
(a) What is graphite? What substance is graphite made?
(b) Describe the structure of graphite with the help of a labeled diagram.
(c) Why is graphite a good conductor of electricity but diamond is a non-conductor of electricity
(d) State any two uses of graphite.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:We know that the carbon has valency of four, and so it has the tendency to form many allotropes with various shapes. The well-known allotropes of carbon are diamond and graphite.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) We must remember that a crystalline form of the carbon with the atoms of carbon arranged in a hexagonal structure is graphite. The colour of graphite is greyish black and is an opaque substance. Graphite is made up of carbon.
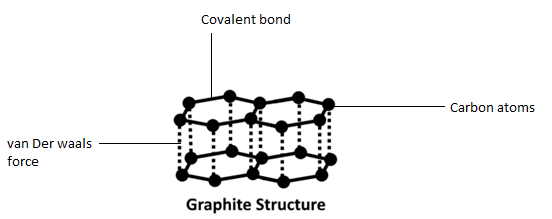
(b) We know that the graphite has carbon triple bonded molecular lattices, which are bonded in covalent bonds. The atoms of carbon form layers with hexagonal arrangement of atoms. The different layers of carbon atoms present in graphite are bounded by weak van der Waals forces. In graphite, the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and each carbon is linked to three other carbon atoms by forming hexagonal rings. Each carbon atom consists of an unhybridized ${\text{p}}$ orbital that undergoes sideways overlap to form three $p\pi - p\pi $ double bonds. Hence, graphite has a two-dimensional sheet-like structure consisting of a number of hexagonal rings fused together. The sheet-like structure makes graphite a soft material.
(c) We must remember that diamond does not conduct electricity, whereas graphite conducts electricity because in graphite there are delocalized electrons that move between layers, whereas in diamond the particles are not charged to move freely.
(d) We can use graphite in batteries, refractories, brake linings, and as lubricants.
Note: As we know a huge amount of pressure has to be applied to break the covalent bonds in graphite. On applying the pressure, the hexagonal rings in graphite deforms and the deformed hexagonal rings tends to form boat-shaped structure. When this happens, the graphite forms into a metastable allotrope of carbon called a hexagonal diamond.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) We must remember that a crystalline form of the carbon with the atoms of carbon arranged in a hexagonal structure is graphite. The colour of graphite is greyish black and is an opaque substance. Graphite is made up of carbon.
(b) We know that the graphite has carbon triple bonded molecular lattices, which are bonded in covalent bonds. The atoms of carbon form layers with hexagonal arrangement of atoms. The different layers of carbon atoms present in graphite are bounded by weak van der Waals forces. In graphite, the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and each carbon is linked to three other carbon atoms by forming hexagonal rings. Each carbon atom consists of an unhybridized ${\text{p}}$ orbital that undergoes sideways overlap to form three $p\pi - p\pi $ double bonds. Hence, graphite has a two-dimensional sheet-like structure consisting of a number of hexagonal rings fused together. The sheet-like structure makes graphite a soft material.

(c) We must remember that diamond does not conduct electricity, whereas graphite conducts electricity because in graphite there are delocalized electrons that move between layers, whereas in diamond the particles are not charged to move freely.
(d) We can use graphite in batteries, refractories, brake linings, and as lubricants.
Note: As we know a huge amount of pressure has to be applied to break the covalent bonds in graphite. On applying the pressure, the hexagonal rings in graphite deforms and the deformed hexagonal rings tends to form boat-shaped structure. When this happens, the graphite forms into a metastable allotrope of carbon called a hexagonal diamond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




