
According to the law of Independent Assortment in a dihybrid cross
a. There are four genotypes in F2
b. F2 contains 16 phenotypes
c. There is a single individual which is a homozygous recessive for both the characters
d. It is not possible to forecast the different phenotype
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: The law of Independent Assortment states that during the formation of gametes, one pair of trait segregates from another pair of trait independently. This law was given by Gregor Mendel in 1865. The ratio of the dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. The Law of Independent Assortment states is also known as the third law of Mendel or the third law of inheritance.
Complete answer:
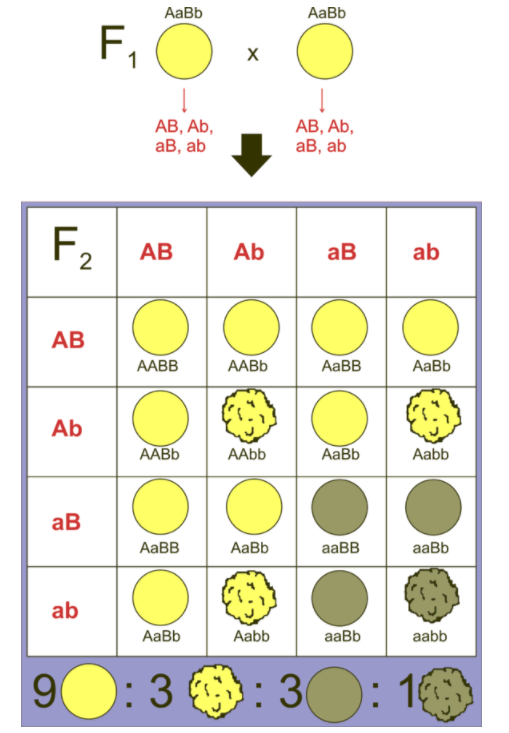
- Mendel conducted an experiment of a dihybrid cross on a pea plant and gave the third law of the principle of inheritance. It is called the law of independent assortment.
- This law states that in the F2 generation 16 progeny are obtained. Out of this 16 progeny, 4 types of phenotypes and 9 types of genotypes appear.
- In 16 progenies, 6 progeny shows genetic recombinations, 1 homozygous dominant for both characters(AABB) 8 are heterozygous dominant for round and yellow, and one progeny is homozygous recessive for both characters(aabb).
- According to this law, during the formation of gametes genes separate independently from one another.
- The Law of independent assortment can be observed in Prophase I in the pachytene stage.
- A mendelian dihybrid cross is the best example of an independent assortment. The combination of round green and wrinkled yellow describes that genes for the color of the seed and shape of the seed are assorted independently.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
- The ratio of the cross is 9:3:3:1.
- In this cross, 9 offspring are yellow and round.
- 3 are yellow and wrinkled
- 3 are green and round.
- 1 is green and wrinkled.
Note: The Law of independent assortment states that during the gamete formation, one pair of traits separate from another pair of traits, independent of each other. Independent assortment of genes is important because it produces new genetic combinations that increase genetic variations within a population. It takes place with linked genes or genes that share the same chromosome.
Complete answer:
- Mendel conducted an experiment of a dihybrid cross on a pea plant and gave the third law of the principle of inheritance. It is called the law of independent assortment.
- This law states that in the F2 generation 16 progeny are obtained. Out of this 16 progeny, 4 types of phenotypes and 9 types of genotypes appear.
- In 16 progenies, 6 progeny shows genetic recombinations, 1 homozygous dominant for both characters(AABB) 8 are heterozygous dominant for round and yellow, and one progeny is homozygous recessive for both characters(aabb).
- According to this law, during the formation of gametes genes separate independently from one another.
- The Law of independent assortment can be observed in Prophase I in the pachytene stage.
- A mendelian dihybrid cross is the best example of an independent assortment. The combination of round green and wrinkled yellow describes that genes for the color of the seed and shape of the seed are assorted independently.

Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
- The ratio of the cross is 9:3:3:1.
- In this cross, 9 offspring are yellow and round.
- 3 are yellow and wrinkled
- 3 are green and round.
- 1 is green and wrinkled.
Note: The Law of independent assortment states that during the gamete formation, one pair of traits separate from another pair of traits, independent of each other. Independent assortment of genes is important because it produces new genetic combinations that increase genetic variations within a population. It takes place with linked genes or genes that share the same chromosome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




