
After ozonolysis of benzene (not hydrolysis), the product is
A. Benzene triozonide
B. Glyoxal
C. Ethanediol
D. All of them
Answer
500.4k+ views
Hint: Ozonolysis produces a substance with ozone molecules replacing the double bonds. It causes the molecule to break down where a carbon-oxygen-carbon connection exists. The final product is a crystalline solid that is white at low temperatures and turns yellow as it approaches the melting point.
Complete answer:
Ozonolysis is a chemical process in which ozone causes the oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated bond in a molecule. The final product will be an organic molecule with multiple carbon–carbon bonds replaced by oxygen bonds.
During ozonolysis of benzene, ozone is added to each pi bond of the benzene ring. Hence the product will be such that in the place of a double bond, there will be $2$ oxygen atoms attached as a chain outside the ring in between the $2$ carbon atoms, and there will be an oxygen atom inside the ring in between the carbon atoms. The product will be Benzene triozonide.
The reaction takes place as follows:
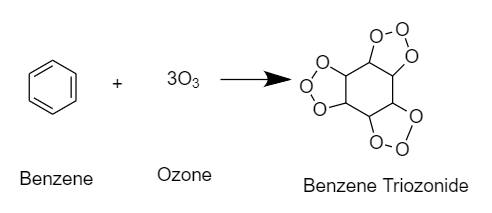
Hence, the correct option is A. Benzene triozonide .
Note:
Ozonolysis is an organic process in which ozone cleaves the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds. Alkenes and alkynes form organic compounds with a carbonyl group, whereas azo compounds form nitrosamines. The reaction's outcome is determined by the type of multiple bonds being oxidised as well as the work-up conditions.
Complete answer:
Ozonolysis is a chemical process in which ozone causes the oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated bond in a molecule. The final product will be an organic molecule with multiple carbon–carbon bonds replaced by oxygen bonds.
During ozonolysis of benzene, ozone is added to each pi bond of the benzene ring. Hence the product will be such that in the place of a double bond, there will be $2$ oxygen atoms attached as a chain outside the ring in between the $2$ carbon atoms, and there will be an oxygen atom inside the ring in between the carbon atoms. The product will be Benzene triozonide.
The reaction takes place as follows:

Hence, the correct option is A. Benzene triozonide .
Note:
Ozonolysis is an organic process in which ozone cleaves the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds. Alkenes and alkynes form organic compounds with a carbonyl group, whereas azo compounds form nitrosamines. The reaction's outcome is determined by the type of multiple bonds being oxidised as well as the work-up conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




