
A stationary sound wave is having a frequency of $165Hz$. If the speed of sound in air is $330m{{s}^{-1}}$, then the distance between a node and the adjacent antinode will be,
$\begin{align}
& A.30cm \\
& B.40cm \\
& C.50cm \\
& D.60cm \\
\end{align}$
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: First of all find out the wavelength of the wave. For that we have to divide the velocity with the frequency of the wave. Then using this wavelength find the distance between the adjacent node and antinode. For a clear cut idea draw a figure also. These details will help you in solving this question.
Complete answer:
First of all let us mention what all are given in the question. The velocity of the sound wave in air is given as,
$V=330m{{s}^{-1}}$
The frequency of this wave have been mentioned as,
$f=165Hz$
As we all know, the wavelength of the sound wave mentioned can be found out using the formula,
$\lambda =\dfrac{V}{f}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\lambda =\dfrac{330}{165}=2m=200cm$
The distance between an antinode and a node can be found using the figure,
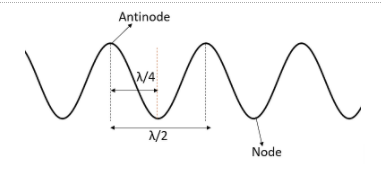
That is we can see that the distance between the node and antinode is given by,
$d=\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$
Substituting the value of wavelength in it will give,
$d=\dfrac{200}{4}=50cm$.
Therefore the correct answer is option C.
Note: In a standing wave the nodes are defined as a series of positions at equally spaced intervals where the amplitude of the wave in motion is zero. At these points the two waves add with a phase which is opposite and then they cancel out each other. They will be occurring at every half wavelength interval of distance. At the midpoint in between each pair of nodes are the positions with the amplitude is maximum. These points are referred to as the antinodes. These points are the location on a wave where the two waves add with the similar phase and reinforce each other. They will be occurring at each interval of half the wavelength distance.
Complete answer:
First of all let us mention what all are given in the question. The velocity of the sound wave in air is given as,
$V=330m{{s}^{-1}}$
The frequency of this wave have been mentioned as,
$f=165Hz$
As we all know, the wavelength of the sound wave mentioned can be found out using the formula,
$\lambda =\dfrac{V}{f}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\lambda =\dfrac{330}{165}=2m=200cm$
The distance between an antinode and a node can be found using the figure,

That is we can see that the distance between the node and antinode is given by,
$d=\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$
Substituting the value of wavelength in it will give,
$d=\dfrac{200}{4}=50cm$.
Therefore the correct answer is option C.
Note: In a standing wave the nodes are defined as a series of positions at equally spaced intervals where the amplitude of the wave in motion is zero. At these points the two waves add with a phase which is opposite and then they cancel out each other. They will be occurring at every half wavelength interval of distance. At the midpoint in between each pair of nodes are the positions with the amplitude is maximum. These points are referred to as the antinodes. These points are the location on a wave where the two waves add with the similar phase and reinforce each other. They will be occurring at each interval of half the wavelength distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




