
What is action potential? Describe how the nerve impulse is propagated in a non-myelinated and myelinated nerve fibre.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The cells of the nervous system called neurons are responsible for the transfer of nerve impulses from one cell to the other. In addition to it, we should also know that the rate of transfer of nerve impulse depends upon the type of nerve cell through which it is propagated.
Complete step by step answer: Action potential is nothing but the nerve signals. In order to transmit the nerve signal to the target tissues, neurons generate this action potential. When the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls, action potentials are induced by the neurons. Change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve cell is called action potential (AP). Change in the polarity of the axon is seen as the nerve impulse travels down. Sodium and potassium gated ion channels open as soon as they receive the impulse and close once it reaches its threshold potential. Depolarization of the cell is caused by the sodium ions which move into the axon whereas when potassium ions move out of the axon it leads to repolarization.
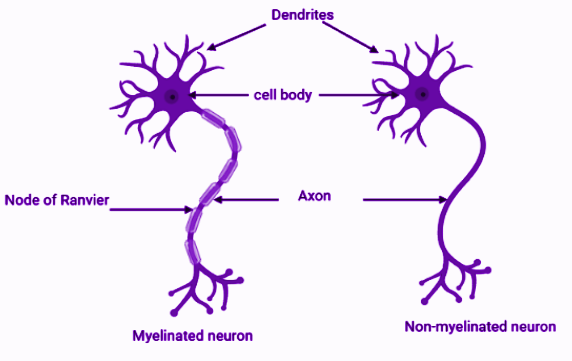
The nerve fibres that possess myelin sheath on the axon is called myelinated nerve fibres. The presence of gaps in the myelinated nerve fibre is called the node of Ranvier. The conduction of nerve impulse in myelinated nerve fibre is resisted by the myelin sheath present on the axon and acts as an insulator. The myelin sheath is absent on the node of Ranvier and thus conducts the passage of nerve impulse. The type of conduction in which the nerve impulse travels down, it appears that they jump from one node to another node is called saltatory conduction. The conduction of nerve impulse in non-myelinated nerve fibre is the same as that of the myelinated sheath but the only difference is that the myelin sheath is absent in non-myelinated sheath.
Note: The conduction of nerve impulse is faster in non-myelinated nerve fiber as compared to the myelinated nerve fibre due to the absence of myelin sheath. Only excitatory cells such as nerve cells and muscle cells are capable of initiating action potential. Conduction of impulse takes place only in one
direction that is towards the axon.
Complete step by step answer: Action potential is nothing but the nerve signals. In order to transmit the nerve signal to the target tissues, neurons generate this action potential. When the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls, action potentials are induced by the neurons. Change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve cell is called action potential (AP). Change in the polarity of the axon is seen as the nerve impulse travels down. Sodium and potassium gated ion channels open as soon as they receive the impulse and close once it reaches its threshold potential. Depolarization of the cell is caused by the sodium ions which move into the axon whereas when potassium ions move out of the axon it leads to repolarization.

The nerve fibres that possess myelin sheath on the axon is called myelinated nerve fibres. The presence of gaps in the myelinated nerve fibre is called the node of Ranvier. The conduction of nerve impulse in myelinated nerve fibre is resisted by the myelin sheath present on the axon and acts as an insulator. The myelin sheath is absent on the node of Ranvier and thus conducts the passage of nerve impulse. The type of conduction in which the nerve impulse travels down, it appears that they jump from one node to another node is called saltatory conduction. The conduction of nerve impulse in non-myelinated nerve fibre is the same as that of the myelinated sheath but the only difference is that the myelin sheath is absent in non-myelinated sheath.
Note: The conduction of nerve impulse is faster in non-myelinated nerve fiber as compared to the myelinated nerve fibre due to the absence of myelin sheath. Only excitatory cells such as nerve cells and muscle cells are capable of initiating action potential. Conduction of impulse takes place only in one
direction that is towards the axon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




