
What is the action of hot hydroiodic acid on isopropyl methyl ether?
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The carbon-oxygen bond in ethers can be cleaved by heating with the halogen acid such as hydroiodic acid $\text{ HI }$ . The general reaction of the ether with the hydroiodic acid is as shown below,
$\begin{matrix}
\text{R}-\text{O}-\text{R} & \text{+} & \text{HX} & \xrightarrow{\text{373 K}} & \text{ROH} & \text{+} & \text{RX} \\
\text{(Ether)} & {} & \text{(Halogen acid)} & {} & \text{(Alcohol)} & {} & \text{(Alkyl halide)} \\
\end{matrix}$
Complete Solution :
Ethers are the least reactive of the functional groups. Carbon-oxygen bond in ethers can be cleaved under drastic conditions.
Hot hydroiodic acid reacts with the isopropyl methyl ether. This results in the cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bonds. Thus reaction of isopropyl methyl ether hot hydroiodic acid gives Propan-2- ol, and iodomethane or methyl iodide.
The cleavage of the reaction of isopropyl methyl ether follows the following mechanism:
1. The ether molecule being base gets protonated ether or oxonium salt.
The reaction takes place in the presence of hydroiodic acid because these reagents are sufficiently acidic.
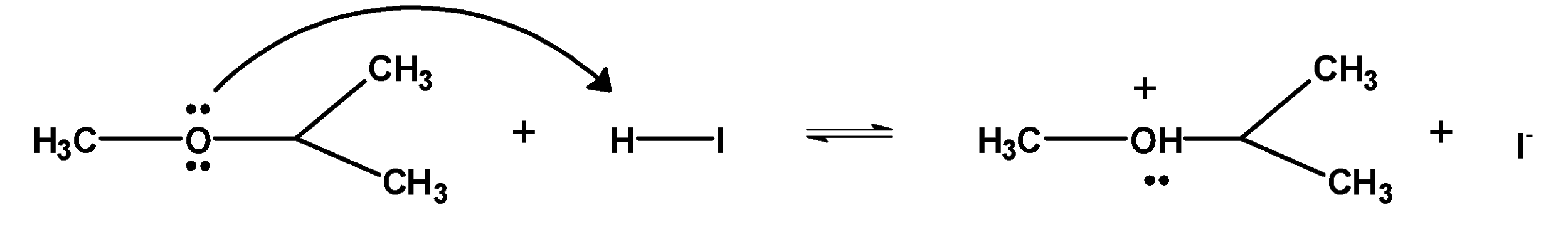
2. Iodide ion $\text{ }{{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ }$ is a good nucleophile. The protonated ether undergoes nucleophilic attack by iodide ion and displace an alcohol molecule by $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ mechanism and therefore, forms alkyl alcohol and alkyl halide.
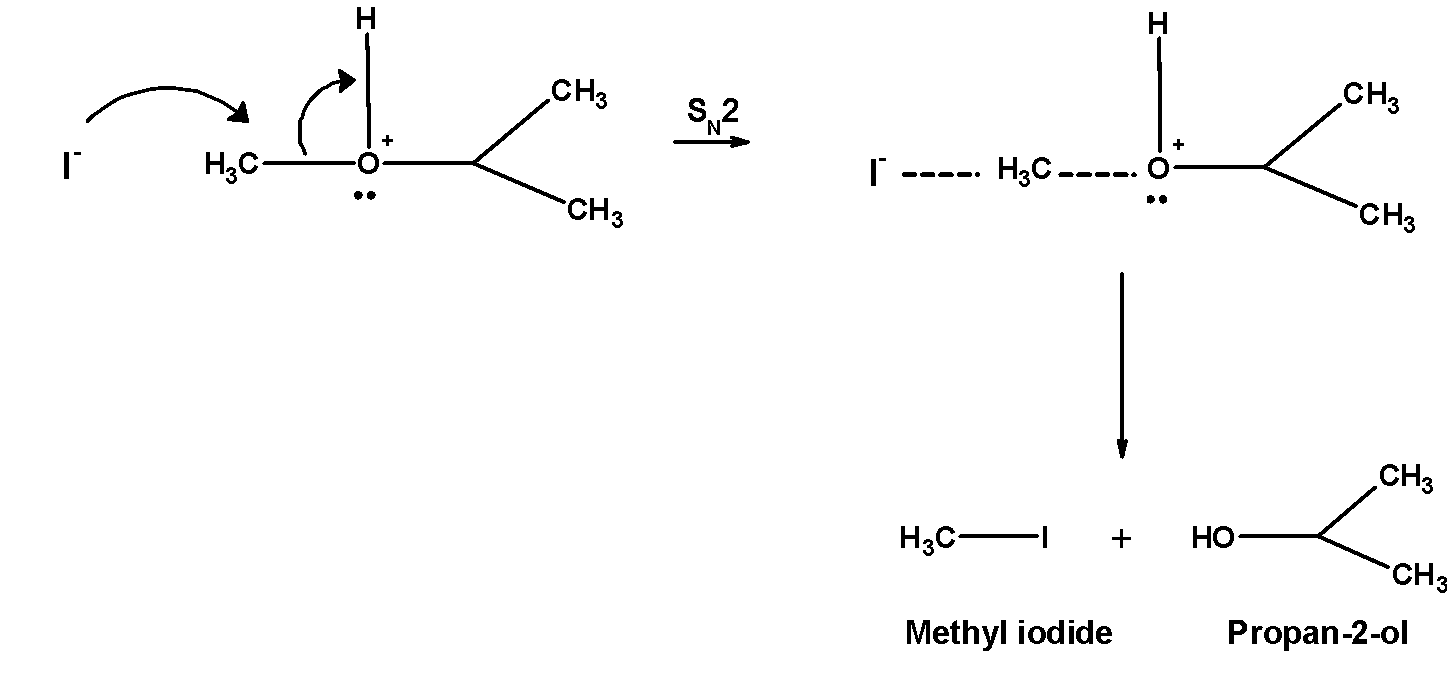
Remember that, in the case of unsymmetrical ethers with two different alkyl groups, the size of the cleavage is such that the halide is formed from the alkyl group which is smaller in size. The reaction proceeds via $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ the mechanism. The $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ mechanism favours well with primary carbon atom .f primary and secondary alkyl groups are present then halide attack on the less hindered alkyl group.
Thus reaction of isopropyl methyl ether hot hydroiodic acid gives Propan-2- ol, and iodomethane or methyl iodide.
Note: When $\text{ HI }$is in excess and the reaction is carried out at a high temperature, methanol formed reacts with another molecule of $\text{ HI }$ and is converted into methyl iodide.
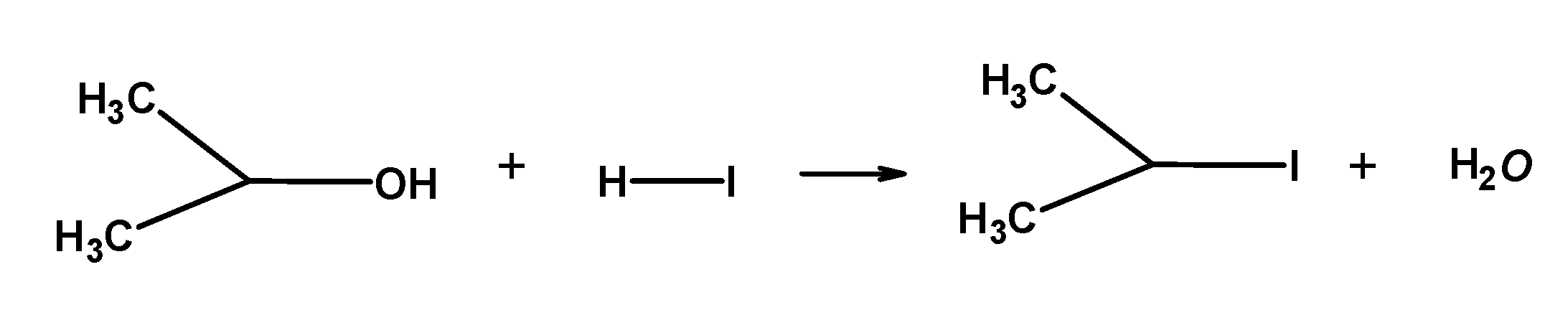
The order of reactivity of halogen acid is: $\text{ HI }>\text{ HBr }>\text{ HCl }$
$\begin{matrix}
\text{R}-\text{O}-\text{R} & \text{+} & \text{HX} & \xrightarrow{\text{373 K}} & \text{ROH} & \text{+} & \text{RX} \\
\text{(Ether)} & {} & \text{(Halogen acid)} & {} & \text{(Alcohol)} & {} & \text{(Alkyl halide)} \\
\end{matrix}$
Complete Solution :
Ethers are the least reactive of the functional groups. Carbon-oxygen bond in ethers can be cleaved under drastic conditions.
Hot hydroiodic acid reacts with the isopropyl methyl ether. This results in the cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bonds. Thus reaction of isopropyl methyl ether hot hydroiodic acid gives Propan-2- ol, and iodomethane or methyl iodide.
The cleavage of the reaction of isopropyl methyl ether follows the following mechanism:
1. The ether molecule being base gets protonated ether or oxonium salt.
The reaction takes place in the presence of hydroiodic acid because these reagents are sufficiently acidic.
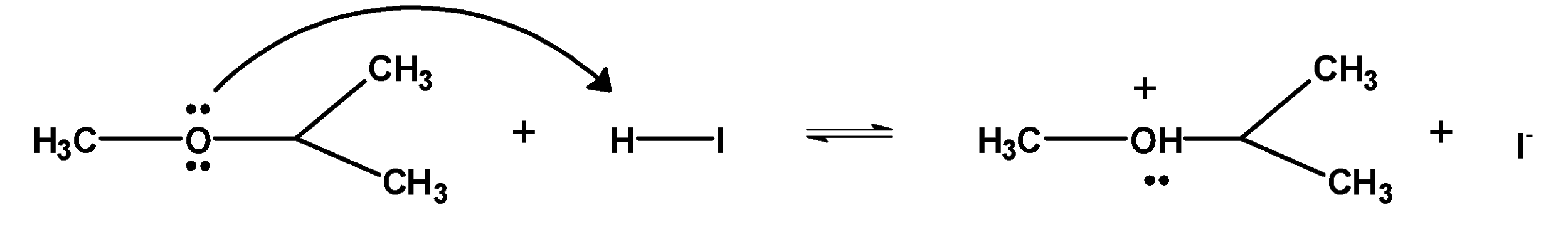
2. Iodide ion $\text{ }{{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ }$ is a good nucleophile. The protonated ether undergoes nucleophilic attack by iodide ion and displace an alcohol molecule by $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ mechanism and therefore, forms alkyl alcohol and alkyl halide.
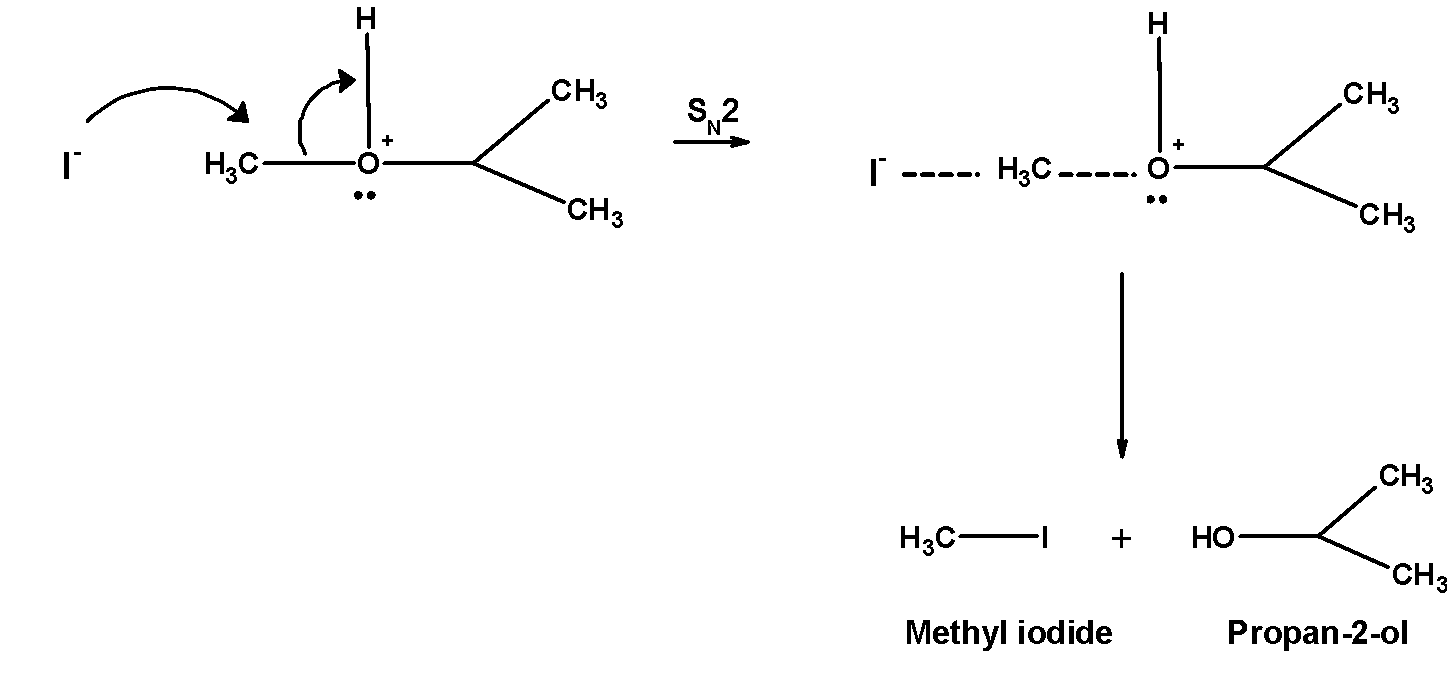
Remember that, in the case of unsymmetrical ethers with two different alkyl groups, the size of the cleavage is such that the halide is formed from the alkyl group which is smaller in size. The reaction proceeds via $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ the mechanism. The $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ mechanism favours well with primary carbon atom .f primary and secondary alkyl groups are present then halide attack on the less hindered alkyl group.
Thus reaction of isopropyl methyl ether hot hydroiodic acid gives Propan-2- ol, and iodomethane or methyl iodide.
Note: When $\text{ HI }$is in excess and the reaction is carried out at a high temperature, methanol formed reacts with another molecule of $\text{ HI }$ and is converted into methyl iodide.
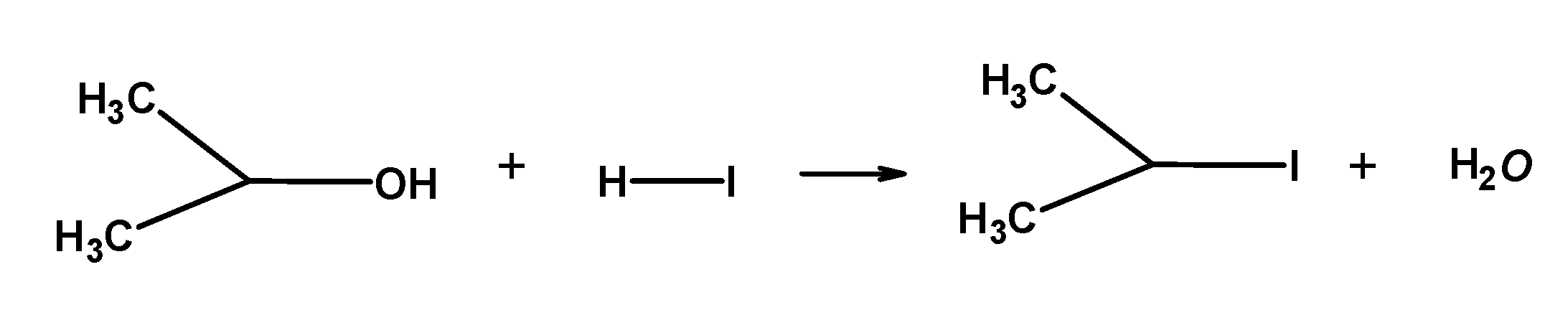
The order of reactivity of halogen acid is: $\text{ HI }>\text{ HBr }>\text{ HCl }$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




