
How is a Type 1 error more dangerous than Type 2 error in Statistics?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: We cannot say that Type 1 error is more dangerous than Type 2 error. It depends upon the societies or individuals. For that we are going to first understand what Type 1 and Type 2 errors are in Statistics. Then we will demonstrate through an example that it depends on the societies and individuals whether one error is more dangerous than the other one.
Complete answer:
Type 1 error comes into play when we reject the null hypothesis but in fact it is true. And type 2 error comes into play when rejecting the alternative hypothesis but in fact it is true.
Now, let us understand the terms “null hypothesis” and “alternative hypothesis” using an example. Let the example be that in a courtroom a defendant is innocent. This is the null hypothesis that the defendant is innocent. Then rejecting the null hypothesis (means defendant is guilty) but in reality the defendant is innocent is Type 1 error.
The term “alternative hypothesis” means that we are considering the opposite of the null hypothesis which is that the defendant is guilty. Now, Type 2 error rejects the alternative hypothesis means the defendant is innocent but in fact the defendant is guilty.
Now, generally in societies, Type 1 error is more dangerous than Type 2 error because you are convicting the innocent person. But if you can see then Type 2 error is also dangerous because freeing a guilty can bring more chaos in societies because now the guilty can do more harm to society.
At last, it depends on the frame of individuals or societies which we are taking into consideration to predict whether Type 1 error or Type 2 error is more dangerous.
Note: In the below, we are making a table from which you can easily remember a Type 1 error and Type 2 error. The table is showing that false positive is Type 1 error and true negative is Type 2 error.
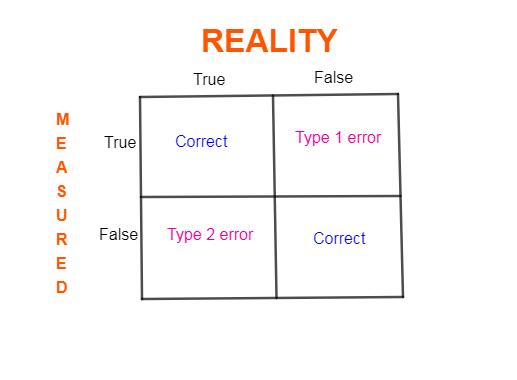
Complete answer:
Type 1 error comes into play when we reject the null hypothesis but in fact it is true. And type 2 error comes into play when rejecting the alternative hypothesis but in fact it is true.
Now, let us understand the terms “null hypothesis” and “alternative hypothesis” using an example. Let the example be that in a courtroom a defendant is innocent. This is the null hypothesis that the defendant is innocent. Then rejecting the null hypothesis (means defendant is guilty) but in reality the defendant is innocent is Type 1 error.
The term “alternative hypothesis” means that we are considering the opposite of the null hypothesis which is that the defendant is guilty. Now, Type 2 error rejects the alternative hypothesis means the defendant is innocent but in fact the defendant is guilty.
Now, generally in societies, Type 1 error is more dangerous than Type 2 error because you are convicting the innocent person. But if you can see then Type 2 error is also dangerous because freeing a guilty can bring more chaos in societies because now the guilty can do more harm to society.
At last, it depends on the frame of individuals or societies which we are taking into consideration to predict whether Type 1 error or Type 2 error is more dangerous.
Note: In the below, we are making a table from which you can easily remember a Type 1 error and Type 2 error. The table is showing that false positive is Type 1 error and true negative is Type 2 error.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




