
A Travelling microscope is used during the experiment to measure the
A. focal length of a convex mirror
B. focal length of a convex lens
C. refractive index of glass slab
D. resistivity of a given wire
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The purpose of the microscope is to aim at reference points with much higher accuracy as compared to than it is possible through the naked eye. Short distances can be measured precisely using a microscope. Travelling microscope has an accuracy of 0.01mm. In a typical Travelling microscope, the main scale divisions are of magnitude 0.05cm and the vernier scale contains 50 divisions.
Complete step by step answer:
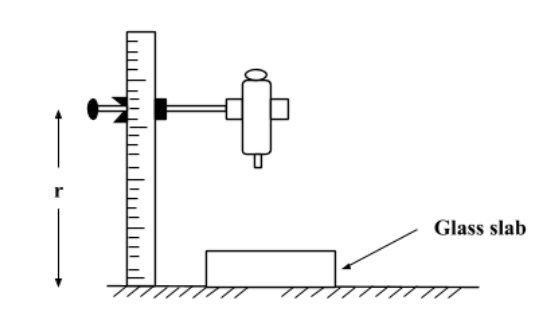
There are different types of microscopes but the most popular ones are Compound, Stereo, Digital, and Pocket. Travelling microscope is an example of a Compound microscope. It provides a 2-D image. It is fitted on a vertical scale. It has a vernier scale along the main scale and can be moved upward or downward according to our requirements. It has an accuracy of 0.01mm. It uses geometrical concepts of ray optics. It is used for measuring short distances. Concave mirror and Plano concave mirror are used in the microscope. In a typical Travelling microscope, the main scale divisions are of magnitude 0.05cm and the vernier scale contains 50 divisions. So with such a small scale, focal length can’t be measured either of a convex mirror or a convex lens. While using a Travelling microscope, we place the specimen on stage. Some microscopes have a mechanical stage which allows for very minute slide movements. Hence, we can say the refractive index of a glass slab can be measured during an experiment using a Travelling microscope.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Different microscopes are used in different experiments for different measurements. While two microscopes can be used for the same measurement and a single microscope can be used for various measurements. So students need to understand at which place which microscope is to be used.
Complete step by step answer:

There are different types of microscopes but the most popular ones are Compound, Stereo, Digital, and Pocket. Travelling microscope is an example of a Compound microscope. It provides a 2-D image. It is fitted on a vertical scale. It has a vernier scale along the main scale and can be moved upward or downward according to our requirements. It has an accuracy of 0.01mm. It uses geometrical concepts of ray optics. It is used for measuring short distances. Concave mirror and Plano concave mirror are used in the microscope. In a typical Travelling microscope, the main scale divisions are of magnitude 0.05cm and the vernier scale contains 50 divisions. So with such a small scale, focal length can’t be measured either of a convex mirror or a convex lens. While using a Travelling microscope, we place the specimen on stage. Some microscopes have a mechanical stage which allows for very minute slide movements. Hence, we can say the refractive index of a glass slab can be measured during an experiment using a Travelling microscope.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Different microscopes are used in different experiments for different measurements. While two microscopes can be used for the same measurement and a single microscope can be used for various measurements. So students need to understand at which place which microscope is to be used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




