
All canonical structures of a molecule?
A.Must have different number of unpaired electrons
B.Must have different number of paired electrons
C.Must be always equivalent
D.Need not be always equivalent but they should not differ much in stability.
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint:We need to understand what are canonical structures and their properties of existence. In chemistry we know that resonance is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or ions by the combination of several contributing structures or forms also known as resonance structures or canonical structures. A canonical structure is also known as a resonance structure.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to recall the theory of resonating structures. Resonating structures have similar energy and paired and unpaired electrons and are also known as canonical structures. These are a set of two or more Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons i.e., electrons are distributed around the structure differently.
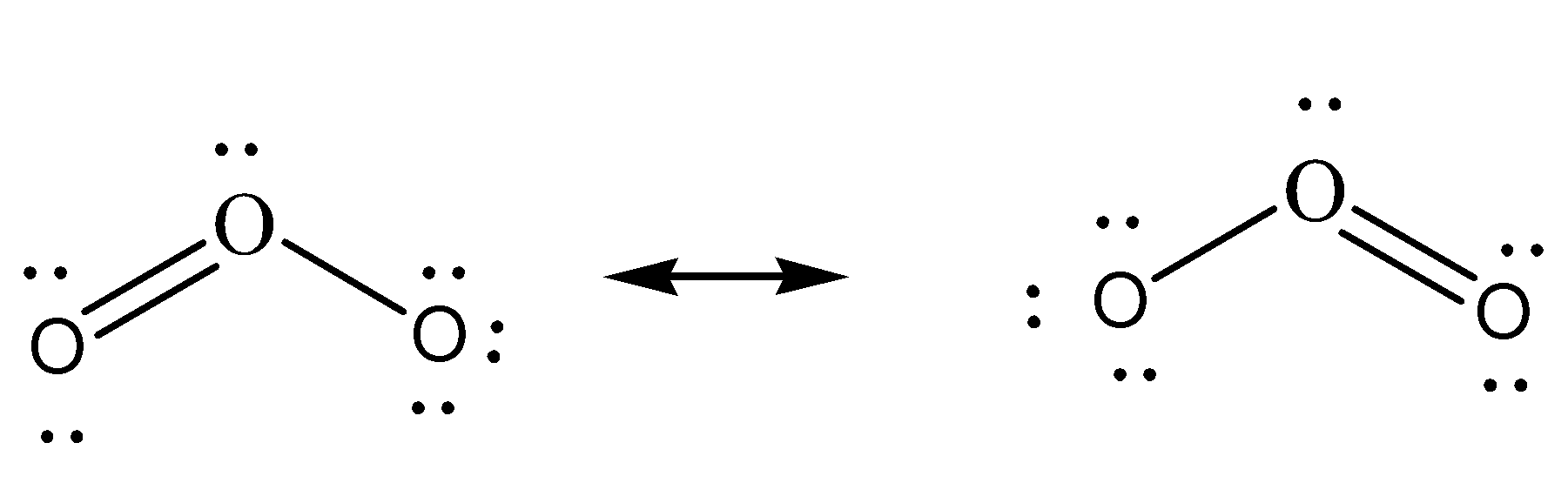
Resonating structures of ozone
Taking the example of ozone, the given structures are equivalent Lewis dot structures, where the number and positions of the atoms are same but the positions of the electrons and bonds are different and double-headed arrows are used to link the resonating structures.
From the example of resonating structures, we can conclude that the resonating structures
-Must have the same number of unpaired electrons.
-Must have same number of paired electrons
-Must be equivalent
-Must have as many as possible resonating structures to attain stability.
Hence, the correct option is option (C).
Note:
It must be noted that the concept of resonance comes under the Valence bond theory of bonding that describes the delocalization of electrons within molecules. The resonance structures are drawn with a double-headed arrow between them. A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer structures.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to recall the theory of resonating structures. Resonating structures have similar energy and paired and unpaired electrons and are also known as canonical structures. These are a set of two or more Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons i.e., electrons are distributed around the structure differently.

Resonating structures of ozone
Taking the example of ozone, the given structures are equivalent Lewis dot structures, where the number and positions of the atoms are same but the positions of the electrons and bonds are different and double-headed arrows are used to link the resonating structures.
From the example of resonating structures, we can conclude that the resonating structures
-Must have the same number of unpaired electrons.
-Must have same number of paired electrons
-Must be equivalent
-Must have as many as possible resonating structures to attain stability.
Hence, the correct option is option (C).
Note:
It must be noted that the concept of resonance comes under the Valence bond theory of bonding that describes the delocalization of electrons within molecules. The resonance structures are drawn with a double-headed arrow between them. A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




