
A solution of cyclohexene in benzene is stirred at ${{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ , while concentrated sulphuric acid is added, after washing away the acid and removing excess benzene, what product is obtained?
A. $1 - $phenylcyclohexene
B. cyclohexyl benzene
C. Trans$ - 1,2 - $diphenyl cyclohexane
D. $1,1 - $diphenyl cyclohexane
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:To answer this question we should talk about electrophile and nucleophile. We have cyclohexane in benzene and concentrated sulphuric acid. The concentrated sulphuric acid gives proton. So, it can be used for the preparation of an electrophile. Benzene can work as a nucleophile. So, an electrophilic substitution reaction can take place.
Complete step-by-step answer:A solution of cyclohexene in benzene is stirred at ${{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ , then concentrated sulphuric acid is added. The concentrated sulphuric acid gives proton. The cyclohexene attacks the concentrated sulphuric acid and gets protonated to generate a cation which works as an electrophile.
The formation of electrophile is shown as follows:
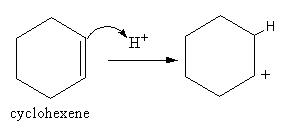
Benzene has three pi bonds, so benzene is electron-rich, so benzene works as a nucleophile. So, benzene attacks at the cation of cyclohexene and gets attached. So, the benzene gets a positive charge. Then by the removal of a proton the double bond forms again. The product is known as cyclohexyl benzene.
The reaction is shown as follows:
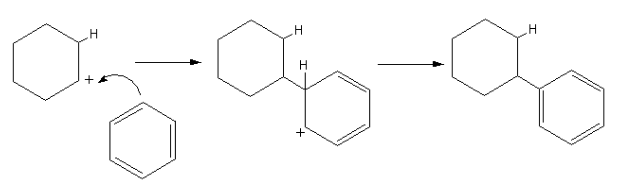
So, after the addition of concentrated sulphuric acid, the reaction takes place and the reaction mixture contains the leftover acid, benzene, and product cyclohexyl benzene. After washing away the acid and removing excess benzene, the product is obtained is cyclohexyl benzene.
Therefore, option (B) cyclohexyl benzene, is correct.
Note:The above reaction is an aromatic substitution reaction. The substation takes place on an aromatic benzene ring, so this reaction is an aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction carbocation forms so, the rate of reaction also depends upon the stability of carbocation. The order of stability of carbocation is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$.
Complete step-by-step answer:A solution of cyclohexene in benzene is stirred at ${{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ , then concentrated sulphuric acid is added. The concentrated sulphuric acid gives proton. The cyclohexene attacks the concentrated sulphuric acid and gets protonated to generate a cation which works as an electrophile.
The formation of electrophile is shown as follows:

Benzene has three pi bonds, so benzene is electron-rich, so benzene works as a nucleophile. So, benzene attacks at the cation of cyclohexene and gets attached. So, the benzene gets a positive charge. Then by the removal of a proton the double bond forms again. The product is known as cyclohexyl benzene.
The reaction is shown as follows:

So, after the addition of concentrated sulphuric acid, the reaction takes place and the reaction mixture contains the leftover acid, benzene, and product cyclohexyl benzene. After washing away the acid and removing excess benzene, the product is obtained is cyclohexyl benzene.
Therefore, option (B) cyclohexyl benzene, is correct.
Note:The above reaction is an aromatic substitution reaction. The substation takes place on an aromatic benzene ring, so this reaction is an aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction carbocation forms so, the rate of reaction also depends upon the stability of carbocation. The order of stability of carbocation is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




