
A tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant. Draw the monohybrid cross to show \[{F_1}\] and \[{F_2}\] generation. Write the phenotypic and genotypic ratio.
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: In this type of cross, Mendel selected two sets of pure breeding pea plants with contrasting characters for height. The tall pea plants were above six in height and the dwarf pea plants were with the average height of one. Mendel called these plants homozygous tall and homozygous dwarf. These were called pure strains.
Complete answer:
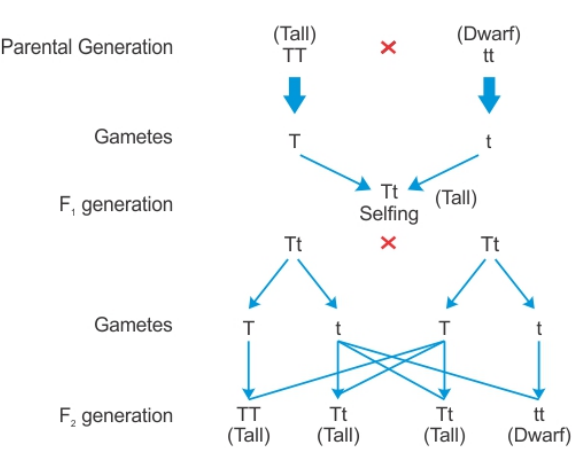
A cross that Mendel made to study the inheritance of one pair of contrasting characters is known as a monohybrid cross.
Mendel cross-pollinated homozygous tall plants with homozygous dwarf plants. These plants formed the parent generation (\[P\]generation).
The pollen grains were collected from a flower of a tall plant and dusted over the pistil of an emasculated flower of a dwarf plant.
The seeds produced by cross pollinating these parent generation plants were collected and grown to produce hybrid plants. These belonged to the first filial generation. All the plants of \[{F_1}\] generation are tall.
The plants of \[{F_1}\] generation were self-pollinated and seeds were collected. The plants raised from these seeds of \[{F_1}\] plants belonged to the second filial generation.
Mendel noted that \[75\% \]plants of \[{F_2}\] generation were tall and \[25\% \] dwarf.
He concluded that in \[{F_2}\] generation, the tall and dwarf plants were produced in \[3:1\](phenotypic ratio) and \[1:2:1\] (genotypic ratio).
All the \[{F_1}\] plants are hybrids and have factors\[Tt\]. They are tall because the \[T\] factor dominates \[t\]factor. Thus, tallness is a dominant character and shortness a recessive character. This is called the Law of dominance and recessiveness.
The determiners or genes (\[T\] & \[t\]) are separate entities. When gametes are formed, these unit factors segregate and each gamete gets only one of the two alternative factors (either \[T\] or \[t\]). Thus, \[{F_1}\] plants produce two types of gametes in equal numbers. This is called the Law of segregation.
Note:
Mendel repeated similar experiments with other characters like flower colour, seed colour, seed coat character, etc. He noted that the results of all these experiments showed a similar pattern of heritance:
One of the contrasting features of a pair was not represented in the \[{F_1}\] generation.
This contrasting feature reappeared in \[{F_2}\] generation.
Complete answer:
A cross that Mendel made to study the inheritance of one pair of contrasting characters is known as a monohybrid cross.
Mendel cross-pollinated homozygous tall plants with homozygous dwarf plants. These plants formed the parent generation (\[P\]generation).
The pollen grains were collected from a flower of a tall plant and dusted over the pistil of an emasculated flower of a dwarf plant.
The seeds produced by cross pollinating these parent generation plants were collected and grown to produce hybrid plants. These belonged to the first filial generation. All the plants of \[{F_1}\] generation are tall.
The plants of \[{F_1}\] generation were self-pollinated and seeds were collected. The plants raised from these seeds of \[{F_1}\] plants belonged to the second filial generation.
Mendel noted that \[75\% \]plants of \[{F_2}\] generation were tall and \[25\% \] dwarf.
He concluded that in \[{F_2}\] generation, the tall and dwarf plants were produced in \[3:1\](phenotypic ratio) and \[1:2:1\] (genotypic ratio).
All the \[{F_1}\] plants are hybrids and have factors\[Tt\]. They are tall because the \[T\] factor dominates \[t\]factor. Thus, tallness is a dominant character and shortness a recessive character. This is called the Law of dominance and recessiveness.
The determiners or genes (\[T\] & \[t\]) are separate entities. When gametes are formed, these unit factors segregate and each gamete gets only one of the two alternative factors (either \[T\] or \[t\]). Thus, \[{F_1}\] plants produce two types of gametes in equal numbers. This is called the Law of segregation.

Note:
Mendel repeated similar experiments with other characters like flower colour, seed colour, seed coat character, etc. He noted that the results of all these experiments showed a similar pattern of heritance:
One of the contrasting features of a pair was not represented in the \[{F_1}\] generation.
This contrasting feature reappeared in \[{F_2}\] generation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




