
Acetylene on ozonolysis gives glyoxal.
A.True
B.False
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:Alkynes undergo ozonolysis to give an acid anhydride or a diketone as the final product. The fragmentation is not complete in this reaction (alkenes undergo complete fragmentation). Acetylene contains a triple bond. Draw the structure of the ozonide formed on ozonolysis. The multiple carbon-carbon bond is replaced by a carbonyl group. Glyoxal has the chemical formula $CHO - CHO$.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is a method of oxidative cleavage of alkenes and alkynes using ozone that means cleavage of bonds, occurring with oxidation.
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen and is reactive. It gets added to an alkene or alkyne to form ozonide.
The ozonide is then cleaved by $Zn - {H_2}O$ to form smaller molecules.
The reaction is as follows:
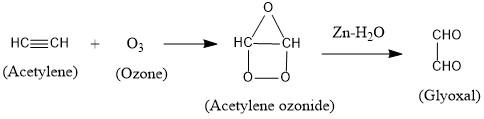
Reaction mechanism:
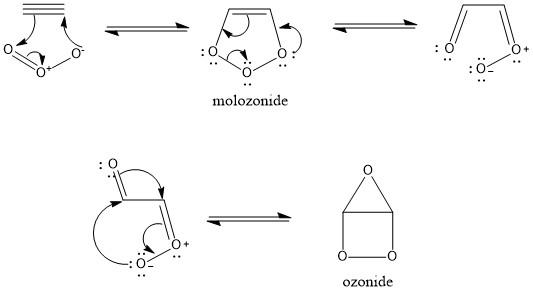
The first step in the mechanism of ozonolysis is the initial electrophilic addition of ozone to the carbon-carbon triple bond. This forms the molozonide intermediate.
It is an unstable intermediate and continues further with the reaction. It undergoes fragmentation to form a molecule with a carbonyl group and a carbonyl oxide group.
The carbonyl and the carbonyl oxide rearrange itself and form a stable ozonide intermediate. This undergoes a reductive workup using zinc in water. In this step, we add a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed (ozonide) into (glyoxal in this case).
The third oxygen atom of the ozone is attached to the reducing agent which then turns into ZnO during the reductive workup.
Therefore, acetylene undergoes ozonolysis to form glyoxal.
Hence the correct answer is (A) True.
Note: If the reaction happens in the presence of water, the acid anhydride undergoes hydrolyzation to give two carboxylic acids.
Ozonolysis can also be used to determine the position of the triple bond in an unknown alkyne.
The reductive workup can also be carried out using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is a method of oxidative cleavage of alkenes and alkynes using ozone that means cleavage of bonds, occurring with oxidation.
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen and is reactive. It gets added to an alkene or alkyne to form ozonide.
The ozonide is then cleaved by $Zn - {H_2}O$ to form smaller molecules.
The reaction is as follows:

Reaction mechanism:

The first step in the mechanism of ozonolysis is the initial electrophilic addition of ozone to the carbon-carbon triple bond. This forms the molozonide intermediate.
It is an unstable intermediate and continues further with the reaction. It undergoes fragmentation to form a molecule with a carbonyl group and a carbonyl oxide group.
The carbonyl and the carbonyl oxide rearrange itself and form a stable ozonide intermediate. This undergoes a reductive workup using zinc in water. In this step, we add a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed (ozonide) into (glyoxal in this case).
The third oxygen atom of the ozone is attached to the reducing agent which then turns into ZnO during the reductive workup.
Therefore, acetylene undergoes ozonolysis to form glyoxal.
Hence the correct answer is (A) True.
Note: If the reaction happens in the presence of water, the acid anhydride undergoes hydrolyzation to give two carboxylic acids.
Ozonolysis can also be used to determine the position of the triple bond in an unknown alkyne.
The reductive workup can also be carried out using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




