
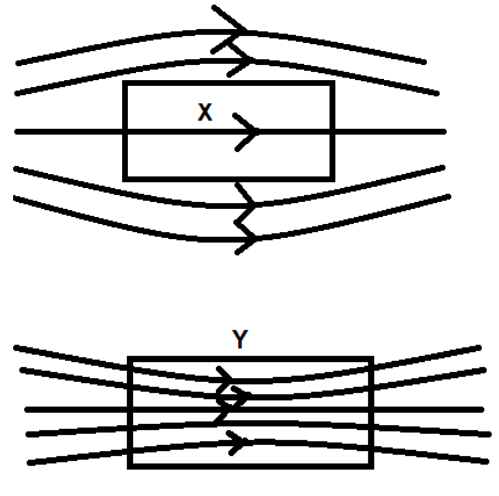
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in the figure below when two specimens X and Y are placed in it. Identify X and Y.

Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Different metals behave uniquely in magnetic fields. Some of them attract the field and concentrate them, whereas some others repel the field. This is a natural property of the metal to either get attracted or repelled by a magnetic field.
Complete step-by-step solution
All substances which are not ferromagnetic in nature, i.e., those which have the natural magnetic field, here either diamagnetic or paramagnetic in nature. These two are fundamental properties of a substance. We can understand the two types of magnetic substances.
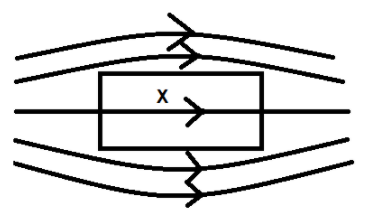
Diamagnetic substances: These are substances. which tend to get repelled by an external magnetic field. The diamagnetic materials have a tendency to move from a strong magnetic field to a weaker region of the external field. The reason behind this repelling nature of the diamagnetic substances is the molecular property of the substance. These substances are entitled to have a zero resultant magnetic moment in them due to the orbiting electrons. As a result of the external field, the atoms develop an opposing magnetic field thus, repulsion takes place.
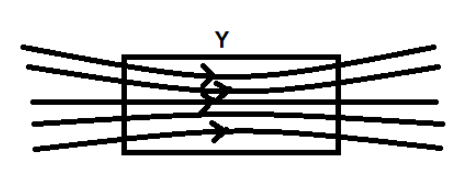
Paramagnetic substances: These are substances, which tend to weakly attract the applied external magnetic field. They do not attract as strongly as the ferromagnets do. They possess resultant magnetic moments in their atoms, which get attracted by the field. The higher the magnitude of the moment greatly it is attracted to the magnetic field.
From the above description of the materials, we can understand that-
X is a diamagnetic substance
Y is a paramagnetic substance.
Additional Information: Paramagnetism is inversely proportional to temperature.
Note: Ferromagnets are strong paramagnets with exceptional magnetic qualities. They get converted to paramagnets when they are exposed to harsh temperatures or other unfavorable conditions, i.e., above the Curie temperature of the ferromagnet.
Complete step-by-step solution
All substances which are not ferromagnetic in nature, i.e., those which have the natural magnetic field, here either diamagnetic or paramagnetic in nature. These two are fundamental properties of a substance. We can understand the two types of magnetic substances.
Diamagnetic substances: These are substances. which tend to get repelled by an external magnetic field. The diamagnetic materials have a tendency to move from a strong magnetic field to a weaker region of the external field. The reason behind this repelling nature of the diamagnetic substances is the molecular property of the substance. These substances are entitled to have a zero resultant magnetic moment in them due to the orbiting electrons. As a result of the external field, the atoms develop an opposing magnetic field thus, repulsion takes place.

Paramagnetic substances: These are substances, which tend to weakly attract the applied external magnetic field. They do not attract as strongly as the ferromagnets do. They possess resultant magnetic moments in their atoms, which get attracted by the field. The higher the magnitude of the moment greatly it is attracted to the magnetic field.

From the above description of the materials, we can understand that-
X is a diamagnetic substance
Y is a paramagnetic substance.
Additional Information: Paramagnetism is inversely proportional to temperature.
Note: Ferromagnets are strong paramagnets with exceptional magnetic qualities. They get converted to paramagnets when they are exposed to harsh temperatures or other unfavorable conditions, i.e., above the Curie temperature of the ferromagnet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




