
In forest ecosystem, pyramid of number is
(a) Upright
(b) Inverted
(c) Any of the two
(d) None of the above.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: It describes the total number of individual organisms at each level in the food chain of an ecosystem.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the definition of the ecological pyramid of the forest ecosystem.
An ecological pyramid indicates the relation of biomass, productiveness or strength at different trophic levels. The primary producers are usually shown at the lowest and apex predators on the top. The pyramids are specific for specific ecosystems. The pyramid of numbers indicates the range of individual organisms at successive trophic levels.
The producers are huge size trees that make the bottom of the Pyramid in the forest ecosystem.
The herbivores along with fruit-consuming birds, deer, elephants, etc. make the primary customers and are much less than number one producers. After that, the range is going down at every successive level.
Thus, a Pyramid of numbers in forest area surroundings is in part upright or spindle-shaped.
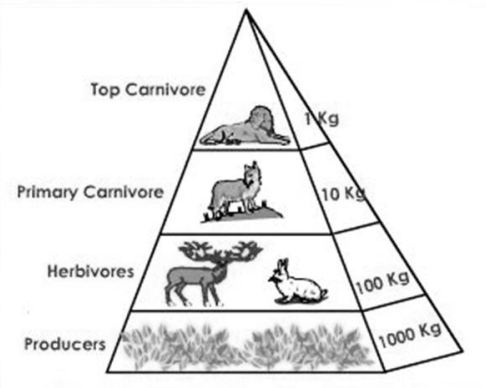
Fig- Pyramid of number in forest ecosystem.
Now lets us find the solution from given options -
Pyramid of number is normally upright as a maximum range of organisms arise on the producer level that is observed via means of the smaller range of herbivores, fewer number one carnivores and still the fewer higher levels of carnivores. So, the numbers of organisms pass on reducing with the growth in every trophic level.
The pyramid of biomass might also additionally be"inverted". For example, in a pond ecosystem, the crop of phytoplankton, the major producers, at any given point might be decreased than the mass of the heterotrophs, inclusive of fish and insects.
Thus, the right answer is, ‘Upright’.
Note:This Pyramid suggests the numbers of the producers, herbivores and the carnivores at their successive trophic levels.
This pyramid may be both upright, or inverted or in part upright.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the definition of the ecological pyramid of the forest ecosystem.
An ecological pyramid indicates the relation of biomass, productiveness or strength at different trophic levels. The primary producers are usually shown at the lowest and apex predators on the top. The pyramids are specific for specific ecosystems. The pyramid of numbers indicates the range of individual organisms at successive trophic levels.
The producers are huge size trees that make the bottom of the Pyramid in the forest ecosystem.
The herbivores along with fruit-consuming birds, deer, elephants, etc. make the primary customers and are much less than number one producers. After that, the range is going down at every successive level.
Thus, a Pyramid of numbers in forest area surroundings is in part upright or spindle-shaped.

Fig- Pyramid of number in forest ecosystem.
Now lets us find the solution from given options -
Pyramid of number is normally upright as a maximum range of organisms arise on the producer level that is observed via means of the smaller range of herbivores, fewer number one carnivores and still the fewer higher levels of carnivores. So, the numbers of organisms pass on reducing with the growth in every trophic level.
The pyramid of biomass might also additionally be"inverted". For example, in a pond ecosystem, the crop of phytoplankton, the major producers, at any given point might be decreased than the mass of the heterotrophs, inclusive of fish and insects.
Thus, the right answer is, ‘Upright’.
Note:This Pyramid suggests the numbers of the producers, herbivores and the carnivores at their successive trophic levels.
This pyramid may be both upright, or inverted or in part upright.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




