
(a) What are the three classes of matter? Give one example of each type.
(b) Draw the flowchart for the schematic representation of different types of matter.
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: All in your environment is made up of matter. Atoms and substances are made up of minuscule pieces of matter. The atoms that make up the objects you see and touch every day are made up of these atoms. All that has mass and occupies space is referred to as matter (it has volume).
Complete answer:
-Matter is described as something that takes up space, has mass, and exerts resistance. The mass of a body is the sum of matter found within it. Strong, liquid, and gaseous matter are the three physical states of matter. Matter is classified chemically into pure and impure (mixture) substances.
Solid, liquid, and gas are the three distinct physical states of matter that matter can take in most environments.
Solid: A substance that preserves its size and form in the absence of a container; a substance whose molecules can only vibrate freely.
Example: Brick
Liquid: Since its molecules are loosely packed and continually moving, this material flows and maintains no definite form. It conforms to the shape of its container while maintaining the same amount.
Example: Water
Gas: A material that can only be stored if it is fully encased in a jar (or kept together by gravitational pull); a substance whose molecules have minimal intermolecular interactions and can freely travel.
Example: Hydrogen
b)
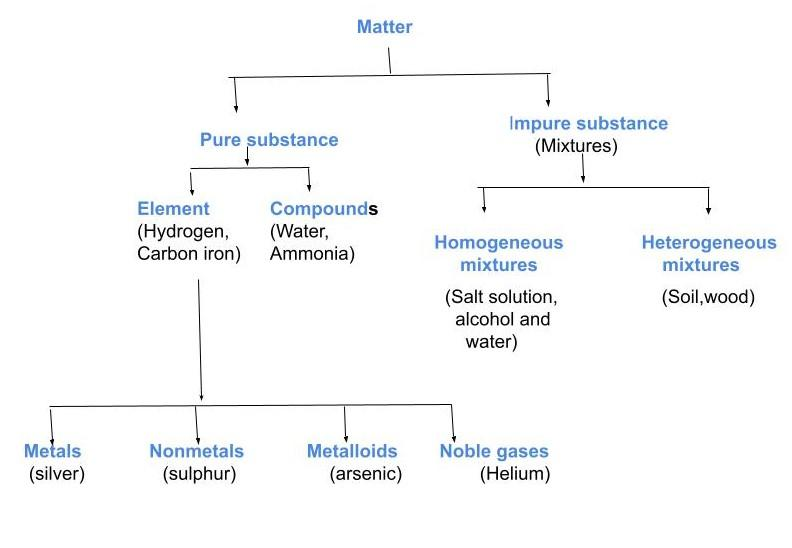
Note:
Antimatter is matter made up of antiparticles of the particles that make up ordinary matter. When a particle and its antiparticle collide, they annihilate; that is, according to Albert Einstein's equation \[E{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{c^2},\] they can both be converted into other particles with equal energy.
Complete answer:
-Matter is described as something that takes up space, has mass, and exerts resistance. The mass of a body is the sum of matter found within it. Strong, liquid, and gaseous matter are the three physical states of matter. Matter is classified chemically into pure and impure (mixture) substances.
Solid, liquid, and gas are the three distinct physical states of matter that matter can take in most environments.
Solid: A substance that preserves its size and form in the absence of a container; a substance whose molecules can only vibrate freely.
Example: Brick
Liquid: Since its molecules are loosely packed and continually moving, this material flows and maintains no definite form. It conforms to the shape of its container while maintaining the same amount.
Example: Water
Gas: A material that can only be stored if it is fully encased in a jar (or kept together by gravitational pull); a substance whose molecules have minimal intermolecular interactions and can freely travel.
Example: Hydrogen
b)

Note:
Antimatter is matter made up of antiparticles of the particles that make up ordinary matter. When a particle and its antiparticle collide, they annihilate; that is, according to Albert Einstein's equation \[E{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}m{c^2},\] they can both be converted into other particles with equal energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





