
What is an additional polymerization? Explain the free radical addition polymerization mechanism by taking an example.
Answer
503.7k+ views
Hint : An additional polymer is a polymer which forms by simple linking of monomers without the co-generation of the other products. These polymers are formed by the addition of some simple monomer units repeatedly. The addition mainly takes place in free radical mechanisms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A polymer which is formed by direct addition of repeated molecules of monomer possessing double or triple bond, without the elimination of any small molecule is known as addition polymerization. Some of the examples of polymers formed as a result of additional polymerization are polythene, PVC etc.
Let us discuss the free radical addition polymerization of ethene in the presence of benzoyl peroxide to form polythene.
Step-1: Chain initiation step- Dissociation of the oxygen bonds of benzoyl peroxide due to which a temporary intermediate is formed and then it is quickly converted into carbon dioxide and two phenyl radicals. The reaction takes place as follows:
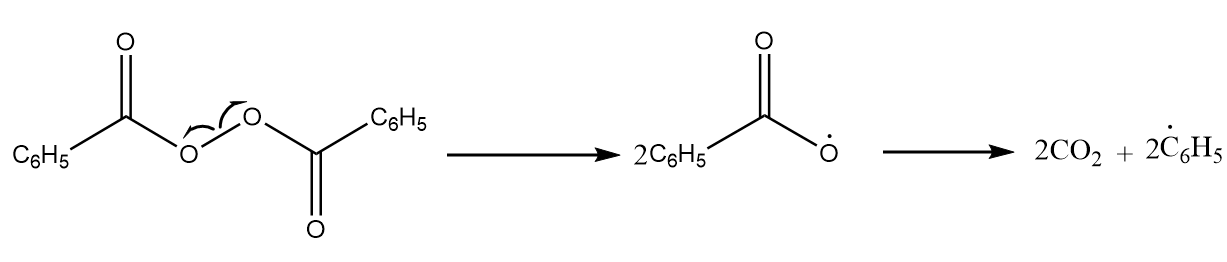
These radicals act as an electrophile and attack the double bond of the ethene molecule, a stable intermediate. The reaction proceeds as follows:
$ 2{C_6}H_5^ \bullet + {H_2}C = C{H_2} \to {C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - CH_2^ \bullet $
Step-2: Chain propagation- The newly formed radical intermediate undergoes polymerization reaction i.e., adds on itself by attacking the other molecule of ethene. The reaction takes as follows:
$ {C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - CH_2^ \bullet + nC{H_2} = C{H_2} \to {C_6}{H_5} - {(C{H_2} - C{H_2})_n} - CH_2^ \bullet $
Polyethylene units have a tendency to grow from 4-5 monomer units to very large molecules. The number of ethene monomer units and the molecular weight in the polyethene molecule can be controlled by the reaction temperature, the radical concentration and varying catalyst in the reaction.
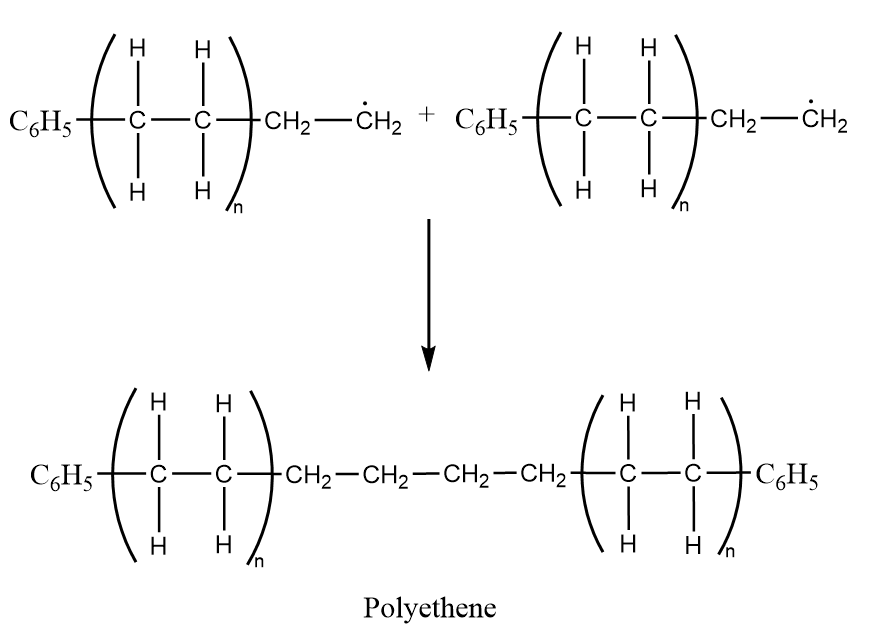
Step-3: Chain termination- At last the reaction is terminated when two radicals react with each other to produce diphenyl and polyethylene as a product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
$ {C_6}H_5^ \bullet + {C_6}H_5^ \bullet \to {C_6}{H_5} - {C_6}{H_5} $
Note :
Remember that the free radical polymerization has found applications including manufacture of polystyrene, elastomers, chemical surfactants and lubricants. When two or more types of monomers undergo addition polymerization, the resulting polymer is known as addition copolymer.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A polymer which is formed by direct addition of repeated molecules of monomer possessing double or triple bond, without the elimination of any small molecule is known as addition polymerization. Some of the examples of polymers formed as a result of additional polymerization are polythene, PVC etc.
Let us discuss the free radical addition polymerization of ethene in the presence of benzoyl peroxide to form polythene.
Step-1: Chain initiation step- Dissociation of the oxygen bonds of benzoyl peroxide due to which a temporary intermediate is formed and then it is quickly converted into carbon dioxide and two phenyl radicals. The reaction takes place as follows:

These radicals act as an electrophile and attack the double bond of the ethene molecule, a stable intermediate. The reaction proceeds as follows:
$ 2{C_6}H_5^ \bullet + {H_2}C = C{H_2} \to {C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - CH_2^ \bullet $
Step-2: Chain propagation- The newly formed radical intermediate undergoes polymerization reaction i.e., adds on itself by attacking the other molecule of ethene. The reaction takes as follows:
$ {C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - CH_2^ \bullet + nC{H_2} = C{H_2} \to {C_6}{H_5} - {(C{H_2} - C{H_2})_n} - CH_2^ \bullet $
Polyethylene units have a tendency to grow from 4-5 monomer units to very large molecules. The number of ethene monomer units and the molecular weight in the polyethene molecule can be controlled by the reaction temperature, the radical concentration and varying catalyst in the reaction.
Step-3: Chain termination- At last the reaction is terminated when two radicals react with each other to produce diphenyl and polyethylene as a product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
$ {C_6}H_5^ \bullet + {C_6}H_5^ \bullet \to {C_6}{H_5} - {C_6}{H_5} $

Note :
Remember that the free radical polymerization has found applications including manufacture of polystyrene, elastomers, chemical surfactants and lubricants. When two or more types of monomers undergo addition polymerization, the resulting polymer is known as addition copolymer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




