
(A) Using the phenomenon of polarization, show how transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
(B) Two polaroid ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$ are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity ${I_0}$ is incident on ${P_1}$ . A third polaroid ${P_3}$ is kept in between ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$ such that its pass axis makes an angle $30^\circ $ with ${P_1}$ . Determine the intensity of light transmitted through ${P_1}$ , ${P_2}$ and ${P_3}$.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Polarization of light is a phenomenon where the transverse waves vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of light. The motion remains in a constant direction perpendicular to the plane of vibration. Some material used as a polarizer is Nicol prism.
Complete step by step solution:
A) Light is mixtures of waves vibrating in all directions but when polarized, the vibration remains constant in one direction.
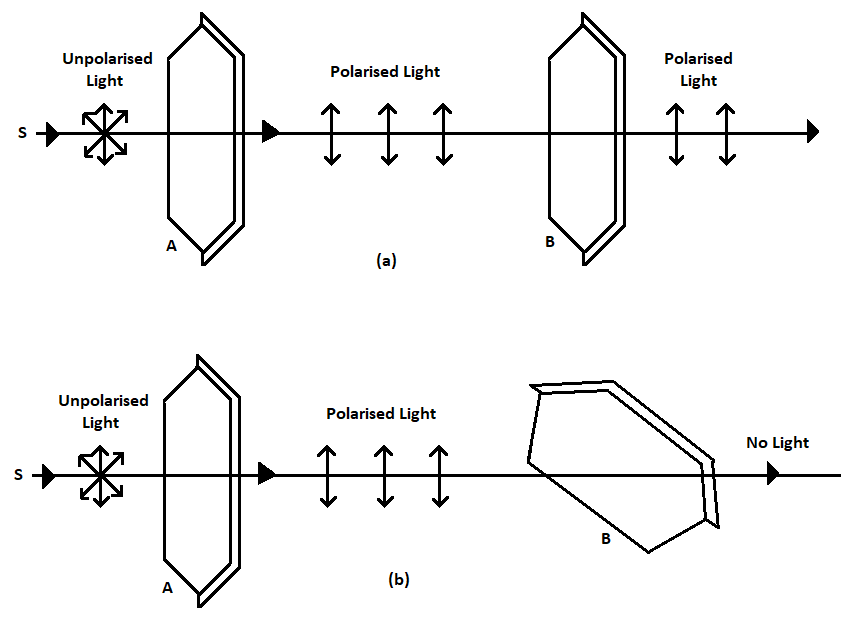
The above diagram demonstrates how a transverse light is converted to polarised light, the material used is a polariser which allows only perpendicular vibrated light to pass through it and eliminate every other light which transverse in in other direction other than perpendicular plane. In the first diagram the transverse light is polarised twice to filter out the remaining unpolarized light so that the output light is pure polarised light.
In the second diagram when the polariser is kept inclined to the plane no light passes through it as the polarised light cannot pass the inclined polariser since they transverse in only perpendicular direction.
Given:
${P_1}\& {P_2}$ are kept perpendicular to each other.
Another polaroid ${P_3}$ is kept between ${P_1}\& {P_2}$ such that ${P_3}$ is making an angle $30^\circ $ with ${P_1}$ .
The required ${I_0}$ can be calculated as follows:
As Malus law states that the intensity of a beam after passing a polariser becomes half of the original intensity i.e. $I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}$
So, when the light pass through ${P_1}$ , the original intensity will be reduced to half of its value i.e. ${I_1} = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}$.
The intensity of polarized light passing through an inclined polariser of angle $\theta $ becomes $I = {I_0}{\cos ^2}\theta $.
When ${I_1}$ pass through ${P_3}$ , the intensity will become
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}{\cos ^2}30^\circ $
i.e. \[I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}{(\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2})^2}\]
which gives $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8}$
The above intensity will again pass through ${P_2}$ and the final intensity will be obtained as:
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8}{\cos ^2}60^\circ $
i.e. $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8} \times \dfrac{1}{4}$
which gives $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{{32}}$
Therefore, the above intensity is the required final intensity.
Note: Polarizer plays an important role in nature and some small creatures like bees and ants are able to sense polarized light and they orient themselves in the direction of blue lights. Phenomenons of polarised light are used in photography, LCD etc.
Complete step by step solution:
A) Light is mixtures of waves vibrating in all directions but when polarized, the vibration remains constant in one direction.

The above diagram demonstrates how a transverse light is converted to polarised light, the material used is a polariser which allows only perpendicular vibrated light to pass through it and eliminate every other light which transverse in in other direction other than perpendicular plane. In the first diagram the transverse light is polarised twice to filter out the remaining unpolarized light so that the output light is pure polarised light.
In the second diagram when the polariser is kept inclined to the plane no light passes through it as the polarised light cannot pass the inclined polariser since they transverse in only perpendicular direction.
Given:
${P_1}\& {P_2}$ are kept perpendicular to each other.
Another polaroid ${P_3}$ is kept between ${P_1}\& {P_2}$ such that ${P_3}$ is making an angle $30^\circ $ with ${P_1}$ .
The required ${I_0}$ can be calculated as follows:
As Malus law states that the intensity of a beam after passing a polariser becomes half of the original intensity i.e. $I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}$
So, when the light pass through ${P_1}$ , the original intensity will be reduced to half of its value i.e. ${I_1} = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}$.
The intensity of polarized light passing through an inclined polariser of angle $\theta $ becomes $I = {I_0}{\cos ^2}\theta $.
When ${I_1}$ pass through ${P_3}$ , the intensity will become
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}{\cos ^2}30^\circ $
i.e. \[I = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}{(\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2})^2}\]
which gives $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8}$
The above intensity will again pass through ${P_2}$ and the final intensity will be obtained as:
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8}{\cos ^2}60^\circ $
i.e. $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{8} \times \dfrac{1}{4}$
which gives $I = \dfrac{{3{I_0}}}{{32}}$
Therefore, the above intensity is the required final intensity.
Note: Polarizer plays an important role in nature and some small creatures like bees and ants are able to sense polarized light and they orient themselves in the direction of blue lights. Phenomenons of polarised light are used in photography, LCD etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




