
An ideal flow of any fluid must fulfill the following
A. Newton’s law of viscosity
B. Newton’s law of motion
C. Pascal’s law
D. Continuity equation
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: For any type of flow of liquids, the “Continuity equation” must be satisfied. This is to satisfy the conservation of mass for the flow of liquid.
Complete step by step answer:
An ideal flow of any fluid must fulfill the “Continuity equation”. The continuity equation applies to all fluids whether incompressible (ideal) or compressible (non-ideal), Newtonian or non-Newtonian fluids. Continuity equation expresses the law of conservation of mass at each point in a fluid and therefore must be satisfied at every point in the field of flow.
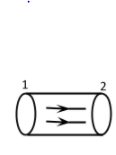
Let us consider a pipe of non-uniform length. The area at point 1 is greater than that of point 2. If mass ${m_1}$ of liquid is entering from point 1 and mass ${m_2}$of liquid is going out from point 2 in the field of flow, then by the law of conservation of mass, ${m_1}$must be equal to ${m_2}$.
So, ${m_1} = {m_2}\,...............\left( i \right)$
Let density of the liquid is $\rho $ and volume flowed from point 1 to point 2 in the field of flow are ${V_1}$and ${V_2}$respectively, then from equation (i).
${m_1} = {m_2}$
or $\rho {V_1} = \rho {V_2}$
or ${V_1} = {V_2}........\left( {ii} \right)$
Now dividing both side of equation (ii) by time `t’ , we have
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{t} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{t}.........\left( {iii} \right)$
The quantity $\dfrac{{volume}}{{time}}$in the field of flow represents volume flow rate (R) by which the liquid flows.
So, from equation (iii), we have
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{t} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{t}$
Or ${R_1} = {R_2}$
If the liquid enters into a pipe with rate ${R_1}$and goes out with rate ${R_2}$, then ${R_1} = {R_2}$.
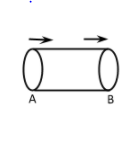
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The rate of flow of liquid at any two points into the flow field must be the same. We can also say that when a fluid is in motion , its motion is in accordance with conservation of mass, that is mass rate of flow is the same across the length of flow of liquid which is nothing but an equation of continuity.
Complete step by step answer:
An ideal flow of any fluid must fulfill the “Continuity equation”. The continuity equation applies to all fluids whether incompressible (ideal) or compressible (non-ideal), Newtonian or non-Newtonian fluids. Continuity equation expresses the law of conservation of mass at each point in a fluid and therefore must be satisfied at every point in the field of flow.

Let us consider a pipe of non-uniform length. The area at point 1 is greater than that of point 2. If mass ${m_1}$ of liquid is entering from point 1 and mass ${m_2}$of liquid is going out from point 2 in the field of flow, then by the law of conservation of mass, ${m_1}$must be equal to ${m_2}$.
So, ${m_1} = {m_2}\,...............\left( i \right)$
Let density of the liquid is $\rho $ and volume flowed from point 1 to point 2 in the field of flow are ${V_1}$and ${V_2}$respectively, then from equation (i).
${m_1} = {m_2}$
or $\rho {V_1} = \rho {V_2}$
or ${V_1} = {V_2}........\left( {ii} \right)$
Now dividing both side of equation (ii) by time `t’ , we have
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{t} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{t}.........\left( {iii} \right)$
The quantity $\dfrac{{volume}}{{time}}$in the field of flow represents volume flow rate (R) by which the liquid flows.
So, from equation (iii), we have
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{t} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{t}$
Or ${R_1} = {R_2}$
If the liquid enters into a pipe with rate ${R_1}$and goes out with rate ${R_2}$, then ${R_1} = {R_2}$.

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The rate of flow of liquid at any two points into the flow field must be the same. We can also say that when a fluid is in motion , its motion is in accordance with conservation of mass, that is mass rate of flow is the same across the length of flow of liquid which is nothing but an equation of continuity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




