
Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Addition of HBr to propene is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, hydron.
Complete step by step answer:
-Addition of HBr to propene is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, hydron. This electrophile attacks the double bond to form $1^{\circ}$ and $2^{\circ}$ carbocations as shown:
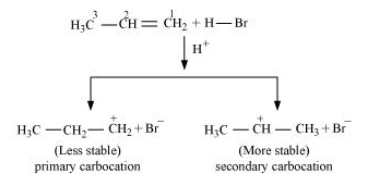
-Secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations. Hence, the former predominates since it will form at a faster rate. Thus, in the next step, Br- attacks the carbocation to form 2 - bromopropane as the major product.
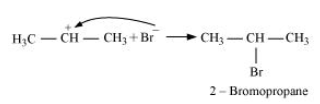
-This reaction follows Markovnikov's rule where the negative part of the addendum is attached to the carbon atom having a lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
-In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, an additional reaction takes place anti to Markovnikov's rule. The reaction follows a free radical chain mechanism as:
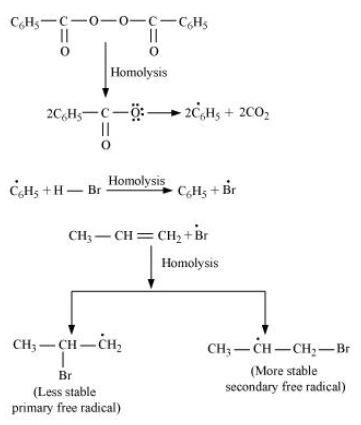
-Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals. Hence, the former predominates since it forms at a faster rate. Thus, 1 - bromopropane is obtained as the major product.
-In the presence of peroxide, Br free radical acts as an electrophile. Hence, two different products are obtained in addition to HBr to propene in the absence and presence of peroxide.
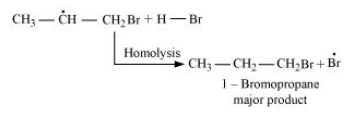
Note: Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals. Hence, the former predominates since it forms at a faster rate. In the presence of peroxide, Br free radical acts as an electrophile.
Complete step by step answer:
-Addition of HBr to propene is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, hydron. This electrophile attacks the double bond to form $1^{\circ}$ and $2^{\circ}$ carbocations as shown:

-Secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations. Hence, the former predominates since it will form at a faster rate. Thus, in the next step, Br- attacks the carbocation to form 2 - bromopropane as the major product.

-This reaction follows Markovnikov's rule where the negative part of the addendum is attached to the carbon atom having a lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
-In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, an additional reaction takes place anti to Markovnikov's rule. The reaction follows a free radical chain mechanism as:

-Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals. Hence, the former predominates since it forms at a faster rate. Thus, 1 - bromopropane is obtained as the major product.
-In the presence of peroxide, Br free radical acts as an electrophile. Hence, two different products are obtained in addition to HBr to propene in the absence and presence of peroxide.

Note: Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals. Hence, the former predominates since it forms at a faster rate. In the presence of peroxide, Br free radical acts as an electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




