
When acetaldehyde reacts with phenylhydrazine, it forms
A.Acetaldoxime
B.Hydrazone
C.Phenylhydrazone
D.Methylamine
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint:Aldehydes are functional groups with carbonyl groups bonded to a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom. Acetaldehyde is an important aldehyde which when reacts with phenylhydrazine gives aldehyde phenylhydrazine. Phenylhydrazine is used to convert various sugar mixtures to phenylhydrazones.
Complete answer:
Aldehydes are important functional groups in which the carbonyl group is bonded to a carbon atom and to a hydrogen atom. They are generally prepared by oxidation of alcohols and therefore, when they are reduced they give primary alcohols as a product. The lower members of aldehydes are soluble in water as they form hydrogen bonds with water molecules but solubility decreases as the length of the chain of the compound increases. Therefore, higher members are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents like benzene.
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound which is a very important aldehyde which occurs naturally and is widely used in industries on a large scale. It has a molecular formula of $C{H_3}CHO$ . It is a very reactive and toxic compound which is found in alcohol products. This acetaldehyde present in alcohol damages our liver by affecting the production of key proteins which are important for our body to function properly. Phenylhydrazine is a chemical compound with the molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_5}NHN{H_2}$ . It decomposes slowly to give ammonia, nitrogen and benzene ring. It is used to convert mixtures of simple sugars into phenylhydrazones.
In the presence of oxygen, hydrazine burns exothermically liberating a lot of hot gases which makes it possible to use hydrazine as rocket fuel.
Thus for the above question Acetaldehyde reacts with phenylhydrazine to give aldehyde phenylhydrazine which is known as phenylhydrazones.
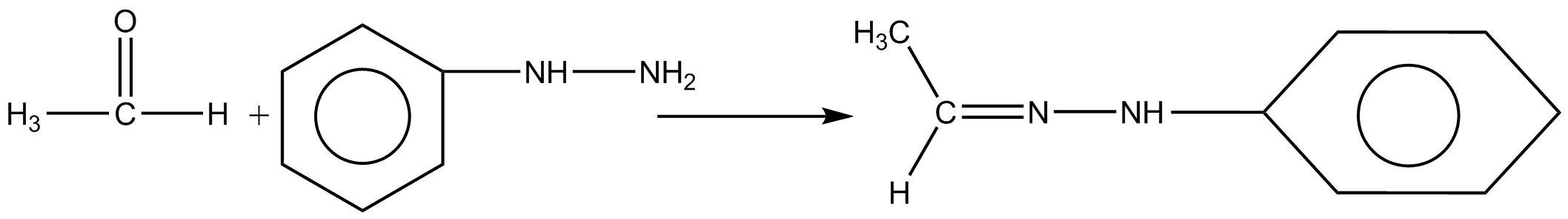
Thus, the correct option is (C) phenylhydrazones.
Note:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo many reactions due to the acidic nature of the $\alpha $ - hydrogen present in their compound. This acidity of the $\alpha $ - hydrogen is due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group present and the resonance effect of the conjugate base which makes it stable.
Complete answer:
Aldehydes are important functional groups in which the carbonyl group is bonded to a carbon atom and to a hydrogen atom. They are generally prepared by oxidation of alcohols and therefore, when they are reduced they give primary alcohols as a product. The lower members of aldehydes are soluble in water as they form hydrogen bonds with water molecules but solubility decreases as the length of the chain of the compound increases. Therefore, higher members are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents like benzene.
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound which is a very important aldehyde which occurs naturally and is widely used in industries on a large scale. It has a molecular formula of $C{H_3}CHO$ . It is a very reactive and toxic compound which is found in alcohol products. This acetaldehyde present in alcohol damages our liver by affecting the production of key proteins which are important for our body to function properly. Phenylhydrazine is a chemical compound with the molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_5}NHN{H_2}$ . It decomposes slowly to give ammonia, nitrogen and benzene ring. It is used to convert mixtures of simple sugars into phenylhydrazones.
In the presence of oxygen, hydrazine burns exothermically liberating a lot of hot gases which makes it possible to use hydrazine as rocket fuel.
Thus for the above question Acetaldehyde reacts with phenylhydrazine to give aldehyde phenylhydrazine which is known as phenylhydrazones.

Thus, the correct option is (C) phenylhydrazones.
Note:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo many reactions due to the acidic nature of the $\alpha $ - hydrogen present in their compound. This acidity of the $\alpha $ - hydrogen is due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group present and the resonance effect of the conjugate base which makes it stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




