
Amphitrichous flagellation has
A. Flagella absent
B. Flagella at one end
C. Flagella at both the ends
D. Flagella all around
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Flagella is a long whip like appendage that functions as a cellular organ of locomotion, found in some bacteria, protozoan and some specialized eukaryotic cells such as sperms. In some eukaryotic cells flagella is covered by the cell membrane.
In eukaryotes flagella moves in “s” shaped motion.
Complete answer:
Appendages are an extra growth of any body part (such as in extremities) which can also be a natural protuberated part. It is mainly found on the sides. Lateral appendage generally means limbs on the sides.
- Appendages include parts of mouth, parts of tail, gills in many animals, legs which can be for walking, climbing etc.
- Appendages help in movement from one place to another, feeding and grooming.
- In bacteria’s flagella is one the example of lateral appendages.
- Flagella are a long locomotory structure present in many single cell organisms which help them in locomotion.
- In some eukaryotic cells flagella is covered by the cell membrane.
- In eukaryotes flagella moves in “s” shaped motion. But we are not able to see the flagella on a microscope.
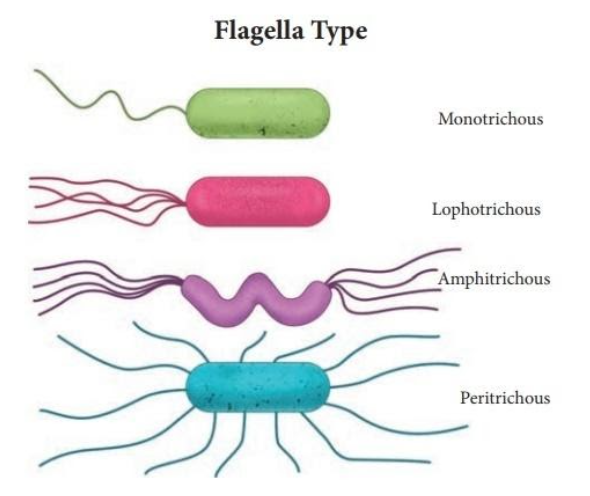
There are mainly four types of flagella.
- Monotrichous: It means having one flagellum. For example: vibrio cholera
- Amphitrichous: It means single flagellum on both sides. For example: Alkalinegens faecalis.
- Lophotrichous: Tufts of flagella at one or both sides. For example: spirillum
- Peritrichous: they have flagella spread across the body except the poles. For example: E.coli.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Cilia: It is a tiny, hair-like projection found on the cell surface of various mammals. It can be single or present in groups.
Pseudopodia: It is cytoplasmic outgrowth seen in amoeba.
Pseudopodia also helps in locomotion in amoeba. Due to the presence of pseudopodia in amoeba it helps in altering the shape of amoeba.
In eukaryotes flagella moves in “s” shaped motion.
Complete answer:
Appendages are an extra growth of any body part (such as in extremities) which can also be a natural protuberated part. It is mainly found on the sides. Lateral appendage generally means limbs on the sides.
- Appendages include parts of mouth, parts of tail, gills in many animals, legs which can be for walking, climbing etc.
- Appendages help in movement from one place to another, feeding and grooming.
- In bacteria’s flagella is one the example of lateral appendages.
- Flagella are a long locomotory structure present in many single cell organisms which help them in locomotion.
- In some eukaryotic cells flagella is covered by the cell membrane.
- In eukaryotes flagella moves in “s” shaped motion. But we are not able to see the flagella on a microscope.
There are mainly four types of flagella.
- Monotrichous: It means having one flagellum. For example: vibrio cholera
- Amphitrichous: It means single flagellum on both sides. For example: Alkalinegens faecalis.
- Lophotrichous: Tufts of flagella at one or both sides. For example: spirillum
- Peritrichous: they have flagella spread across the body except the poles. For example: E.coli.

Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Cilia: It is a tiny, hair-like projection found on the cell surface of various mammals. It can be single or present in groups.
Pseudopodia: It is cytoplasmic outgrowth seen in amoeba.
Pseudopodia also helps in locomotion in amoeba. Due to the presence of pseudopodia in amoeba it helps in altering the shape of amoeba.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




