
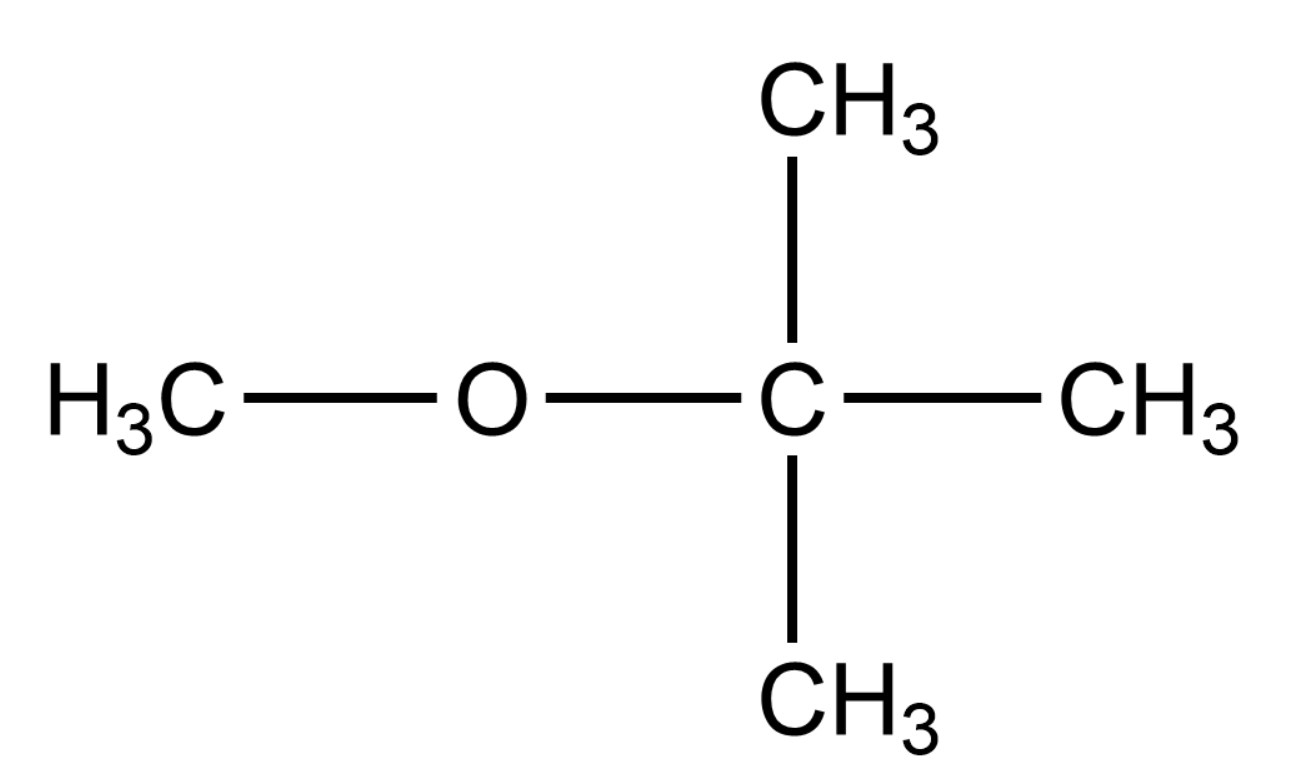
What is the action of hot and cold HI on ethyl methyl ether? Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:

Answer
504k+ views
Hint: When hot hydrogen iodide is reacted with ethyl methyl ether, we get ethyl iodide, methyl iodide and water. This is by undergoing the substitution reaction with HI
Cold solution of HI forms ethyl methyl oxonium ion which is positively charged and iodide ion.
Complete answer:
Ethers react with hydroiodic acids to form an alcohol and corresponding haloalkane. However with hot halogen acids only the haloalkanes are formed. This is because as soon as the alcohol is formed, it will react with hydroiodic acid and get converted to the corresponding halo alkane and water.
\[C{H_3} - O - {C_2}{H_5}\xrightarrow{{Hot{\text{ }}HI}}{C_2}{H_5}I + C{H_3}I + {H_2}O\]
In the case of cold HI we will get only the oxonium salt and iodide ion. This is because in the presence of a strong acid at low temperature, the lone pair of electrons in the ether will get protonated by the acid. The product formed, oxonium salt, is stable at low temperatures only. The oxonium ion can give back ether in aqueous medium.
\[C{H_3} - O - {C_2}{H_5}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Cold }}HI}}{C_2}{H_5} - {O^ + } - C{H_3} + {I^ - }\]
The IUPAC name of the given compound is Methyl tert-butyl ether. The word tert means that the Carbon atom is in its tertiary form in the compound.
Note:
When we are given haloacids, we can always say that HI will react more vigorously than Hydro bromic acid than hydrochloric acid.
The reaction of ethers with hydroiodic acid forms the basis of Zeisel’s method for detection and estimation of alkoxy groups in a compound.
Cold solution of HI forms ethyl methyl oxonium ion which is positively charged and iodide ion.
Complete answer:
Ethers react with hydroiodic acids to form an alcohol and corresponding haloalkane. However with hot halogen acids only the haloalkanes are formed. This is because as soon as the alcohol is formed, it will react with hydroiodic acid and get converted to the corresponding halo alkane and water.
\[C{H_3} - O - {C_2}{H_5}\xrightarrow{{Hot{\text{ }}HI}}{C_2}{H_5}I + C{H_3}I + {H_2}O\]
In the case of cold HI we will get only the oxonium salt and iodide ion. This is because in the presence of a strong acid at low temperature, the lone pair of electrons in the ether will get protonated by the acid. The product formed, oxonium salt, is stable at low temperatures only. The oxonium ion can give back ether in aqueous medium.
\[C{H_3} - O - {C_2}{H_5}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Cold }}HI}}{C_2}{H_5} - {O^ + } - C{H_3} + {I^ - }\]
The IUPAC name of the given compound is Methyl tert-butyl ether. The word tert means that the Carbon atom is in its tertiary form in the compound.
Note:
When we are given haloacids, we can always say that HI will react more vigorously than Hydro bromic acid than hydrochloric acid.
The reaction of ethers with hydroiodic acid forms the basis of Zeisel’s method for detection and estimation of alkoxy groups in a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




