
An equilateral glass prism is made of a material of refractive index 1.500. Find its angle of minimum deviation.
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: We need to note the criteria for minimum deviation to occur in an equilateral prism. As we know for minimum deviation to occur, the angle of refraction of the light should be equal to half of the angle of the prism. Then using Snell’s law we can calculate the angle of incidence. By substituting the angle of incidence in the formula, we get the minimum deviation.
Complete step by step answer:
The rays go through minimum deviation only when they pass symmetrically through the prism.
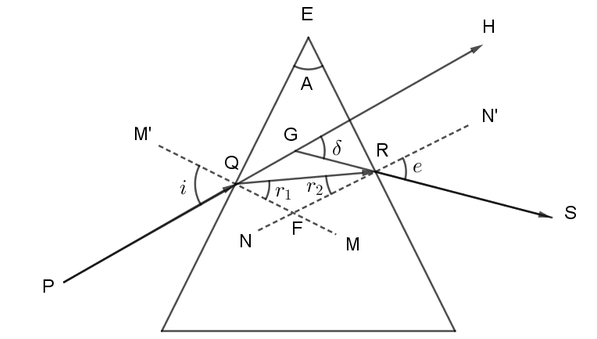
Minimum deviation $\delta =2i-A$
An equilateral prism has a prism angle A$={{60}^{\circ }}$
For minimum deviation, the angle of refraction should be half of the prism angle.
So $r=\dfrac{A}{2}={{30}^{\circ }}$
Now by using Snell’s law
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$ (Where ${{n}_{a}}$is refractive index in air and ${{n}_{g}}$ is refractive index in glass)
$\sin i=1.5\sin 30$
$i={{48.6}^{\circ }}$
Minimum deviation $\delta =2\times 48.6-60={{37.2}^{\circ }}$
Note:
Angle of prism is the angle made by the two sides of the prism through which the incident light enters and the emergent light exits. In a prism, with increase in the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation decreases. This happens to a particular angle only. The position of the angle of incidence where the angle of deviation in a prism is minimum is called the Minimum Deviation Position of the prism and that very deviation angle is known as the Minimum Angle of Deviation. It is also responsible for phenomena like halos and sundogs, produced by the deviation of sunlight by the hexagonal ice crystals in the air bending light.
Complete step by step answer:
The rays go through minimum deviation only when they pass symmetrically through the prism.

Minimum deviation $\delta =2i-A$
An equilateral prism has a prism angle A$={{60}^{\circ }}$
For minimum deviation, the angle of refraction should be half of the prism angle.
So $r=\dfrac{A}{2}={{30}^{\circ }}$
Now by using Snell’s law
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$ (Where ${{n}_{a}}$is refractive index in air and ${{n}_{g}}$ is refractive index in glass)
$\sin i=1.5\sin 30$
$i={{48.6}^{\circ }}$
Minimum deviation $\delta =2\times 48.6-60={{37.2}^{\circ }}$
Note:
Angle of prism is the angle made by the two sides of the prism through which the incident light enters and the emergent light exits. In a prism, with increase in the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation decreases. This happens to a particular angle only. The position of the angle of incidence where the angle of deviation in a prism is minimum is called the Minimum Deviation Position of the prism and that very deviation angle is known as the Minimum Angle of Deviation. It is also responsible for phenomena like halos and sundogs, produced by the deviation of sunlight by the hexagonal ice crystals in the air bending light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




