
A uniform but increasing with time magnetic field exists in a cylindrical region. The direction of force on an electron at P is
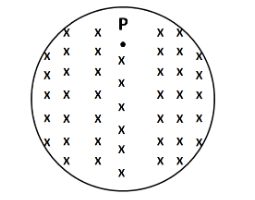
(A) Towards right
(B) Towards left
(C) Into the plane of paper
(D) Out of the plane of paper

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: The magnetic field which exists inside the cylindrical region is varying with time. So electric fields will be induced in the cylindrical region. The direction of the electric force on the electron will be opposite to the electric field.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$ \vec F = q\vec E $ , here $ \vec F $ is the force on a charge $ q $ due to an electric field $ \vec E $ .
Complete step-by-step solution
We know that the time varying magnetic field produces electric fields, which exist in loops. The direction of the electric fields, whether clockwise or anticlockwise, will be decided by Lenz's law. Since the magnetic field in the cylindrical region is increasing with time into the plane of the paper, the magnetic flux will also increase into the pane of the paper. So the direction of the induced electric fields will be such that the magnetic flux generated inside the cylindrical region is outside the plane of the paper.
From the right hand thumb rule, we get the direction of the loops of the electric field as anticlockwise. So the induced electric fields can be shown as in the following figure.
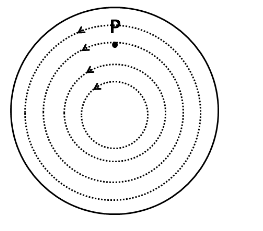
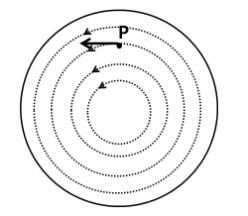
We know that the direction of the electric field at a point inside a region of the electric field lines is along the tangent to the electric field line at that point. So the direction of the electric field is as shown below.
We know that the force on a charged particle by the electric field is given by
$ \vec F = q\vec E $
Substituting $ q = - e $ for the electron at P, we get
$ \vec F = - e\vec E $
The above expression shows that the force on the electron must be opposite to the direction of the electric field at P. From the above figure, the direction of the electric field is towards the left. Thus, the direction of force on the electron is towards the right.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note
Do not use the expression for the magnetic force on a charged particle due to a magnetic field for getting the direction of the force. Although the magnetic field exists in the cylindrical region, since the electron is at rest, no magnetic force will be experienced by it.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$ \vec F = q\vec E $ , here $ \vec F $ is the force on a charge $ q $ due to an electric field $ \vec E $ .
Complete step-by-step solution
We know that the time varying magnetic field produces electric fields, which exist in loops. The direction of the electric fields, whether clockwise or anticlockwise, will be decided by Lenz's law. Since the magnetic field in the cylindrical region is increasing with time into the plane of the paper, the magnetic flux will also increase into the pane of the paper. So the direction of the induced electric fields will be such that the magnetic flux generated inside the cylindrical region is outside the plane of the paper.
From the right hand thumb rule, we get the direction of the loops of the electric field as anticlockwise. So the induced electric fields can be shown as in the following figure.

We know that the direction of the electric field at a point inside a region of the electric field lines is along the tangent to the electric field line at that point. So the direction of the electric field is as shown below.

We know that the force on a charged particle by the electric field is given by
$ \vec F = q\vec E $
Substituting $ q = - e $ for the electron at P, we get
$ \vec F = - e\vec E $
The above expression shows that the force on the electron must be opposite to the direction of the electric field at P. From the above figure, the direction of the electric field is towards the left. Thus, the direction of force on the electron is towards the right.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note
Do not use the expression for the magnetic force on a charged particle due to a magnetic field for getting the direction of the force. Although the magnetic field exists in the cylindrical region, since the electron is at rest, no magnetic force will be experienced by it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




