
ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. If AD intersects BC at O, show that
\[\dfrac{{ar\left( {ABC} \right)}}{{ar\left( {DBC} \right)}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{DO}}\]

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: Here we will first draw the perpendiculars on the base BC from the point A and point D. Then we will show the triangles similar to get the relation between the perpendiculars and the sides AO and DO. Then we will find the ratio of the area of the required triangles and use the obtained relation to get the desired equation.
Formula Used:
We will use the formula Area of the triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{Base}} \times {\rm{Height}}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will construct a perpendicular AX on the base BC and a perpendicular DY on the base BC. Therefore, we get
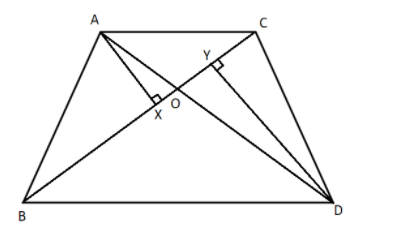
Now we will take the triangles AXO and triangle DYO and we will show that it’s the similar triangles. Therefore, we get
In \[\Delta AXO\] and \[\Delta DYO\],
$\Rightarrow$ \[\angle AXO = \angle DYO = 90^\circ \]
And
$\Rightarrow$ \[\angle AOX = \angle DOY\] because these are the vertical opposite angles.
Hence, by the rule of Angle-Angle (AA) similarity rule we can say that the triangles AXO is similar to the triangle DYO i.e. \[\Delta AXO \approx \Delta DYO\].
As these triangles are similar then the corresponding sides of the similar triangles are always proportional to each other. Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow$ \[\dfrac{{AX}}{{DY}} = \dfrac{{XO}}{{YO}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{DO}}\]……………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now we will find the ratio of the area of the triangle ABC to the area of the triangle DBC. Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow$ \[\dfrac{{ar\left( {ABC} \right)}}{{ar\left( {DBC} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times AX}}{{\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times DY}} = \dfrac{{AX}}{{DY}}\]
By using the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ar\left( {ABC} \right)}}{{ar\left( {DBC} \right)}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{DO}}\]
Hence proved.
Note: Triangle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that has three sides. There are different types of triangles such as isosceles triangle, equilateral triangle, right angled triangle, etc. Similar triangles are triangles that have an exact similar shape but the size of the triangles may vary. We should note that the area of the triangle is equal to half the product of the base of the triangle and the height of the triangle.
Also, the Angle-Angle (AA) similarity rule states that if in two triangles, two pairs of corresponding angles are same or equal, then the triangles are said to be similar triangles.
Formula Used:
We will use the formula Area of the triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{Base}} \times {\rm{Height}}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will construct a perpendicular AX on the base BC and a perpendicular DY on the base BC. Therefore, we get

Now we will take the triangles AXO and triangle DYO and we will show that it’s the similar triangles. Therefore, we get
In \[\Delta AXO\] and \[\Delta DYO\],
$\Rightarrow$ \[\angle AXO = \angle DYO = 90^\circ \]
And
$\Rightarrow$ \[\angle AOX = \angle DOY\] because these are the vertical opposite angles.
Hence, by the rule of Angle-Angle (AA) similarity rule we can say that the triangles AXO is similar to the triangle DYO i.e. \[\Delta AXO \approx \Delta DYO\].
As these triangles are similar then the corresponding sides of the similar triangles are always proportional to each other. Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow$ \[\dfrac{{AX}}{{DY}} = \dfrac{{XO}}{{YO}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{DO}}\]……………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now we will find the ratio of the area of the triangle ABC to the area of the triangle DBC. Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow$ \[\dfrac{{ar\left( {ABC} \right)}}{{ar\left( {DBC} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times AX}}{{\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times DY}} = \dfrac{{AX}}{{DY}}\]
By using the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ar\left( {ABC} \right)}}{{ar\left( {DBC} \right)}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{DO}}\]
Hence proved.
Note: Triangle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that has three sides. There are different types of triangles such as isosceles triangle, equilateral triangle, right angled triangle, etc. Similar triangles are triangles that have an exact similar shape but the size of the triangles may vary. We should note that the area of the triangle is equal to half the product of the base of the triangle and the height of the triangle.
Also, the Angle-Angle (AA) similarity rule states that if in two triangles, two pairs of corresponding angles are same or equal, then the triangles are said to be similar triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




