
Alkaline hydrolysis of which among the following compounds leads to the formation of a racemate?
(A) 1-bromo-1-phenylethane
(B) 1-chloro-3-methylbutane
(C) Bromo ethane
(D) 1-chloropropane
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The process of converting an optically active (d- or l-) compound refers to the racemization. This racemic modification is related to stereochemical aspects of nucleophilic substitution reactions. The relationship with haloalkanes and alkaline hydrolysis will be explained based on the racemization process.
Complete step by step answer:
Racemate or racemic mixture of a chiral compound that consists of a 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers and the racemization is to become a racemate.
The following reaction represents alkaline hydrolysis of haloalkanes will be:
$RX+KOH\to ROH+HX$
Where R =alkyl group and X = halogens
Apply the above reaction to given haloalkanes,
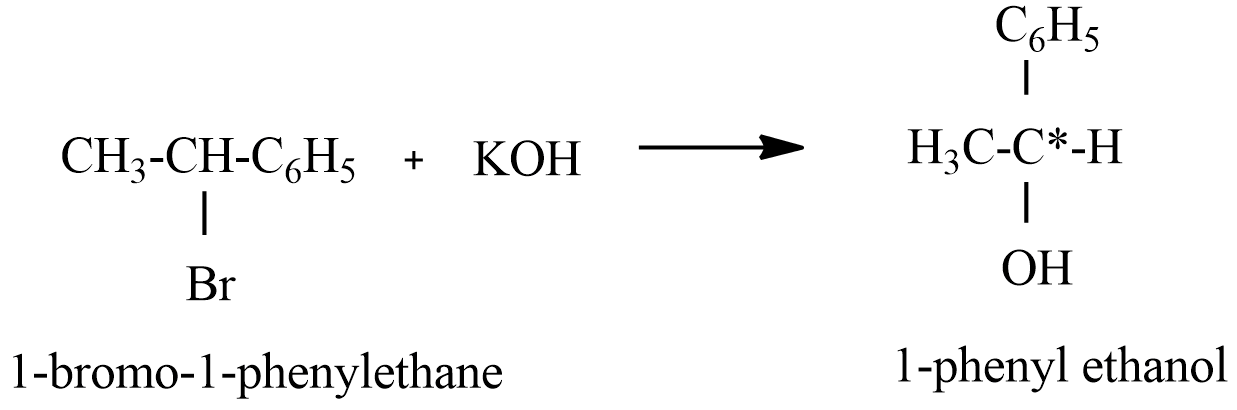
(A) 1-Bromo-1-phenylethane reaction with alkaline KOH
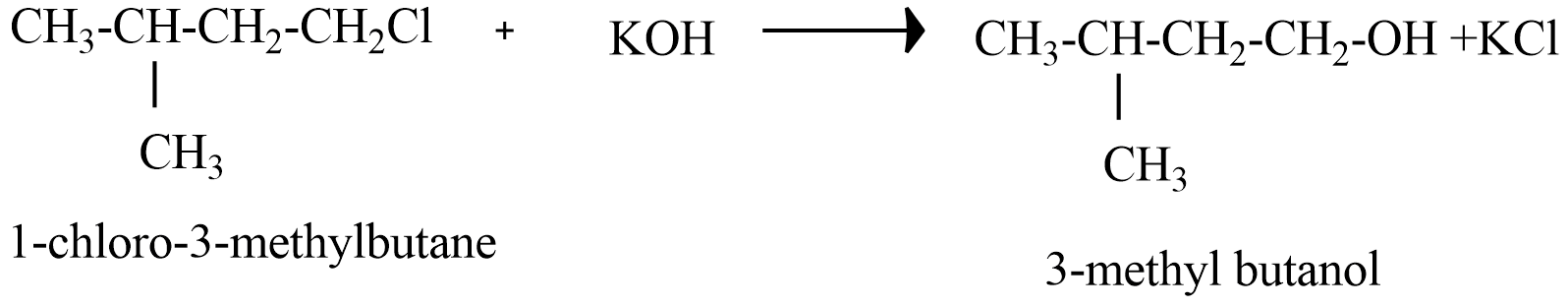
(B) 1-chloro-3-methyl butane reaction with alkaline KOH
(C) Bromo ethane reacts with KOH,
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Br+KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+KBr$
(D) 1-chloro propane involves in alkaline hydrolysis
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+KCl$
Since, the products of (B), (C), and (D) do not form Racemate because there is no chiral carbon atom in the products.
The product formed in reaction A having chiral carbon, this hydrolysis will lead to the formation of a racemate or racemic mixture.
Note: The conversation of half of its dextro form into levo form so that the mixture is optically inactive due to the presence of equal amounts of two enantiomers involves the racemization process. This process can be brought by the action of heat, chemical reagents, and autorecemisation. The thermodynamically favorable method is racemization and proceeds spontaneously if a suitable pathway is accessible for the interconversion of the enantiomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Racemate or racemic mixture of a chiral compound that consists of a 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers and the racemization is to become a racemate.
The following reaction represents alkaline hydrolysis of haloalkanes will be:
$RX+KOH\to ROH+HX$
Where R =alkyl group and X = halogens
Apply the above reaction to given haloalkanes,
(A) 1-Bromo-1-phenylethane reaction with alkaline KOH

(B) 1-chloro-3-methyl butane reaction with alkaline KOH

(C) Bromo ethane reacts with KOH,
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Br+KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+KBr$
(D) 1-chloro propane involves in alkaline hydrolysis
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+KCl$
Since, the products of (B), (C), and (D) do not form Racemate because there is no chiral carbon atom in the products.
The product formed in reaction A having chiral carbon, this hydrolysis will lead to the formation of a racemate or racemic mixture.
Note: The conversation of half of its dextro form into levo form so that the mixture is optically inactive due to the presence of equal amounts of two enantiomers involves the racemization process. This process can be brought by the action of heat, chemical reagents, and autorecemisation. The thermodynamically favorable method is racemization and proceeds spontaneously if a suitable pathway is accessible for the interconversion of the enantiomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




