
A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of the eye with respect to the position of the bulb is shown in fig. as A, B, C and D. In which of the shown figures, the light will be visible to the eye?
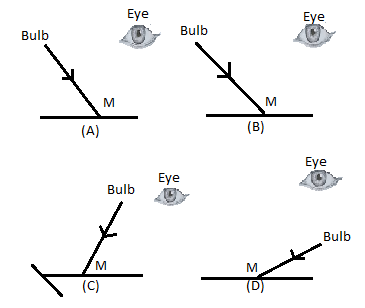
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Use Snell’s law of reflection of the incident ray.
This law gives the relation between the incident ray of light and the reflected ray of light.
Complete step by step answer:
A mirror M is placed on a cardboard which is placed on a table.
The light incident from the bulb gets reflected from the mirror.
According to Snell’s law of reflection, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection with the normal are the same.
Consider the figure C.
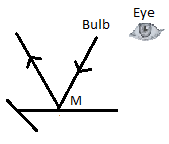
In the above figure, the reflected ray of light on reflection from the mirror is shown.
The figure shows that the eye is not in the path of the reflected ray of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure C, light will not be visible to the eye.
Consider the figure C.
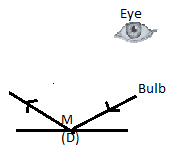
In the above figure, the reflected ray of light on reflection from the mirror is shown.
The figure shows that the eye is not in the path of the reflected lay of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure D, light will not be visible to the eye.
Consider the figures A and B.
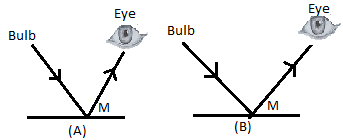
In the above figures, the reflected rays of light on reflection from the mirror are shown.
The figure shows that the eye is in the path of the reflected ray of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure A and figure B, light will be visible to the eye.
So, the correct answers are “Options A and B”.
Note:
The normal in all the figures A, B, C and D is not shown in figures but it is perpendicular to the mirror M.
As per the laws of reflection we have angle of incidence equal to angle of reflection. Figure A and B are the ones with the bulb on the path of incidence and eye in the path of reflection.
This law gives the relation between the incident ray of light and the reflected ray of light.
Complete step by step answer:
A mirror M is placed on a cardboard which is placed on a table.
The light incident from the bulb gets reflected from the mirror.
According to Snell’s law of reflection, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection with the normal are the same.
Consider the figure C.

In the above figure, the reflected ray of light on reflection from the mirror is shown.
The figure shows that the eye is not in the path of the reflected ray of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure C, light will not be visible to the eye.
Consider the figure C.

In the above figure, the reflected ray of light on reflection from the mirror is shown.
The figure shows that the eye is not in the path of the reflected lay of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure D, light will not be visible to the eye.
Consider the figures A and B.

In the above figures, the reflected rays of light on reflection from the mirror are shown.
The figure shows that the eye is in the path of the reflected ray of light from the bulb.
Hence, in figure A and figure B, light will be visible to the eye.
So, the correct answers are “Options A and B”.
Note:
The normal in all the figures A, B, C and D is not shown in figures but it is perpendicular to the mirror M.
As per the laws of reflection we have angle of incidence equal to angle of reflection. Figure A and B are the ones with the bulb on the path of incidence and eye in the path of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




