
According to Boyle’s law, PV=constant, at constant temperature. Which of the following graphs is correct?

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Recall that Boyle’s law suggests that the volume occupied by a given quantity of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure exerted on it at a constant temperature. Thus, any increase or decrease in volume is warranted by a simultaneous corresponding decrease of increase in pressure. These statements should help in determining the nature of the graph, provided that the product PV remains constant for a given amount of gas.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what exactly Boyle’s Law entails.
Boyle’s law is an empirical relation that was formulated on the basis of the behaviour of a gas of a given mass which was subjected to an exertion of pressure while maintaining a constant temperature. It was observed that the absolute pressure exerted by a given quantity of gas was inversely proportional to the volume that the mass of gas occupies, provided the temperature and the amount of gas remained unchanged within a closed system. This law was the first physical law to be expressed in terms of an equation that described the dependency of two variable quantities.
It is empirically given as: $P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}$, whereas mathematically it can be expressed as:
$PV=k$, where k is a constant. This suggests that the product of pressure and volume remains a constant for a given quantity of confined gas and this holds true as long as the temperature remains invariant.
From this law, we can infer that changing the pressure exerted on the gas by some factor would inevitably change the volume of the gas by the same factor such that the product of the two remains the same, irrespective of any changes specific to just pressure or volume. Thus, any change in either quantity induces an inversely proportional change in the other, keeping the PV value constant for a given mass of gas that is subjected to no temperature changes.
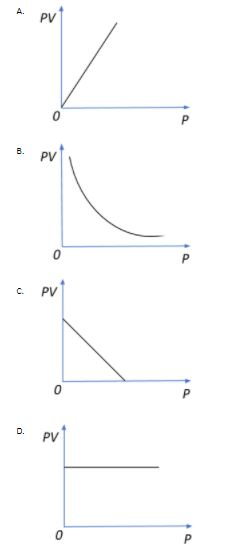
Thus, if we plot a PV versus P graph, we see that no matter how we change the pressure, the product PV remains constant since even V undergoes an equivalent change for any change in P for this closed system.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that Boyle’s law is an ideal gas law. Real gases, however, exhibit deviations from this law. This is because at the time of the formulation of this law, very high pressures or very low temperatures could not be produced, and all the experiments were carried out at moderate temperatures where most gases behave like ideal gases. This deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour is quantized by the compressibility factor (Z), which is nothing but a correction factor given as a ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at same temperature and pressure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what exactly Boyle’s Law entails.
Boyle’s law is an empirical relation that was formulated on the basis of the behaviour of a gas of a given mass which was subjected to an exertion of pressure while maintaining a constant temperature. It was observed that the absolute pressure exerted by a given quantity of gas was inversely proportional to the volume that the mass of gas occupies, provided the temperature and the amount of gas remained unchanged within a closed system. This law was the first physical law to be expressed in terms of an equation that described the dependency of two variable quantities.
It is empirically given as: $P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}$, whereas mathematically it can be expressed as:
$PV=k$, where k is a constant. This suggests that the product of pressure and volume remains a constant for a given quantity of confined gas and this holds true as long as the temperature remains invariant.
From this law, we can infer that changing the pressure exerted on the gas by some factor would inevitably change the volume of the gas by the same factor such that the product of the two remains the same, irrespective of any changes specific to just pressure or volume. Thus, any change in either quantity induces an inversely proportional change in the other, keeping the PV value constant for a given mass of gas that is subjected to no temperature changes.
Thus, if we plot a PV versus P graph, we see that no matter how we change the pressure, the product PV remains constant since even V undergoes an equivalent change for any change in P for this closed system.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that Boyle’s law is an ideal gas law. Real gases, however, exhibit deviations from this law. This is because at the time of the formulation of this law, very high pressures or very low temperatures could not be produced, and all the experiments were carried out at moderate temperatures where most gases behave like ideal gases. This deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour is quantized by the compressibility factor (Z), which is nothing but a correction factor given as a ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at same temperature and pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




