
Among the following, the branched chain polymer is:
A.PVC
B.polyester
C.low density polyethylene
D.nylon-6,6
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: A polymer is a macromolecule or large molecule which is essentially a combination of many subunits. Polymers may be naturally found in plants and animals (natural polymer) or may be man-made (synthetic polymers).
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when linear chains of one polymer form some branches, then, such polymers are known as branched chain polymers. Low-density polyethylene has a branched chain structure. We can draw its structure in the following way.
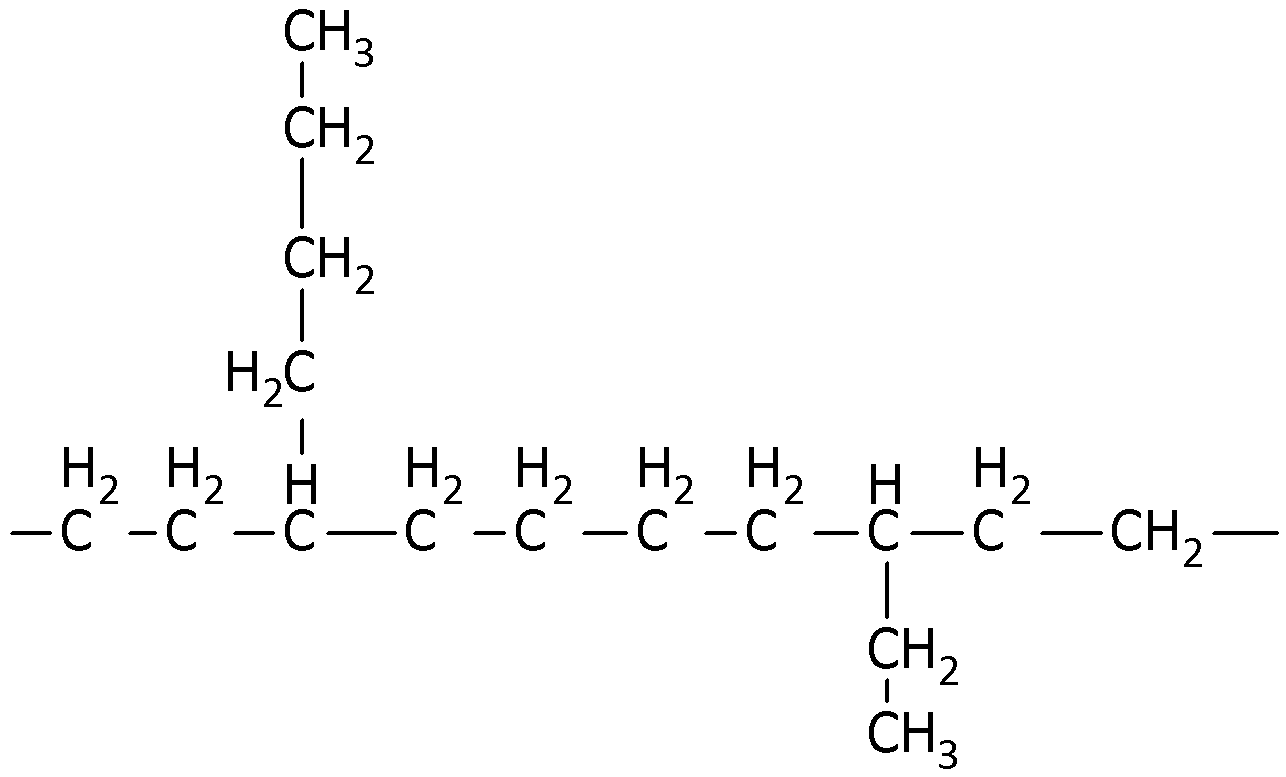
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Polymers are classified in the following way:
1)Linear polymers
2)Branched chain polymers
3) Cross-linked polymers.
In terms of the polymerization, polymers are classified as,
1) Addition polymerization
2) Condensation polymerization
In terms of the monomers, polymers are classified as,
1) Homomer
2) Heteropolymer
In terms of the molecular forces, polymers are classified as,
1) Elastomers
2) Fibres
3) Thermoplastics
4) Thermosetting polymers
In terms of the backbone chain, polymers are classified as,
1) Organic polymers
2) Inorganic polymers
Note:
There are two types of average molecular masses of Polymers. These are:
1)Number Average Molecular Masses
2) Weight Average Molecular Mass
Some important properties of polymers are:
1) As chain length and cross-linking increases the tensile strength of the polymer increases.
2) Polymers do not melt down, they change from crystalline state to semi-crystalline state.
3) Polymers with Van der Waals that links chains are weak, but they produce the polymer with a low melting point
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when linear chains of one polymer form some branches, then, such polymers are known as branched chain polymers. Low-density polyethylene has a branched chain structure. We can draw its structure in the following way.

So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Polymers are classified in the following way:
1)Linear polymers
2)Branched chain polymers
3) Cross-linked polymers.
In terms of the polymerization, polymers are classified as,
1) Addition polymerization
2) Condensation polymerization
In terms of the monomers, polymers are classified as,
1) Homomer
2) Heteropolymer
In terms of the molecular forces, polymers are classified as,
1) Elastomers
2) Fibres
3) Thermoplastics
4) Thermosetting polymers
In terms of the backbone chain, polymers are classified as,
1) Organic polymers
2) Inorganic polymers
Note:
There are two types of average molecular masses of Polymers. These are:
1)Number Average Molecular Masses
2) Weight Average Molecular Mass
Some important properties of polymers are:
1) As chain length and cross-linking increases the tensile strength of the polymer increases.
2) Polymers do not melt down, they change from crystalline state to semi-crystalline state.
3) Polymers with Van der Waals that links chains are weak, but they produce the polymer with a low melting point
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




