
ABO blood grouping in humans is an example of
(a) Polygenic inheritance
(b)Multiple allelism
(c)Epistasis
(d)Pleiotropism
(e)Incomplete dominance
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called the locus on a chromosome. Generally, there are only two alleles for a gene in a diploid organism. It is the condition wherein three or more alleles of a gene are present.
Complete answer:
In multiple allelism, when there is a gene existing in more than two allelic forms. In general, multiple allelism is the condition wherein three or more alleles of a gene are present. Therefore, the term multiple alleles pertain to the presence of three or more alleles for a particular gene. Multiple allelism is better to understand with the help of ABO blood group system in humans. The inheritance of ABO blood group is a gene I (in which I represent isohemagglutinin) that remains in the 3 allelic expressions: ${ I }^{ A }$, ${ I }^{ B }$, and ${ I }^{ O }$.${ I }^{ A }$ and ${ I }^{ B }$ are codominant in humans. In which ${ I }^{ A }$ is responsible for type A antigens and ${ I }^{ B }$ is responsible for type B antigens, respectively, on the cell surface of erythrocytes. ${ I }^{ O }$ is a recessive allele and it does not produce antigen. If there are more than two alleles present in the population, then the individual comprising the population would possess only two such alleles. Although, the inheritance of ${ I }^{ A }$ and ${ I }^{ B }$ alleles results in having a blood type AB in the case of ABO blood group system.
Additional Information: Multiple alleles are situated on homologous chromosomes at the same locus and there is no crossing over between the members of multiple alleles. Crossing over takes place between two different genes only (i.e., inter-genetic recombination) and does not occur within a gene (intragenic recombination). Multiple alleles never show complementation with each other. With the help of the complementation test, the allelic and non-allelic genes may be differentiated well. The production of wild type phenotype in a trans-heterozygote for 2 mutant alleles is known as the complementation test.
So, the correct answer is ‘Multiple allelism’.
Note: The wild type (normal) allele is nearly always dominant while the other mutant alleles in the series may show dominance or there may be an intermediate phenotypic effect. When any of the two multiple alleles are crossed, the phenotype is of a mutant type and not the wild type.
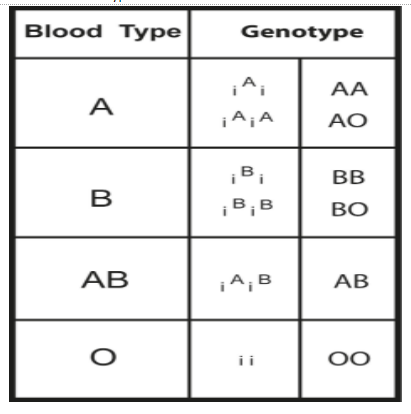
Complete answer:
In multiple allelism, when there is a gene existing in more than two allelic forms. In general, multiple allelism is the condition wherein three or more alleles of a gene are present. Therefore, the term multiple alleles pertain to the presence of three or more alleles for a particular gene. Multiple allelism is better to understand with the help of ABO blood group system in humans. The inheritance of ABO blood group is a gene I (in which I represent isohemagglutinin) that remains in the 3 allelic expressions: ${ I }^{ A }$, ${ I }^{ B }$, and ${ I }^{ O }$.${ I }^{ A }$ and ${ I }^{ B }$ are codominant in humans. In which ${ I }^{ A }$ is responsible for type A antigens and ${ I }^{ B }$ is responsible for type B antigens, respectively, on the cell surface of erythrocytes. ${ I }^{ O }$ is a recessive allele and it does not produce antigen. If there are more than two alleles present in the population, then the individual comprising the population would possess only two such alleles. Although, the inheritance of ${ I }^{ A }$ and ${ I }^{ B }$ alleles results in having a blood type AB in the case of ABO blood group system.
Additional Information: Multiple alleles are situated on homologous chromosomes at the same locus and there is no crossing over between the members of multiple alleles. Crossing over takes place between two different genes only (i.e., inter-genetic recombination) and does not occur within a gene (intragenic recombination). Multiple alleles never show complementation with each other. With the help of the complementation test, the allelic and non-allelic genes may be differentiated well. The production of wild type phenotype in a trans-heterozygote for 2 mutant alleles is known as the complementation test.
So, the correct answer is ‘Multiple allelism’.
Note: The wild type (normal) allele is nearly always dominant while the other mutant alleles in the series may show dominance or there may be an intermediate phenotypic effect. When any of the two multiple alleles are crossed, the phenotype is of a mutant type and not the wild type.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




