
(a) Write a note on Rosenmund reduction.
(b) Why is fluoro acetic acid more acidic than chloroacetic acid?
(c) Draw the resonating structures of carboxylate ions.
Answer
528.7k+ views
Hint: Rosenmund reaction is a reduction reaction carried out in the presence of a catalyst. Electron withdrawing groups increase the acidity of acids but increase the stability of their corresponding conjugate bases.
Complete step by step solution:
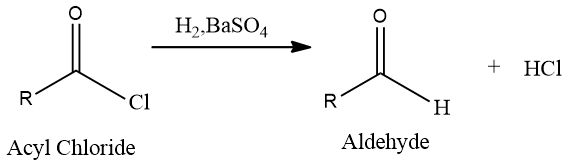
(a) The Rosenmund reduction is a reaction where acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes by employing hydrogen gas over palladium poisoned by barium sulfate. An example of this catalytic hydrogenation of acyl chlorides forming aldehydes is shown below,
Due to the high reactivity of hydrogen gas, it readily initiates a substitution in the acyl chloride, forming HCl and the required aldehyde. Barium sulfate reduces the activity of palladium due to its low surface area meaning it decreases the reducing power of palladium in order to prevent over-reduction of the acid
(b) Fluoroacetic acid is more acidic than chloroacetic acid. Electron withdrawing substituent increases the acidity of a carboxylic acid by dispersing negative charge by inductive effect and stabilizing the carboxylate anion. This effect is stronger in fluoro acetic acid than in chloroacetic acid because −I effect of \[{{F}_{2}}\] is greater than that of \[C{{l}_{2}}\].
(c) The resonating structures of carboxylate ion are drawn as follows:
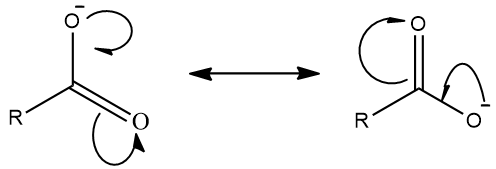
Carboxylate ions get stabilized by resonance. Carboxylate ion is a resonance hybrid of two equivalent structures so that the negative charge is delocalised on both oxygen atoms. This leads to stability.
Note: Rosenmund reaction was named after Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund, who first reported it in 1918. A few of the side products of this process can be avoided if the reaction is conducted in anhydrous solvents.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) The Rosenmund reduction is a reaction where acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes by employing hydrogen gas over palladium poisoned by barium sulfate. An example of this catalytic hydrogenation of acyl chlorides forming aldehydes is shown below,
Due to the high reactivity of hydrogen gas, it readily initiates a substitution in the acyl chloride, forming HCl and the required aldehyde. Barium sulfate reduces the activity of palladium due to its low surface area meaning it decreases the reducing power of palladium in order to prevent over-reduction of the acid

(b) Fluoroacetic acid is more acidic than chloroacetic acid. Electron withdrawing substituent increases the acidity of a carboxylic acid by dispersing negative charge by inductive effect and stabilizing the carboxylate anion. This effect is stronger in fluoro acetic acid than in chloroacetic acid because −I effect of \[{{F}_{2}}\] is greater than that of \[C{{l}_{2}}\].
(c) The resonating structures of carboxylate ion are drawn as follows:

Carboxylate ions get stabilized by resonance. Carboxylate ion is a resonance hybrid of two equivalent structures so that the negative charge is delocalised on both oxygen atoms. This leads to stability.
Note: Rosenmund reaction was named after Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund, who first reported it in 1918. A few of the side products of this process can be avoided if the reaction is conducted in anhydrous solvents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




