
What is an alpha, beta – unsaturated ketone?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: When any functional group is attached in a compound, then the carbon atom that is adjacent to that functional group is called alpha carbon and the hydrogen atoms on that carbon are alpha hydrogen. The carbon that is attached with alpha carbon is called the beta carbon and its hydrogen atoms are beta hydrogen.
Complete answer:
A ketone consists of the functional group called carbonyl group as$\left( -\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,- \right)$. This group is present in the middle of the carbon chain. The carbon attached with the carbon of this carbonyl group is called an alpha – carbon, while the carbon which is attached with the alpha carbon is called the beta – carbon. When a compound contains a double bond at this $\alpha ,\beta $- carbon alongside with the ketone group, then the compound is called an alpha, beta – unsaturated compound. The general structural formula for $\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketone is,
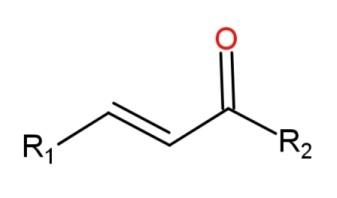 Where R are the alkyl groups
Where R are the alkyl groups
$\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketones are formed as a result of ketol condensation that consist of reacting two ketones same or different in presence of a dilute alkali, which forms a ketol intermediate having an alcohol and a ketone group that on heating produces$\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketone.
An example of self ketol condensation, where both ketones are same (propanone) is:
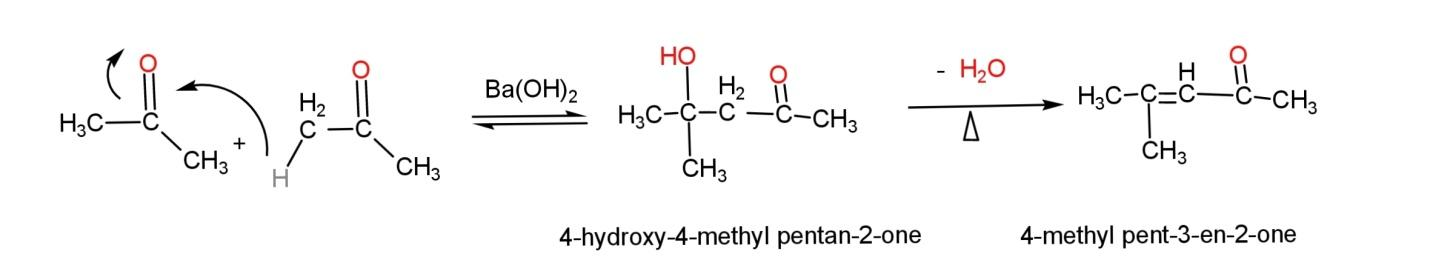
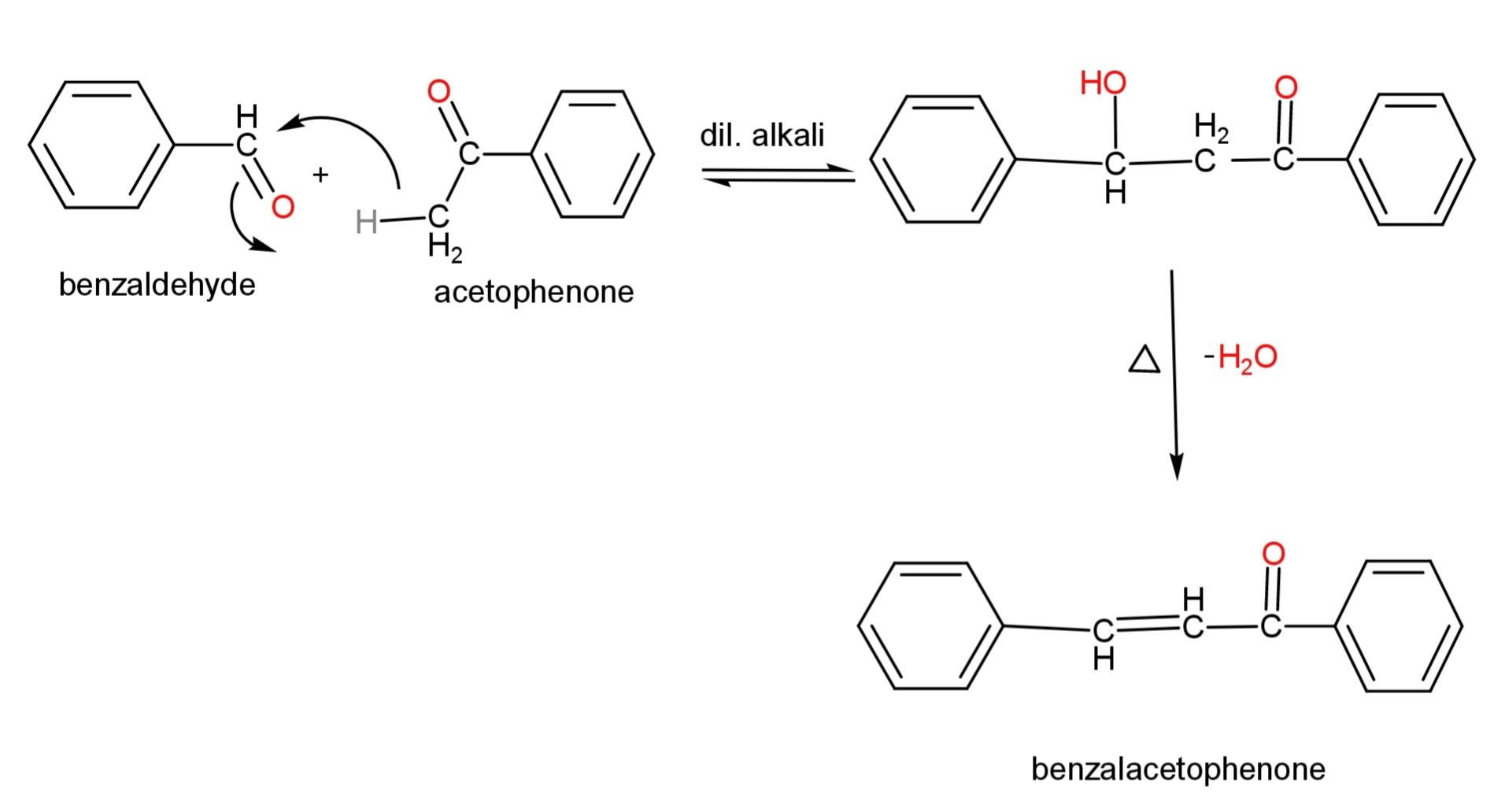
An example of cross ketol condensation, where both are different ketone is,
Hence, an alpha, beta – unsaturated ketone has a double bond on $\alpha ,\beta $- carbon adjacent to the ketone group.
Note:
For the molecules to undergo ketone reaction, it is important that the ketones possess alpha hydrogen, which are the hydrogens present on the carbon which is attached with the ketone group. Alpha hydrogen is acidic and attached with electron withdrawing groups, so the anion formed is stabilized by resonance.
Complete answer:
A ketone consists of the functional group called carbonyl group as$\left( -\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,- \right)$. This group is present in the middle of the carbon chain. The carbon attached with the carbon of this carbonyl group is called an alpha – carbon, while the carbon which is attached with the alpha carbon is called the beta – carbon. When a compound contains a double bond at this $\alpha ,\beta $- carbon alongside with the ketone group, then the compound is called an alpha, beta – unsaturated compound. The general structural formula for $\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketone is,

$\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketones are formed as a result of ketol condensation that consist of reacting two ketones same or different in presence of a dilute alkali, which forms a ketol intermediate having an alcohol and a ketone group that on heating produces$\alpha ,\beta $- unsaturated ketone.
An example of self ketol condensation, where both ketones are same (propanone) is:

An example of cross ketol condensation, where both are different ketone is,

Hence, an alpha, beta – unsaturated ketone has a double bond on $\alpha ,\beta $- carbon adjacent to the ketone group.
Note:
For the molecules to undergo ketone reaction, it is important that the ketones possess alpha hydrogen, which are the hydrogens present on the carbon which is attached with the ketone group. Alpha hydrogen is acidic and attached with electron withdrawing groups, so the anion formed is stabilized by resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




