
An acyclic hydrocarbon P, having molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ , gave acetone as the only organic product through the following sequence of reactions, in which Q is an intermediate organic compound. The structure of compound P is:
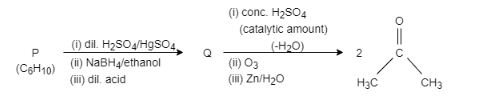
A.\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}-C\equiv C-H\]
B.\[{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C-C\equiv C-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\]
C.${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-C\equiv C-C{{H}_{3}}$
D.${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C-C\equiv CH$
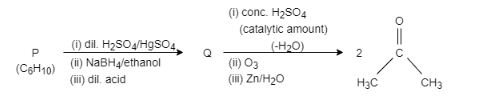
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: Acyclic hydrocarbon is defined as the organic compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon atoms that are linked together in straight chains. Most of the acyclic hydrocarbons are flammable, therefore, they are used as fuels. Acyclic hydrocarbons are non – polar hence, they are insoluble in water.
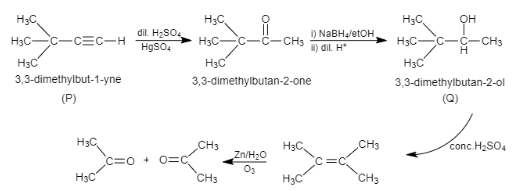
Complete step-by-step answer:In this question, if we need to find the reactant P, we have to consider reverse reaction. In compound Q, dehydration takes place, that means, removal of water, which generates alkene and then this alkene goes through ozonolysis process. It results in the formation of two moles of acetone.
Q is the compound which gets dehydrated and forms alkene and further ozonolysis takes place and forms acetone. Therefore, Q is \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol. To produce \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol, P is reacted with dilute sulphuric acid and mercury sulphate and is further reacted with sodium borohydride and ethanol in presence of dilute acid. Therefore, P is \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]one.
Acetone is defined as a chemical compound with a chemical formula, $C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ . It is a colorless, flammable organic solvent and is also the smallest ketone. It is also known as propanone. It is widely used for cleaning in households and also in industrial solvents because it can dissolve other substances.
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:Ozonolysis is defined as a chemical reaction in which ozone is used to cleave unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, which can result in the formation of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids.
Here, product Q, that is, \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol is an intermediate. Intermediate is defined as a highly reactive short – lived molecule, that quickly converts it into a stable molecule during a chemical reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:In this question, if we need to find the reactant P, we have to consider reverse reaction. In compound Q, dehydration takes place, that means, removal of water, which generates alkene and then this alkene goes through ozonolysis process. It results in the formation of two moles of acetone.
Q is the compound which gets dehydrated and forms alkene and further ozonolysis takes place and forms acetone. Therefore, Q is \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol. To produce \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol, P is reacted with dilute sulphuric acid and mercury sulphate and is further reacted with sodium borohydride and ethanol in presence of dilute acid. Therefore, P is \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]one.
Acetone is defined as a chemical compound with a chemical formula, $C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ . It is a colorless, flammable organic solvent and is also the smallest ketone. It is also known as propanone. It is widely used for cleaning in households and also in industrial solvents because it can dissolve other substances.

Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:Ozonolysis is defined as a chemical reaction in which ozone is used to cleave unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, which can result in the formation of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids.
Here, product Q, that is, \[3,3-\]dimethylbutan\[-2-\]ol is an intermediate. Intermediate is defined as a highly reactive short – lived molecule, that quickly converts it into a stable molecule during a chemical reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




