
Addition of pentavalent impurity to a semiconductor creates many
(A) Free electron
(B) Holes
(C) Valence electrons
(D) Bound electrons
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint:Normally, the pure semiconductor does not conduct electricity, however some of the impurities must be added to donate the free electrons to it for the purpose of the conduction of the electricity. It may cause either n-type conductivity or the p-type conductivity.
Complete step by step answer:
The pure semiconductor has the atoms arranged in such a way that each atom of it is surrounded by the four atoms of itself. This type of arrangement exists because the pure semiconductor has for valence electrons in it. The pentavalent impurities have five valence electrons in it. When this impurity is added to the pure semiconductor, one atom of this impurity forms the bond with the four atoms of the semiconductor with which it is added. Hence the four atoms start bonding and the fifth electron is left free without any bonding.
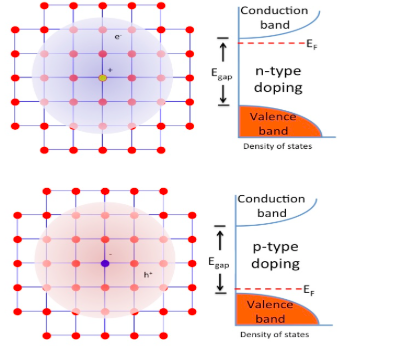
Hence this is known as free electrons that are used for the conduction. Hence when the pentavalent impurity is added with the pure semiconductor, one negative charge will be formed and this is n- type impurity. The semiconductor which joins with the n-type impurity to produce the free electrons are n-type semiconductor. Hence the addition of the pentavalent impurity to a semiconductor produces many free electrons.
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note:The example of the n-type impurity is phosphorous, arsenic, antimony, bismuth etc. These are added with the pure semiconductors like silicon, germanium etc. The p-type semiconductors have the extra unbounded holes, this result only the trivalent impurity added with pure semiconductor. The example for this is aluminum, boron, indium etc.
Complete step by step answer:
The pure semiconductor has the atoms arranged in such a way that each atom of it is surrounded by the four atoms of itself. This type of arrangement exists because the pure semiconductor has for valence electrons in it. The pentavalent impurities have five valence electrons in it. When this impurity is added to the pure semiconductor, one atom of this impurity forms the bond with the four atoms of the semiconductor with which it is added. Hence the four atoms start bonding and the fifth electron is left free without any bonding.

Hence this is known as free electrons that are used for the conduction. Hence when the pentavalent impurity is added with the pure semiconductor, one negative charge will be formed and this is n- type impurity. The semiconductor which joins with the n-type impurity to produce the free electrons are n-type semiconductor. Hence the addition of the pentavalent impurity to a semiconductor produces many free electrons.
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note:The example of the n-type impurity is phosphorous, arsenic, antimony, bismuth etc. These are added with the pure semiconductors like silicon, germanium etc. The p-type semiconductors have the extra unbounded holes, this result only the trivalent impurity added with pure semiconductor. The example for this is aluminum, boron, indium etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




