
(a) What is linearly polarised light. Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised.
(b) Unpolarised light is incident on a polarised light. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Light propagates as transverse electromagnetic waves. The magnitude of the electric field is much larger as compared to the magnitude of the magnetic field. We generally prefer to describe light as electric field oscillations.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Light is an electromagnetic wave emitted by the sun. An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave and consists of oscillations of electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to propagation of the wave.
Ordinary light has oscillations in all directions. This light is called an unpolarised light. When the oscillations are in a single plane, the light is called linearly polarised light.
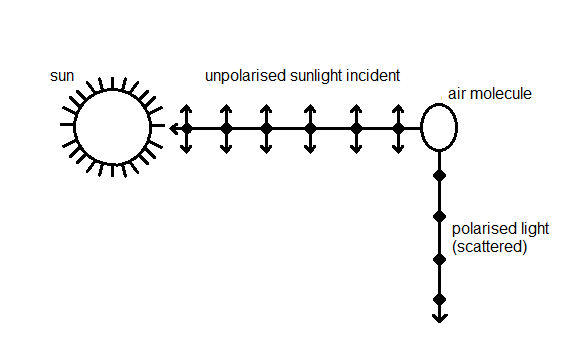
Sunlight is an unpolarised light. When it travels through the earth’s atmosphere, due the tiny particles present, it undergoes scattering. Due to scattering of sunlight polarised and partially polarised light is formed. The polarised light is in the direction perpendicular to the propagation of the original unpolarised light.
The given diagram shows the process of polarisation of sunlight. The dots and double arrows are any two perpendicular planes of oscillations of electric field.
(b) When an unpolarised light passes through a polariser, the intensity of the transmitted polarised light reduces to half of the intensity of polarised light. It does not matter on the angle between the transmission axis and the plane of polarisation. Therefore, even when the polariser is rotated the intensity of the transmitted light becomes half.
Note: Malus law states that the intensity of the polarised light transmitted through the analyser varies as the square of the cosine of the angle between the plane of transmission of the analyser and the plane of the polariser.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Light is an electromagnetic wave emitted by the sun. An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave and consists of oscillations of electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to propagation of the wave.
Ordinary light has oscillations in all directions. This light is called an unpolarised light. When the oscillations are in a single plane, the light is called linearly polarised light.
Sunlight is an unpolarised light. When it travels through the earth’s atmosphere, due the tiny particles present, it undergoes scattering. Due to scattering of sunlight polarised and partially polarised light is formed. The polarised light is in the direction perpendicular to the propagation of the original unpolarised light.
The given diagram shows the process of polarisation of sunlight. The dots and double arrows are any two perpendicular planes of oscillations of electric field.

(b) When an unpolarised light passes through a polariser, the intensity of the transmitted polarised light reduces to half of the intensity of polarised light. It does not matter on the angle between the transmission axis and the plane of polarisation. Therefore, even when the polariser is rotated the intensity of the transmitted light becomes half.
Note: Malus law states that the intensity of the polarised light transmitted through the analyser varies as the square of the cosine of the angle between the plane of transmission of the analyser and the plane of the polariser.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




