
A wire is in the form of a tetrahedron. The resistance of each edge is r. The equivalent resistance between corners 1-2 and 1-3 are respectively:
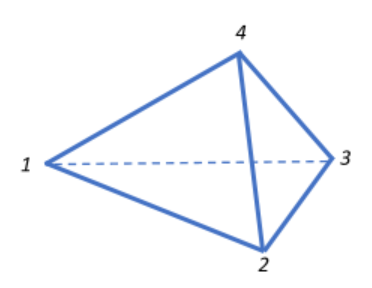
A. $\dfrac{r}{2},\dfrac{r}{2}$
B. $r,r$
C. $\dfrac{r}{2},r$
D. $r,\dfrac{r}{2}$

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Notice that the setup represents a Wheatstone bridge that works on the principle of null deflection, which suggests that as long as the ratio of the resistances are equal, no current will flow through the circuit. Use this to effectively treat each case of connecting 1-2 and 1-3 as the balanced condition and determine the net resistance across the corresponding points by accounting for the series and parallel arrangement of resistances.
Formula used: Effective resistance of two resistors in series: $R_{eff} = R_1 +R_2$
Effective resistance of two resistors in parallel: $R_{eff} = \dfrac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 +R_2}$
Condition for a balanced Wheatstone bridge: $\dfrac{P}{Q} =\dfrac{R}{S}$
Complete step by step answer:
When we look at the arrangement, we see that it is similar to the setup of a Wheatstone bridge containing two simple series-parallel resistances.
We first want to find the effective resistance between 1 and 2. Let us consider we connect a battery across 1 and 2. In this case we can disregard the resistance $R_{34}$ since there will be no current flowing through it and the bridge remains in a balanced condition, and we can treat this edge synonymous to the galvanometer arm of a Wheatstone bridge.
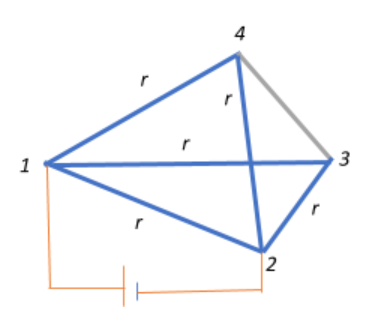
In this case, the effective resistance across 1-2 will be:
$R_{eff_{12}} = (R_{14}+R_{42}) || (R_{13}+R_{32}) || R_{12}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{12}} = (r+r) || (r+r) || (r) = 2r || 2r || r$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R_{eff_{12}}} = \dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{r} = \dfrac{1+1+2}{2r} = \dfrac{4}{2r}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{12}} = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
Similarly, to find the effective resistance between 1 and 3, we connect a battery across 1 and 3. In this case we can disregard the resistance $R_{24}$
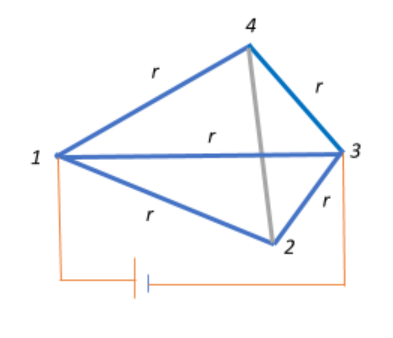
In this case, the effective resistance across 1-3 will be:
$R_{eff_{13}} = (R_{12}+R_{23}) || (R_{14}+R_{43}) || R_{13}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{13}} = (r+r) || (r+r) || (r) = 2r || 2r || r$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R_{eff_{13}}} = \dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{r} = \dfrac{1+1+2}{2r} = \dfrac{4}{2r}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{13}} = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that a Wheatstone bridge, which is also known as a resistance bridge is a setup that is generally used to calculate an unknown resistance in an arm of the bridge by balancing the two arms of the circuit. Thus, the Wheatstone bridge is used for the precise measurement of low resistance since the detection of zero current in the galvanometer is of high precision.
Formula used: Effective resistance of two resistors in series: $R_{eff} = R_1 +R_2$
Effective resistance of two resistors in parallel: $R_{eff} = \dfrac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 +R_2}$
Condition for a balanced Wheatstone bridge: $\dfrac{P}{Q} =\dfrac{R}{S}$
Complete step by step answer:
When we look at the arrangement, we see that it is similar to the setup of a Wheatstone bridge containing two simple series-parallel resistances.
We first want to find the effective resistance between 1 and 2. Let us consider we connect a battery across 1 and 2. In this case we can disregard the resistance $R_{34}$ since there will be no current flowing through it and the bridge remains in a balanced condition, and we can treat this edge synonymous to the galvanometer arm of a Wheatstone bridge.

In this case, the effective resistance across 1-2 will be:
$R_{eff_{12}} = (R_{14}+R_{42}) || (R_{13}+R_{32}) || R_{12}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{12}} = (r+r) || (r+r) || (r) = 2r || 2r || r$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R_{eff_{12}}} = \dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{r} = \dfrac{1+1+2}{2r} = \dfrac{4}{2r}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{12}} = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
Similarly, to find the effective resistance between 1 and 3, we connect a battery across 1 and 3. In this case we can disregard the resistance $R_{24}$

In this case, the effective resistance across 1-3 will be:
$R_{eff_{13}} = (R_{12}+R_{23}) || (R_{14}+R_{43}) || R_{13}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{13}} = (r+r) || (r+r) || (r) = 2r || 2r || r$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R_{eff_{13}}} = \dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{2r} +\dfrac{1}{r} = \dfrac{1+1+2}{2r} = \dfrac{4}{2r}$
$\Rightarrow R_{eff_{13}} = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that a Wheatstone bridge, which is also known as a resistance bridge is a setup that is generally used to calculate an unknown resistance in an arm of the bridge by balancing the two arms of the circuit. Thus, the Wheatstone bridge is used for the precise measurement of low resistance since the detection of zero current in the galvanometer is of high precision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




