
(A) State Ampere’s circuital law. Use this law to obtain the expression for the magnetic field inside an air cored toroid of average radius r having ‘n’ turns per unit length and carrying a steady current I.
(B) An observer to the left of a solenoid of N terms each of cross section area A observes that a steady current I in it flows in the clockwise direction. Depict the magnetic field lines due to the solenoid specifying its polarity and show that it acts as a bar magnet of magnetic moment m = NIA.

Answer
523.5k+ views
Hint: Ampere's Circuital Law states that the closed line integral of magnetic field around a current carrying conductor is equal to absolute permeability times the total current threading the conductor.
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}{I_{enclosed}}$ (B is the magnetic field, length of the conductor and I is the current flowing)
A toroid works as an inductor which boosts the frequency to appropriate levels. Using the above relations we will solve the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
(A) Let us state the ampere's Circuital Law and its derivation with an application of toroid:
Ampere's circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field $(\mathop B\limits^ \to )$ around any closed path or circuit is equal to ${\mu _0}$(absolute permeability of free space) times the total current (I) encircling the closed circuit.
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}{I_{enclosed}}$
This is the mathematical expression of the Ampere's circuital law.
A toroid solenoid is an anchor ring around which a large number of turns of a metallic wire are wound.When current passes through the toroidal solenoid, the magnetic field produced will be same at all points on the circumference of the ring of the toroid and the direction of the magnetic field will be tangent to the ring.
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0} \times (total current)$
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}(2\pi rn)I$................(1)
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = B(2\pi r)$..................(2)
on equating equation 1 and 2
$ \Rightarrow B(2\pi r) = {\mu _0} \times (2\pi rn)I $
$ \Rightarrow B = {\mu _0}nI$
(Cancelling the common terms)
Now, we will calculate the second part of the solution.
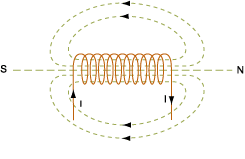
(B) When the current is flowing through the coil having two ends as shown in the figure in the question given the end from which current enters is called as north pole and the other end from which the current leaves is known as south pole.Thus the current carrying coil act as a magnetic dipole which has north and south pole; which is denoted by:
$M = nIA$
(M is the magnetic dipole, n is the number of turns of the coil, I is the current flowing and A is the surface area of the coil).
When the observer sees the toroid in the figure shown, observer sees the south pole of the toroid.
Note: In a current carrying wire the direction of the north pole and the south pole can be detected by using Right hand thumb rule and Maxwell's screw rule. When we grasp the fingers in the around the current carrying wire and points the thumb in the direction of the current flowing .
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}{I_{enclosed}}$ (B is the magnetic field, length of the conductor and I is the current flowing)
A toroid works as an inductor which boosts the frequency to appropriate levels. Using the above relations we will solve the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
(A) Let us state the ampere's Circuital Law and its derivation with an application of toroid:
Ampere's circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field $(\mathop B\limits^ \to )$ around any closed path or circuit is equal to ${\mu _0}$(absolute permeability of free space) times the total current (I) encircling the closed circuit.
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}{I_{enclosed}}$
This is the mathematical expression of the Ampere's circuital law.
A toroid solenoid is an anchor ring around which a large number of turns of a metallic wire are wound.When current passes through the toroidal solenoid, the magnetic field produced will be same at all points on the circumference of the ring of the toroid and the direction of the magnetic field will be tangent to the ring.
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0} \times (total current)$
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}(2\pi rn)I$................(1)
$\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .\mathop {dl}\limits^ \to = B(2\pi r)$..................(2)
on equating equation 1 and 2
$ \Rightarrow B(2\pi r) = {\mu _0} \times (2\pi rn)I $
$ \Rightarrow B = {\mu _0}nI$
(Cancelling the common terms)
Now, we will calculate the second part of the solution.
(B) When the current is flowing through the coil having two ends as shown in the figure in the question given the end from which current enters is called as north pole and the other end from which the current leaves is known as south pole.Thus the current carrying coil act as a magnetic dipole which has north and south pole; which is denoted by:
$M = nIA$
(M is the magnetic dipole, n is the number of turns of the coil, I is the current flowing and A is the surface area of the coil).
When the observer sees the toroid in the figure shown, observer sees the south pole of the toroid.
Note: In a current carrying wire the direction of the north pole and the south pole can be detected by using Right hand thumb rule and Maxwell's screw rule. When we grasp the fingers in the around the current carrying wire and points the thumb in the direction of the current flowing .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




