
A uniform meter rule of mass 100 g is balanced on a fulcrum at mark 40 cm by suspending an unknown mass m at the mark 20 cm.
(i) Find the value of m
(ii) To which side the rule will tilt if the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm?
(iii) What is the resultant moment now?
(iv) How can it be balanced by another mass of 50g?
Answer
523.8k+ views
Hint: When a rule is balanced, then the clockwise moment about a point on the rule is equal to the anticlockwise moment about that same point on the rule, this is stated by the principle of moments. When the balancing mass is moved then the resultant moment is the difference of clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows the rule balanced at mark 40 cm by suspending mass m at the mark 20 cm.
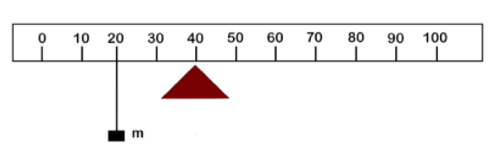
(i) Finding the value of m,
The clockwise moment is given by,
$\Rightarrow M\times {{d}_{1}}$ ….(i)
Where, M is mass of rule i.e. 100g and ${{d}_{1}}$ is the distance of fulcrum from the center of mass of rule.
${{d}_{1}}=50cm-40cm=10cm$ ….(ii)
The anticlockwise moment is given by,
$\Rightarrow m\times {{d}_{2}}$ ….(iii)
Where, m is an unknown mass and ${{d}_{2}}$is the distance of mass m from the fulcrum.
${{d}_{2}}=40cm-20cm=20cm$ ….(iv)
Now equating the clockwise moment equal to the anticlockwise moment, we get,
From (i) and (iii),
$M\times {{d}_{1}}=m\times {{d}_{2}}$ ….(v)
Putting the values from (ii) and (iv) in (v), we get,
$\Rightarrow 100g\times 10cm=m\times 20cm$
$\Rightarrow m=50g$
(ii) If the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm, then the balance will shift and the rule will tilt towards mass m.
(iii) The resultant moment when the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm is given by,
$\Rightarrow m\times d=50g\times 30cm=1500g\cdot cm$ (anticlockwise moment)
Where, $d=40cm-10cm=30cm$
(iv) To balance the rule by another mass of 50g we must place the new mass to the right of the fulcrum so as to counter the anticlockwise moment with clockwise moment,
Let the mark at which mass 50g will be placed be x,
Hence, clockwise moment is,
$\Rightarrow 1000g\cdot cm+50g\times (x-40)$ ….(vi)
And, anticlockwise moment is,
$\Rightarrow 1500g\cdot cm$ ….(vii)
Thus, equating (vi) and (vii) and solving for x, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1000g\cdot cm+50g\times (x-40)=1500g\cdot cm$
$\Rightarrow x=50cm$
Therefore, mass 50g will be placed at mark 50cm to balance the rule.
Note:
Students must be familiar with the principle of moments and the formulae for calculating clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment about a point on the rule. Extra care should be taken when finding the distance from the fulcrum to masses suspended to balance rule.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows the rule balanced at mark 40 cm by suspending mass m at the mark 20 cm.

(i) Finding the value of m,
The clockwise moment is given by,
$\Rightarrow M\times {{d}_{1}}$ ….(i)
Where, M is mass of rule i.e. 100g and ${{d}_{1}}$ is the distance of fulcrum from the center of mass of rule.
${{d}_{1}}=50cm-40cm=10cm$ ….(ii)
The anticlockwise moment is given by,
$\Rightarrow m\times {{d}_{2}}$ ….(iii)
Where, m is an unknown mass and ${{d}_{2}}$is the distance of mass m from the fulcrum.
${{d}_{2}}=40cm-20cm=20cm$ ….(iv)
Now equating the clockwise moment equal to the anticlockwise moment, we get,
From (i) and (iii),
$M\times {{d}_{1}}=m\times {{d}_{2}}$ ….(v)
Putting the values from (ii) and (iv) in (v), we get,
$\Rightarrow 100g\times 10cm=m\times 20cm$
$\Rightarrow m=50g$
(ii) If the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm, then the balance will shift and the rule will tilt towards mass m.
(iii) The resultant moment when the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm is given by,
$\Rightarrow m\times d=50g\times 30cm=1500g\cdot cm$ (anticlockwise moment)
Where, $d=40cm-10cm=30cm$
(iv) To balance the rule by another mass of 50g we must place the new mass to the right of the fulcrum so as to counter the anticlockwise moment with clockwise moment,
Let the mark at which mass 50g will be placed be x,
Hence, clockwise moment is,
$\Rightarrow 1000g\cdot cm+50g\times (x-40)$ ….(vi)
And, anticlockwise moment is,
$\Rightarrow 1500g\cdot cm$ ….(vii)
Thus, equating (vi) and (vii) and solving for x, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1000g\cdot cm+50g\times (x-40)=1500g\cdot cm$
$\Rightarrow x=50cm$
Therefore, mass 50g will be placed at mark 50cm to balance the rule.
Note:
Students must be familiar with the principle of moments and the formulae for calculating clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment about a point on the rule. Extra care should be taken when finding the distance from the fulcrum to masses suspended to balance rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




