
(a) What is a soap? Name one soap.
(b) Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
(c) Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: We have seen soap in daily use for cleaning clothes, utensils, washing hands, while taking bath etc. There are a variety of soaps for a variety of purposes each may or may not be made up of exactly the same materials, but the building blocks of soaps are the same i.e. long chain fatty acids.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Soap is a salt of a long chain fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing and other types of housekeeping purposes. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants and also used as precursors to catalysts.
Name of one soap is sodium stearate.
(b)
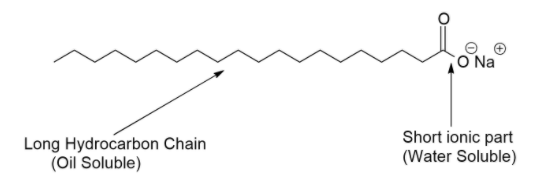
A soap molecule is made up of two parts: A long hydrocarbon part and a short ionic part containing –COO–Na+ group. The long hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic (water-repelling) in nature, so the hydrocarbon part of soap molecule is insoluble in water, but it is soluble in grease and oil. The ionic portion of the soap molecule is hydrophilic in nature and it is due to the polar nature of water molecules. So, the ionic portion of soap is soluble in water but it is insoluble in oil grease. If soap is present on the surface of water, then the hydrophobic tail which is not soluble in water will align along the water surface.
(c)
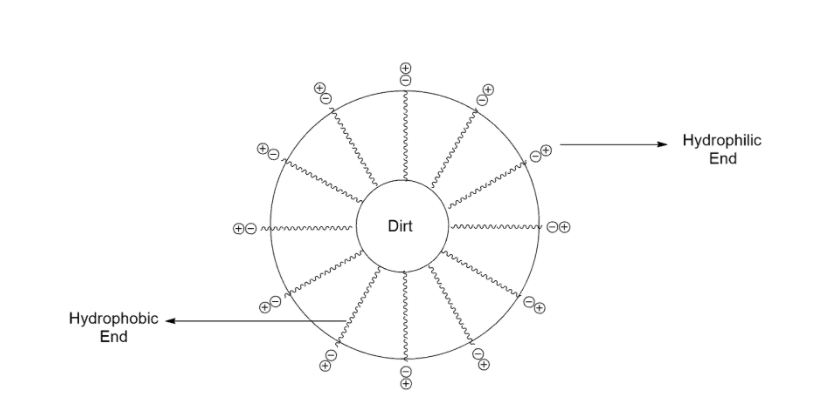
Dirt is mostly oily in nature and so it does not dissolve in water. Potassium (K) or Sodium (Na) salts of long chain fatty make up the molecule of soap so that the carbon chain gets dissolved in oil and the ionic part dissolves in water. Thus, the soap molecules form structures known as micelles. One end of the micelles is towards the oil and the other end faces outside which forms emulsion in water and helps in dissolving the grease or dirt. In a micelle, the soap molecules arranged radially with hydrocarbon ends directed towards the center and the ionic end is directed outwards. On putting a dirty cloth in water containing soap, attach the hydrocarbon part of the soap molecules in the micelle to the oil particles present on the surface of the dirty cloth. In this way the micelle captures the oily or greasy particle by using its hydrocarbon end. The ionic part of the soap molecules in the micelles remain attached to water in form of colloidal solutions. The oily particles present on its surface, entrapped by micelles get cleaned thoroughly by rinsing in water a number of times.
Note: Don't get confused between soap and detergent since they have the same use. Soap is a substance used for cleaning that is made when animal fats or vegetable oils are treated with an alkaline solution. On the other hand, detergent is a substance also used for cleaning, but it is often made from synthetic or man-made materials and can perform better cleaning action than soap under certain conditions
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Soap is a salt of a long chain fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing and other types of housekeeping purposes. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants and also used as precursors to catalysts.
Name of one soap is sodium stearate.
(b)

A soap molecule is made up of two parts: A long hydrocarbon part and a short ionic part containing –COO–Na+ group. The long hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic (water-repelling) in nature, so the hydrocarbon part of soap molecule is insoluble in water, but it is soluble in grease and oil. The ionic portion of the soap molecule is hydrophilic in nature and it is due to the polar nature of water molecules. So, the ionic portion of soap is soluble in water but it is insoluble in oil grease. If soap is present on the surface of water, then the hydrophobic tail which is not soluble in water will align along the water surface.
(c)

Dirt is mostly oily in nature and so it does not dissolve in water. Potassium (K) or Sodium (Na) salts of long chain fatty make up the molecule of soap so that the carbon chain gets dissolved in oil and the ionic part dissolves in water. Thus, the soap molecules form structures known as micelles. One end of the micelles is towards the oil and the other end faces outside which forms emulsion in water and helps in dissolving the grease or dirt. In a micelle, the soap molecules arranged radially with hydrocarbon ends directed towards the center and the ionic end is directed outwards. On putting a dirty cloth in water containing soap, attach the hydrocarbon part of the soap molecules in the micelle to the oil particles present on the surface of the dirty cloth. In this way the micelle captures the oily or greasy particle by using its hydrocarbon end. The ionic part of the soap molecules in the micelles remain attached to water in form of colloidal solutions. The oily particles present on its surface, entrapped by micelles get cleaned thoroughly by rinsing in water a number of times.
Note: Don't get confused between soap and detergent since they have the same use. Soap is a substance used for cleaning that is made when animal fats or vegetable oils are treated with an alkaline solution. On the other hand, detergent is a substance also used for cleaning, but it is often made from synthetic or man-made materials and can perform better cleaning action than soap under certain conditions
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




