ n = \dfrac{{2 \times 1000}}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow n = 500 $
Let us now find the temperature of the gas at point A using the ideal gas law. So, substituting $ {P_A} = 5 \times {10^4} $ and $ {V_A} = 10 $ in
$ {P_A}{V_A} = nR{T_A} $ , we get
$ 5 \times {10^4} \times 10 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_A} $
Solving for the temperature, we get
$ {T_A} = 120.33K $
Similarly, at point B, we can use the ideal gas law and write
$ {P_B}{V_B} = nR{T_B} $
$ 10 \times {10^4} \times 10 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_B} $
Solving for the temperature, we get
$ {T_B} = 240.66K $
For point D,
$ 5 \times {10^4} \times 20 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_D} $
$ \Rightarrow {T_D} = 240.66\;K $
And for point C,
$ 10 \times {10^4} \times 20 = 500 \times 8.314 \times {T_C} $
$ \Rightarrow {T_C} = 481.33\;K $
These values of temperature correspond to option (C).
Note
Since the temperatures for point A are different in all the options, just finding the temperature at point A is sufficient to select one choice from the options. Here, the process of the gas taken by the gas is inconsequential to the temperature of the gas since the temperature of the gas only depends on the pressure and volume at a given point and not on the path taken by the gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




