
A temporary magnet is made up of
(a) cast iron
(b) steel
(c) soft iron
(d) stainless steel
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: In this question use the concept that a magnet is broadly categorized into two categories that is a temporary magnet and a permanent magnet, a temporary magnet is made up of materials that has the tendency to lose its magnetic properties or to get demagnetized after a specific point of time. So choose the best option amongst the given which suits this.
Complete step-by-step answer:
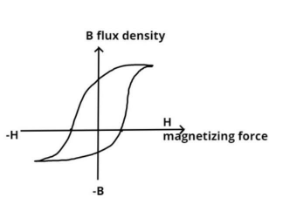
As we know that any magnetic material has some hysteresis loop except air core this hysteresis loop represents the loss in the magnetic system while transferring the power from one terminal to another terminal using a magnetic core for example transformer.
As we know while transferring power from the source end to the receiving end, both power cannot be equal practically as there is some power loss in the core of the material which is called as core loss.
These core loss are of two types:
$\left( i \right)$ Eddy current loss
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Hysteresis loss.
So every hysteresis loss has some B-H curve; we reduce this hysteresis loss but cannot completely eliminate it as air core is not possible, so this curve represents the energy lost per unit volume (i.e. volume of the core).
Now permanent magnets have large hysteresis loops as they are made from hard magnetic material and they retain their magnetism once magnetized, for example Alnico (composition of aluminum, nickel and cobalt).
On the other hand, a temporary magnet has a smaller hysteresis loop as they are made from soft magnetic materials and they do not retain their magnetism once magnetized, for example silicon-iron, aluminum-iron etc.
Hence a temporary magnet is made up of soft-iron.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: The diagrammatic representation shown in the above figure depicts a hysteresis loop, it is basically a 4 quadrant B-H curve. B refers to induced magnetic flux density and H is the magnetizing force. This curve is not only used to compute the hysteresis loss but however can also be used to find retentivity and coercive force.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that any magnetic material has some hysteresis loop except air core this hysteresis loop represents the loss in the magnetic system while transferring the power from one terminal to another terminal using a magnetic core for example transformer.
As we know while transferring power from the source end to the receiving end, both power cannot be equal practically as there is some power loss in the core of the material which is called as core loss.

These core loss are of two types:
$\left( i \right)$ Eddy current loss
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Hysteresis loss.
So every hysteresis loss has some B-H curve; we reduce this hysteresis loss but cannot completely eliminate it as air core is not possible, so this curve represents the energy lost per unit volume (i.e. volume of the core).
Now permanent magnets have large hysteresis loops as they are made from hard magnetic material and they retain their magnetism once magnetized, for example Alnico (composition of aluminum, nickel and cobalt).
On the other hand, a temporary magnet has a smaller hysteresis loop as they are made from soft magnetic materials and they do not retain their magnetism once magnetized, for example silicon-iron, aluminum-iron etc.
Hence a temporary magnet is made up of soft-iron.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: The diagrammatic representation shown in the above figure depicts a hysteresis loop, it is basically a 4 quadrant B-H curve. B refers to induced magnetic flux density and H is the magnetizing force. This curve is not only used to compute the hysteresis loss but however can also be used to find retentivity and coercive force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




