
ABCD is a tetrahedron with pv's of its angular point A (−5,22,5); B(1,2,3);C (4,3,2) and D (−1,2, −3). If the area of the triangle AEF where quadrilaterals ABDE and ABCF are parallelograms is $\sqrt{S}$then find the values of S.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: We know that the diagonal of the parallelogram bisect each other which, means they both of common mid-point. We will calculate the midpoints using mid-point formula Using the above information, we will calculate the coordinates of point E and F. We will calculate the area of triangle AEF and equate it to $\sqrt{S}$.
Complete step by step answer:
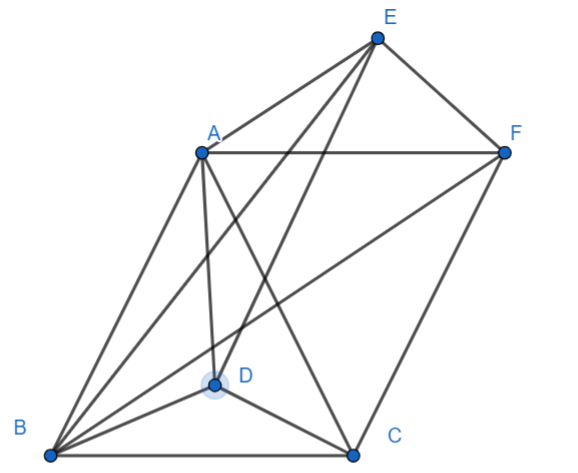
We have the above figure where
A (−5,22,5)
B (1,2,3)
C (4,3,2)
D (−1,2, −3)
In parallelogram ABDE
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other so, diagonal AD and BE will bisect each other and have common mid-point
Mid-pint of AD=mid-point of BE
Let the mid-point of AD be (x,y,z)
The mid-point of AD can be calculated using mid-point formula
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We will put values from coordinates A and D, we will get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-5-1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=-3 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22+2}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5-3}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow z=1 \\
\end{align}\]
The coordinates of mid-point of AD are (-3, 12, 1)
Let the coordinates of point E be (p, q, r)
The coordinates of mid-point of BE will be $\left( \dfrac{1+p}{2},\dfrac{2+q}{2},\dfrac{3+r}{2} \right)$
As we know Mid-pint of AD=mid-point of BE
$\Rightarrow \left( -3,12,1 \right)=\left( \dfrac{1+p}{2},\dfrac{2+q}{2},\dfrac{3+r}{2} \right)$
We can calculate the value of p, q, r using above equation and we will get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=-7 \\
& \Rightarrow q=22 \\
& \Rightarrow r=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Point E is (-7,22, -1)
Similarly, in parallelogram ABCF
Mid-pint of AC=mid-point of BF
Midpoint of AC can be calculated using mid-point formula
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{-5+4}{2} \right)=\dfrac{-1}{2} \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{22+3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{25}{2} \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{5+2}{2} \right)=\dfrac{7}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Midpoint of AC is \[\left( \dfrac{-1}{2},\dfrac{25}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right)\]
Let the coordinates of point F be (h, k, l)
As we know Mid-pint of AC=mid-point of BF
\[\Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{-1}{2},\dfrac{25}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1+h}{2},\dfrac{2+k}{2},\dfrac{3+l}{2} \right)\]
We can calculate the value of h, k, l using above equation and we will get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=-2 \\
& \Rightarrow k=23 \\
& \Rightarrow l=4 \\
\end{align}$
Point F is (-2, 23 ,4)
We know that the area of triangle AEF is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow area\Delta AEF=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=\overrightarrow{E}-\overrightarrow{A} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=(-7+5)\hat{i}+(22-22)\hat{j}+(-1-5)\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=-2\hat{i}-6\hat{k} \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=\overrightarrow{F}-\overrightarrow{A} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=(-2+5)\hat{i}+(23-22)\hat{j}+(4-5)\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=3\hat{i}+\hat{j}-\hat{k} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the cross product of two vectors can be calculated using determinant form
\[\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{\Rightarrow AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
{\hat{i}} & {\hat{j}} & {\hat{k}} \\
-2 & 0 & -6 \\
3 & 1 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
0 & -6 \\
1 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{i}-\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
-2 & -6 \\
3 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{j}+\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
-2 & 0 \\
3 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=6\hat{i}-20\hat{j}-2\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{(-20)}^{2}}+{{(-2)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right|=\sqrt{440} \\
\end{align}\]
As given in the question the area of triangle AEF=$\sqrt{S}$
Therefore, $\sqrt{S}$= \[\sqrt{110}\]
The value of S = 110
Note:
Keep in mind the signs of the coordinates while substituting them in the formula. Use
the determinant method to find the cross product of two vectors it will be easy to calculate.
Properties of the various geometric shape should be known.
Complete step by step answer:

We have the above figure where
A (−5,22,5)
B (1,2,3)
C (4,3,2)
D (−1,2, −3)
In parallelogram ABDE
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other so, diagonal AD and BE will bisect each other and have common mid-point
Mid-pint of AD=mid-point of BE
Let the mid-point of AD be (x,y,z)
The mid-point of AD can be calculated using mid-point formula
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We will put values from coordinates A and D, we will get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-5-1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=-3 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22+2}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5-3}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow z=1 \\
\end{align}\]
The coordinates of mid-point of AD are (-3, 12, 1)
Let the coordinates of point E be (p, q, r)
The coordinates of mid-point of BE will be $\left( \dfrac{1+p}{2},\dfrac{2+q}{2},\dfrac{3+r}{2} \right)$
As we know Mid-pint of AD=mid-point of BE
$\Rightarrow \left( -3,12,1 \right)=\left( \dfrac{1+p}{2},\dfrac{2+q}{2},\dfrac{3+r}{2} \right)$
We can calculate the value of p, q, r using above equation and we will get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=-7 \\
& \Rightarrow q=22 \\
& \Rightarrow r=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Point E is (-7,22, -1)
Similarly, in parallelogram ABCF
Mid-pint of AC=mid-point of BF
Midpoint of AC can be calculated using mid-point formula
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& x=\left( \dfrac{-5+4}{2} \right)=\dfrac{-1}{2} \\
& y=\left( \dfrac{22+3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{25}{2} \\
& z=\left( \dfrac{5+2}{2} \right)=\dfrac{7}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Midpoint of AC is \[\left( \dfrac{-1}{2},\dfrac{25}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right)\]
Let the coordinates of point F be (h, k, l)
As we know Mid-pint of AC=mid-point of BF
\[\Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{-1}{2},\dfrac{25}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1+h}{2},\dfrac{2+k}{2},\dfrac{3+l}{2} \right)\]
We can calculate the value of h, k, l using above equation and we will get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=-2 \\
& \Rightarrow k=23 \\
& \Rightarrow l=4 \\
\end{align}$
Point F is (-2, 23 ,4)
We know that the area of triangle AEF is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow area\Delta AEF=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=\overrightarrow{E}-\overrightarrow{A} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=(-7+5)\hat{i}+(22-22)\hat{j}+(-1-5)\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}=-2\hat{i}-6\hat{k} \\
& \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=\overrightarrow{F}-\overrightarrow{A} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=(-2+5)\hat{i}+(23-22)\hat{j}+(4-5)\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AF}=3\hat{i}+\hat{j}-\hat{k} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the cross product of two vectors can be calculated using determinant form
\[\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{\Rightarrow AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
{\hat{i}} & {\hat{j}} & {\hat{k}} \\
-2 & 0 & -6 \\
3 & 1 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
0 & -6 \\
1 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{i}-\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
-2 & -6 \\
3 & -1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{j}+\left| \left( \begin{matrix}
-2 & 0 \\
3 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right) \right|\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF}=6\hat{i}-20\hat{j}-2\hat{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{(-20)}^{2}}+{{(-2)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{AE}\times \overrightarrow{AF} \right|=\sqrt{440} \\
\end{align}\]
As given in the question the area of triangle AEF=$\sqrt{S}$
Therefore, $\sqrt{S}$= \[\sqrt{110}\]
The value of S = 110
Note:
Keep in mind the signs of the coordinates while substituting them in the formula. Use
the determinant method to find the cross product of two vectors it will be easy to calculate.
Properties of the various geometric shape should be known.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




