
A thin ring of radius r carries a charge q. Find the magnitude of electric field strength on the axis of a ring as a function of distance l from the center. Find the maximum strength, magnitude and the corresponding distance is
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: Assume that the field along the normal is zero. Then find the electric field on the axis of the ring at a distance l from the centre. Apply Coulomb’s law for finding the electric field. After finding the electric field take its derivative with respect to l. Hence to find the maximum electric field equate this derivative equals to zero. Thus by solving them we will get the maximum strength, magnitude and the corresponding distance.
Complete step-by-step solution
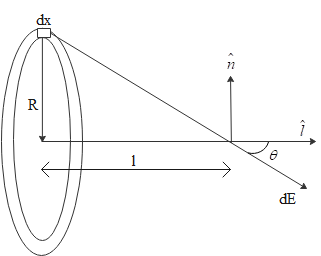
The field along the normal will be zero.
That is, ${{E}_{N}}=0$ and $E={{E}_{l}}$
Now, we know the expression for electric field which could be given by,
$d{{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{dq}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}\cos \theta $
But we know that,
$dq=\dfrac{q}{2\pi R}dx$
Also,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{l}{{{\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}$
Substituting accordingly we get,
$E=\int{d{{E}_{1}}=\int\limits_{0}^{2\pi R}{\dfrac{ql}{2\pi R}\dfrac{dx}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}{{\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{ql}{{{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}$ ……………………………………………………… (1)
Now, for $l\rangle \rangle R$, the ring acts as a point charge.
Thus, $E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{l}^{2}}}$
Then for calculating the maximum value of a quantity we equate the first derivative to zero. That is,
$\dfrac{dE}{dl}=0$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}-\dfrac{3}{2}l{{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}2l=0$
$\Rightarrow {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}}-3{{l}^{2}}=0$
Thus,
$l=\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}}$
Substituting this in (1) we get,
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\left( \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}{{{\left( {{\left( \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}$
$\therefore {{E}_{\max }}=\dfrac{q}{6\sqrt{3}\pi {{\in }_{0}}{{R}^{2}}}$
Additional information: Electric field is defined as the ratio of electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be the direction of the force. The electric field generally goes outward from a positive charge and goes in toward a negative point charge. The magnitude and direction of the electric field is determined by its value. Usually an electric field line starts from a positively charged end and ends in a negatively charged end.
Note: In an electromagnetic wave, the value of energy carried by electric field and magnetic field is the same. So in an EM wave, the electric field is proportional to the magnetic field. And the velocity of light here is the proportionality constant. Thus the maximum value of electric field strength is the product of maximum value of magnetic field and velocity of light.
Complete step-by-step solution

The field along the normal will be zero.
That is, ${{E}_{N}}=0$ and $E={{E}_{l}}$
Now, we know the expression for electric field which could be given by,
$d{{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{dq}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}\cos \theta $
But we know that,
$dq=\dfrac{q}{2\pi R}dx$
Also,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{l}{{{\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}$
Substituting accordingly we get,
$E=\int{d{{E}_{1}}=\int\limits_{0}^{2\pi R}{\dfrac{ql}{2\pi R}\dfrac{dx}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}{{\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{l}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{ql}{{{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}$ ……………………………………………………… (1)
Now, for $l\rangle \rangle R$, the ring acts as a point charge.
Thus, $E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{l}^{2}}}$
Then for calculating the maximum value of a quantity we equate the first derivative to zero. That is,
$\dfrac{dE}{dl}=0$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}-\dfrac{3}{2}l{{\left( {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}2l=0$
$\Rightarrow {{l}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}}-3{{l}^{2}}=0$
Thus,
$l=\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}}$
Substituting this in (1) we get,
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\left( \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}{{{\left( {{\left( \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{R}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}$
$\therefore {{E}_{\max }}=\dfrac{q}{6\sqrt{3}\pi {{\in }_{0}}{{R}^{2}}}$
Additional information: Electric field is defined as the ratio of electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be the direction of the force. The electric field generally goes outward from a positive charge and goes in toward a negative point charge. The magnitude and direction of the electric field is determined by its value. Usually an electric field line starts from a positively charged end and ends in a negatively charged end.
Note: In an electromagnetic wave, the value of energy carried by electric field and magnetic field is the same. So in an EM wave, the electric field is proportional to the magnetic field. And the velocity of light here is the proportionality constant. Thus the maximum value of electric field strength is the product of maximum value of magnetic field and velocity of light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




