
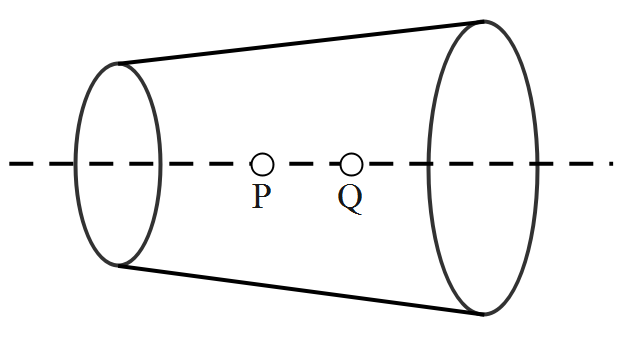
A wire has non-uniform cross-section as shown in figure. A steady current flows through it. The drift speed of electrons at points P and Q is\[{{v}_{P}}\] and\[{{v}_{Q}}\].

Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: The relation between the drift velocity and the area of the conductor is given by the drift velocity formula that is equal to the product of the number of electrons, the electron charge, the drift velocity and the area of the conductor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Theoretical explanation:
The drift velocity of the electrons is given by the formula as follows.
\[i=nevA\]
The drift speed of electrons is inversely proportional to the radius of cross section.
\[v\propto \dfrac{1}{A}\]
Thus here the cross sectional area at point P is smaller than the cross sectional area at point Q.
\[{{A}_{P}}<{{A}_{Q}}\]
Hence, the drift velocity is large for smaller areas and small for larger areas.
\[\begin{align}
& {{A}_{P}}<{{A}_{Q}} \\
& \therefore {{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}} \\
\end{align}\]
The drift speed will relate as per the relation given below,
\[{{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\]
Mathematical representation.
The drift velocity of the electrons is given as follows.
\[i=nevA\]
As the current ‘i’, the number of electrons ‘n’ and the charge on the electron ‘e’ are constant, thus, the relation between the drift velocity and the area of cross section is given as follows.
\[{{v}_{1}}{{A}_{1}}={{v}_{2}}{{A}_{2}}\]
The representation of the above equation in terms of the velocity and the area of P and Q is,
\[{{v}_{P}}{{A}_{P}}={{v}_{Q}}{{A}_{Q}}\]
The area of the cross section of Q is more than that of P.
\[\dfrac{{{v}_{P}}}{{{v}_{Q}}}=\dfrac{{{A}_{Q}}}{{{A}_{P}}}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,({{A}_{Q}}>{{A}_{P}})\]
\[\therefore \dfrac{{{v}_{P}}}{{{v}_{Q}}}>1\]
The drift speed will relate as per the relation given below,
\[\therefore {{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\]
\[\therefore \] For the drift speed of electrons at points P and Q is\[{{v}_{P}}\] and\[{{v}_{Q}}\]is, \[{{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\].
Note: The only equation or formula that gives the relation between the drift velocity of electrons and the area of cross section is the drift velocity of electrons. The current, the number of electrons and the charge on the electron always remain constant.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Theoretical explanation:
The drift velocity of the electrons is given by the formula as follows.
\[i=nevA\]
The drift speed of electrons is inversely proportional to the radius of cross section.
\[v\propto \dfrac{1}{A}\]
Thus here the cross sectional area at point P is smaller than the cross sectional area at point Q.
\[{{A}_{P}}<{{A}_{Q}}\]
Hence, the drift velocity is large for smaller areas and small for larger areas.
\[\begin{align}
& {{A}_{P}}<{{A}_{Q}} \\
& \therefore {{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}} \\
\end{align}\]
The drift speed will relate as per the relation given below,
\[{{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\]
Mathematical representation.
The drift velocity of the electrons is given as follows.
\[i=nevA\]
As the current ‘i’, the number of electrons ‘n’ and the charge on the electron ‘e’ are constant, thus, the relation between the drift velocity and the area of cross section is given as follows.
\[{{v}_{1}}{{A}_{1}}={{v}_{2}}{{A}_{2}}\]
The representation of the above equation in terms of the velocity and the area of P and Q is,
\[{{v}_{P}}{{A}_{P}}={{v}_{Q}}{{A}_{Q}}\]
The area of the cross section of Q is more than that of P.
\[\dfrac{{{v}_{P}}}{{{v}_{Q}}}=\dfrac{{{A}_{Q}}}{{{A}_{P}}}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,({{A}_{Q}}>{{A}_{P}})\]
\[\therefore \dfrac{{{v}_{P}}}{{{v}_{Q}}}>1\]
The drift speed will relate as per the relation given below,
\[\therefore {{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\]
\[\therefore \] For the drift speed of electrons at points P and Q is\[{{v}_{P}}\] and\[{{v}_{Q}}\]is, \[{{v}_{P}}>{{v}_{Q}}\].
Note: The only equation or formula that gives the relation between the drift velocity of electrons and the area of cross section is the drift velocity of electrons. The current, the number of electrons and the charge on the electron always remain constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




