
An equilateral triangle has side length 8. The area of the region containing all points outside the triangle but not more than 3 units from a point on the triangle is
$
A.\;\;9\left( {8 + \pi } \right) \\
B.\;\;8\left( {9 + \pi } \right) \\
C.\;\;9\left( {8 + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) \\
D.\;\;8\left( {9 + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) \\
$
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: An equilateral triangle is one in which all three sides are congruent (same length). Because it also has the property that all three interior angles are equal, it really is the same thing as an equiangular triangle.
All three angles of an equilateral triangle are always 60°. Since the angles are the same and the internal angles of any triangle always add to 180°, each is 60°.
The area of an equilateral triangle can be calculated in the usual way, but in this special case of an equilateral triangle, it is also given by the formula:
\[Area = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{S^2}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
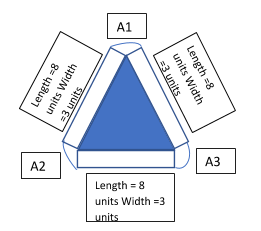
So, as we can see in the figure there are three rectangles
\[
Area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}a{\text{ }}rectangle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}Length {\times} Width \\
\Rightarrow Area = 8 {\times} 3 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 24\;square\;units \\
\]
As there are three rectangles so area will be
\[
\Rightarrow Area = 3 {\times} 24 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 72\;square\;units \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots (1) \\
\]
Here we can note that
Area of $A_1$=Area of $A_2$=Area of $A_3$
Angle $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ making with the equilateral triangle is \[120^\circ \] as it is intersecting the angle with the equilateral triangle.
We will use area of a Sector Formula
\[Area = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta ^\circ }}{{360^\circ }}} \right) \pi {r^2}\]
where:
$\theta ^\circ $ is the central angle in degrees.
r is the radius of the circle of which the sector is part.
π is Pi, approximately 3.142
So, the area of A1
\[
Area = \left( {\dfrac{{120}}{{360}}} \right) {\times} \pi {\times} {3^2} \\
\Rightarrow Area = \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right){\times}\pi {\times}9 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 3\pi \\
\\
\]
As area of sectors $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ are equal so total area of $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ will be: -
\[Total{\text{ }}area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}{A_1},{\text{ }}{A_2}{\text{ }} and {\text{ }}{A_3} = 3{\times}3\pi = 9\pi \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots (2)\]
Using equation (1) and (2)
The area of the region containing all points outside the triangle but not more than 3 units from a point on the triangle is
$ = 72 + 9\pi = 9(8 + \pi ) units$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: There are three rectangular areas, each of which are equal. And, here are also three other "curved" areas, each of these areas are also equal. We will just add the area of all three rectangles and all three curves.
All three angles of an equilateral triangle are always 60°. Since the angles are the same and the internal angles of any triangle always add to 180°, each is 60°.
The area of an equilateral triangle can be calculated in the usual way, but in this special case of an equilateral triangle, it is also given by the formula:
\[Area = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{S^2}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:

So, as we can see in the figure there are three rectangles
\[
Area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}a{\text{ }}rectangle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}Length {\times} Width \\
\Rightarrow Area = 8 {\times} 3 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 24\;square\;units \\
\]
As there are three rectangles so area will be
\[
\Rightarrow Area = 3 {\times} 24 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 72\;square\;units \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots (1) \\
\]
Here we can note that
Area of $A_1$=Area of $A_2$=Area of $A_3$
Angle $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ making with the equilateral triangle is \[120^\circ \] as it is intersecting the angle with the equilateral triangle.
We will use area of a Sector Formula
\[Area = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta ^\circ }}{{360^\circ }}} \right) \pi {r^2}\]
where:
$\theta ^\circ $ is the central angle in degrees.
r is the radius of the circle of which the sector is part.
π is Pi, approximately 3.142
So, the area of A1
\[
Area = \left( {\dfrac{{120}}{{360}}} \right) {\times} \pi {\times} {3^2} \\
\Rightarrow Area = \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right){\times}\pi {\times}9 \\
\Rightarrow Area = 3\pi \\
\\
\]
As area of sectors $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ are equal so total area of $A_1$, $A_2$ and $A_3$ will be: -
\[Total{\text{ }}area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}{A_1},{\text{ }}{A_2}{\text{ }} and {\text{ }}{A_3} = 3{\times}3\pi = 9\pi \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots (2)\]
Using equation (1) and (2)
The area of the region containing all points outside the triangle but not more than 3 units from a point on the triangle is
$ = 72 + 9\pi = 9(8 + \pi ) units$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: There are three rectangular areas, each of which are equal. And, here are also three other "curved" areas, each of these areas are also equal. We will just add the area of all three rectangles and all three curves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





