
An enzyme not used in Krebs’s cycle is:
(a) Aconitase
(b) Decarboxylase
(c) Fumarase
(d) Aldolase
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Krebs’s cycle or citric acid is a cyclic process of 8 enzyme reactions which occur in mitochondria. It converts acetyl CoA to carbon dioxide accompanied by the release of energy. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
Complete step by step answer:
2 molecules of pyruvate are obtained from glycolysis which occurs in the cytosol. Now, this pyruvic acid molecule is acted upon by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. The enzyme catalyzes the addition of coenzyme-A by oxidative decarboxylation. One molecule of NADH is reduced in this reaction. In the next reaction, acetyl CoA which is a 5C containing compound is converted to citrate (6C) by the action of enzyme citrate synthase. Citrate is then converted to Iso-citrate under the action of enzyme aconitase. Over the course of the next 2 reactions, succinate (4C) is obtained. Succinate is then converted to fumarate by a dehydrogenation reaction catalyzed by enzyme fumarase.
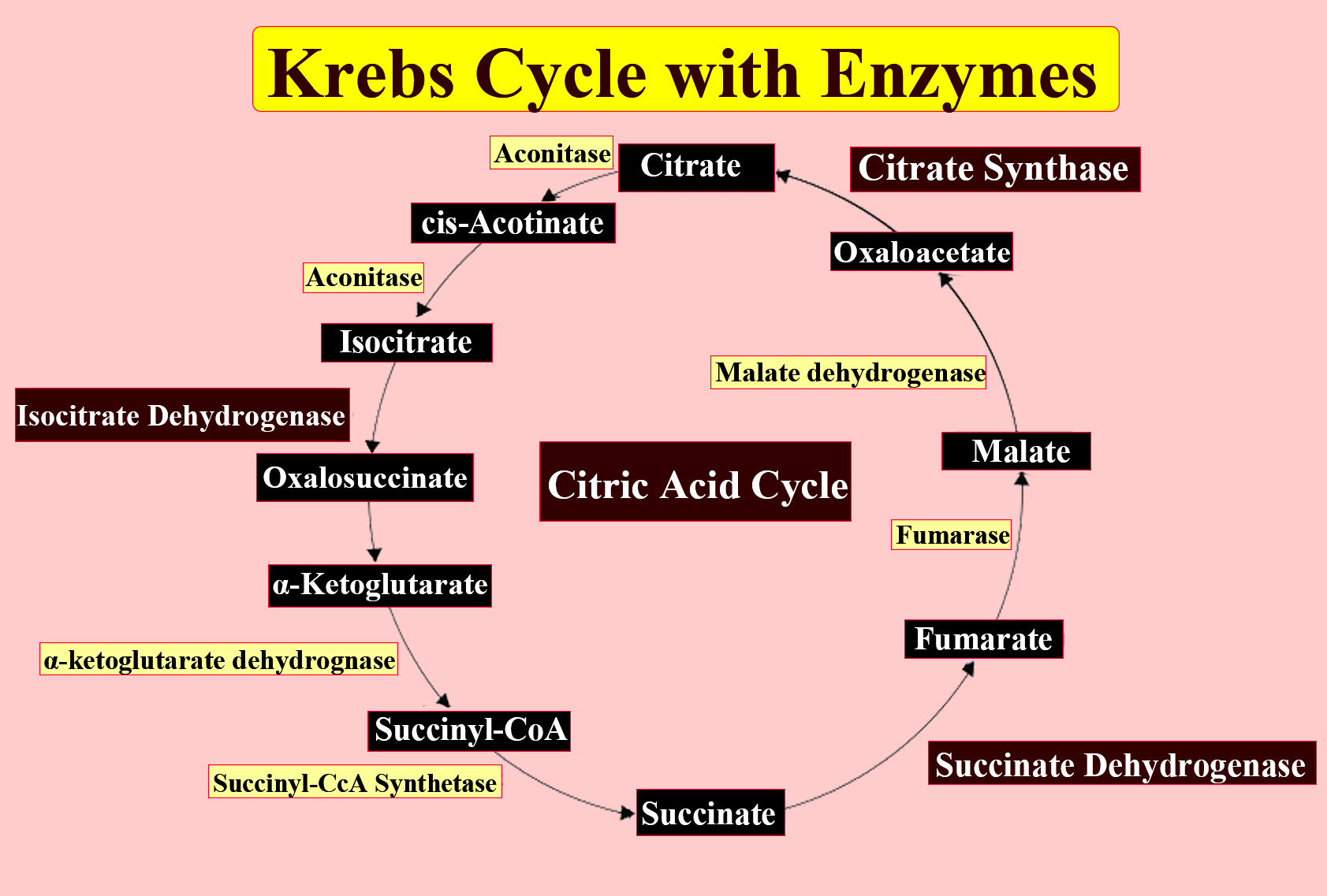
This can be better understood from the diagram given below:
On the other hand, aldolase is an enzyme from the glycolytic pathway. It cleaves one molecule of fructose 1,6 bisphosphate into one molecule of 3 phosphoglyceraldehyde and one of dihydroxyacetone phosphate. So, aldolase is not an enzyme for Krebs’s cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Aldolase’.
Note: Glycolysis and Krebs’s cycle are linked processes that together complete cellular respiration. The end product of glycolysis is 2 molecules of pyruvate. The cycle mentioned above is always operating in two turns i.e. one cycle per pyruvate molecule. After completion of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain, each glucose molecule yields 38ATP molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
2 molecules of pyruvate are obtained from glycolysis which occurs in the cytosol. Now, this pyruvic acid molecule is acted upon by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. The enzyme catalyzes the addition of coenzyme-A by oxidative decarboxylation. One molecule of NADH is reduced in this reaction. In the next reaction, acetyl CoA which is a 5C containing compound is converted to citrate (6C) by the action of enzyme citrate synthase. Citrate is then converted to Iso-citrate under the action of enzyme aconitase. Over the course of the next 2 reactions, succinate (4C) is obtained. Succinate is then converted to fumarate by a dehydrogenation reaction catalyzed by enzyme fumarase.

This can be better understood from the diagram given below:
On the other hand, aldolase is an enzyme from the glycolytic pathway. It cleaves one molecule of fructose 1,6 bisphosphate into one molecule of 3 phosphoglyceraldehyde and one of dihydroxyacetone phosphate. So, aldolase is not an enzyme for Krebs’s cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Aldolase’.
Note: Glycolysis and Krebs’s cycle are linked processes that together complete cellular respiration. The end product of glycolysis is 2 molecules of pyruvate. The cycle mentioned above is always operating in two turns i.e. one cycle per pyruvate molecule. After completion of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain, each glucose molecule yields 38ATP molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




