
Acetone gives positive test with:
A. Fehling's solution
B. Schiff's solution
C. $2,4 - DNP$
D. all of the above
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Before solving the question, the first thing to keep in mind is that acetones belong to the ketone functional group. Ketones do not have the hydrogen (attached to carbon – oxygen double bond) which is present in aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
-Fehling’s solution is a reagent which is used to differentiate between reducing and non-reducing sugars, to determine whether a carbonyl compound is an aldehyde or ketone.
-Schiff’s solution is a reagent which is used to detect presence of aldehydes.
-$2,4 - DNP$ is a qualitative test to check for the presence of carbonyl groups.
We know that acetone belong to the ketone functional group category having the following structure:

-Acetones in general do not respond to Fehling’s test , because they do not have the hydrogen (attached to carbon – oxygen double bond which is present in aldehydes) which will undergo oxidation, hence it is difficult to oxidise them with this solution. Ketones are very less reactive towards oxidation.
-Similarly Schiff’s reagents do not bring about oxidation in ketones. Thus option A and B are incorrect.
-Acetone, however reacts with $2,4 - $ \[dinitrophenylhydrazine\] ( $DNP$ ) to form the compound called as \[2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazone\] which is a yellow coloured precipitate. Reaction is given below:
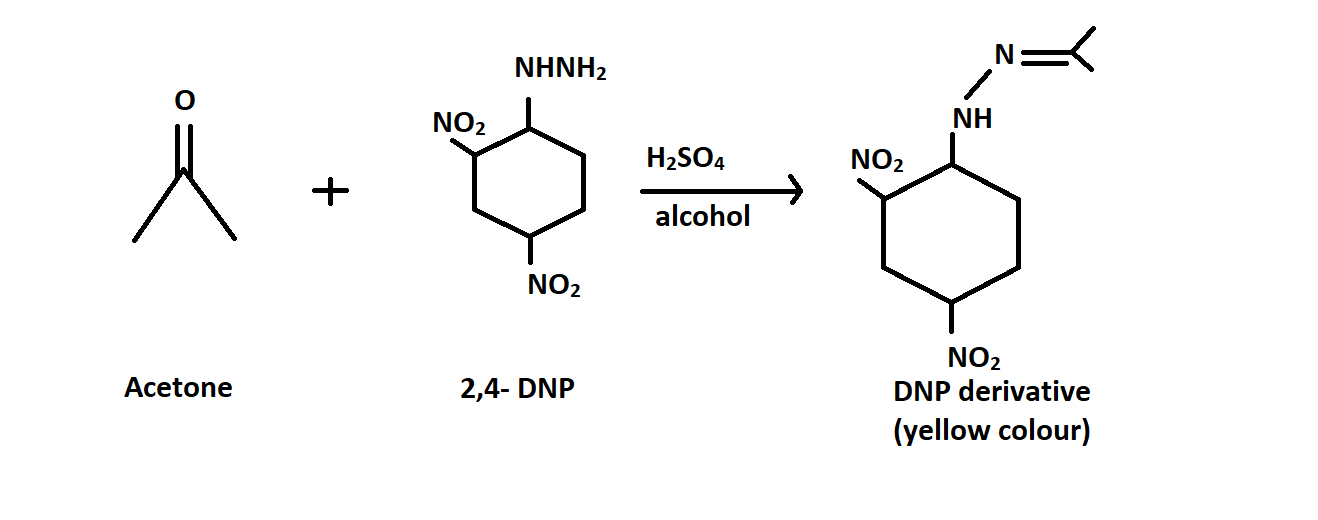
Therefore Option C is correct.
Additional Information:
Fehling’s solution is actually a deep blue alkaline solution prepared by combining two different solutions. First is Fehling’s A which is copper (II) sulphate solution, deep blue in colour and the other is Fehling’s B which is a solution of aqueous sodium potassium tartrate (also known by the name Rochelle salt) which is colourless. These two are mixed and made strongly alkaline by adding potassium hydroxide ( $KOH$ ).
Schiff’s solution is Fuchsine or rosaniline which is a magenta coloured dye having the chemical formula ${C_{20}}{H_{20}}{N_3}.HCl$ and it is decolourised by a sulphurous acid.
\[2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazone\] is red to orange coloured dye with formula ${C_6}{H_3}{(N{O_2})_2}NHN{H_2}$
Note:
We need to be careful with Fehling’s test as some $\alpha - hydroxy$ ketones do give positive tests as these can undergo tautomerization to get converted to aldehyde form which gives a positive test towards the Fehling’s test.
Complete step by step answer:
-Fehling’s solution is a reagent which is used to differentiate between reducing and non-reducing sugars, to determine whether a carbonyl compound is an aldehyde or ketone.
-Schiff’s solution is a reagent which is used to detect presence of aldehydes.
-$2,4 - DNP$ is a qualitative test to check for the presence of carbonyl groups.
We know that acetone belong to the ketone functional group category having the following structure:

-Acetones in general do not respond to Fehling’s test , because they do not have the hydrogen (attached to carbon – oxygen double bond which is present in aldehydes) which will undergo oxidation, hence it is difficult to oxidise them with this solution. Ketones are very less reactive towards oxidation.
-Similarly Schiff’s reagents do not bring about oxidation in ketones. Thus option A and B are incorrect.
-Acetone, however reacts with $2,4 - $ \[dinitrophenylhydrazine\] ( $DNP$ ) to form the compound called as \[2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazone\] which is a yellow coloured precipitate. Reaction is given below:

Therefore Option C is correct.
Additional Information:
Fehling’s solution is actually a deep blue alkaline solution prepared by combining two different solutions. First is Fehling’s A which is copper (II) sulphate solution, deep blue in colour and the other is Fehling’s B which is a solution of aqueous sodium potassium tartrate (also known by the name Rochelle salt) which is colourless. These two are mixed and made strongly alkaline by adding potassium hydroxide ( $KOH$ ).
Schiff’s solution is Fuchsine or rosaniline which is a magenta coloured dye having the chemical formula ${C_{20}}{H_{20}}{N_3}.HCl$ and it is decolourised by a sulphurous acid.
\[2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazone\] is red to orange coloured dye with formula ${C_6}{H_3}{(N{O_2})_2}NHN{H_2}$
Note:
We need to be careful with Fehling’s test as some $\alpha - hydroxy$ ketones do give positive tests as these can undergo tautomerization to get converted to aldehyde form which gives a positive test towards the Fehling’s test.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




