
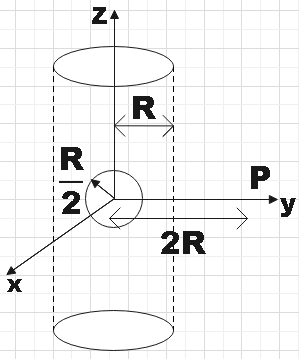
An infinitely long solid cylinder of radius R has a uniform volume charge density $\rho $. It has a spherical cavity of radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ with its centre on the axis of the cylinder as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the electric field at the point P, which is at a distance 2R from the axis of the cylinder is given by the expression$\dfrac{23\rho R}{16k{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ . The value of k is:
A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9

Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could find the electric field at a point at a certain distance for an infinitely long cylinder and also for a sphere. Then by taking their sum will give you the net electric field at that point. You could then compare that electric field with the one given in the question and hence get the value of k.
Formula used:
Electric field due to infinite cylinder,
${{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{2R}$
Electric field due to sphere,
${{E}_{S}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{{{d}^{2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have to first find the net electric field at point P which would be the sum of that due to the cylinder and that due to the cavity present in it.
For the cylinder volume charge density$\rho $ , the linear charge density could be given by,
$\lambda =\rho \times A$ ………………………………….. (1)
Electric field due to the infinite cylinder could be given as,
${{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{2R}$
From (1),
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\left( \rho A \right)}{2R}=\dfrac{\rho \pi {{R}^{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}R}$
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{\rho \pi R}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{\rho R}{4{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ ………………………………….. (2)
Now, the electric field due to the spherical cavity will be,
${{E}_{S}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{{{d}^{2}}}$
But,
$Q=-\rho V=-\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{3}}\rho $
Also,
$d=2R$
${{E}_{S}}=-\dfrac{4\pi {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{3}} \rho }{3\times 4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( 2R \right)}^{2}}}=-\dfrac{\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ ………………………………….. (3)
Electric field at P will be the sum of (2) and (3).
$E={{E}_{C}}+{{E}_{S}}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{\rho R}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\left( \dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{96} \right)$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{23\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{{{0}_{{}}}}}}$ ………………………………………. (4)
But we are given the net electric field at point P to be,
$E=\dfrac{23\rho R}{16k{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ …………………………………… (5)
Equating (4) and (5) we get,
$\dfrac{23\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{23\rho R}{16k{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
$\Rightarrow 4k=24$
$\therefore k=6$
Therefore, we found the value of k to be 6.
Note: We normally use the constant ‘k’ to denote $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ in majority of the formulas related to electrodynamics. So one shouldn’t confuse it with the one mentioned in the question. We have made minor modifications according to the question in the standard equations for the electric field due to the sphere and infinite cylinder.
Formula used:
Electric field due to infinite cylinder,
${{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{2R}$
Electric field due to sphere,
${{E}_{S}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{{{d}^{2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have to first find the net electric field at point P which would be the sum of that due to the cylinder and that due to the cavity present in it.
For the cylinder volume charge density$\rho $ , the linear charge density could be given by,
$\lambda =\rho \times A$ ………………………………….. (1)
Electric field due to the infinite cylinder could be given as,
${{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{2R}$
From (1),
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2\left( \rho A \right)}{2R}=\dfrac{\rho \pi {{R}^{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}R}$
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{C}}=\dfrac{\rho \pi R}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{\rho R}{4{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ ………………………………….. (2)
Now, the electric field due to the spherical cavity will be,
${{E}_{S}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{{{d}^{2}}}$
But,
$Q=-\rho V=-\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{3}}\rho $
Also,
$d=2R$
${{E}_{S}}=-\dfrac{4\pi {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{3}} \rho }{3\times 4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( 2R \right)}^{2}}}=-\dfrac{\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ ………………………………….. (3)
Electric field at P will be the sum of (2) and (3).
$E={{E}_{C}}+{{E}_{S}}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{\rho R}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\left( \dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{96} \right)$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{23\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{{{0}_{{}}}}}}$ ………………………………………. (4)
But we are given the net electric field at point P to be,
$E=\dfrac{23\rho R}{16k{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ …………………………………… (5)
Equating (4) and (5) we get,
$\dfrac{23\rho R}{96{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{23\rho R}{16k{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
$\Rightarrow 4k=24$
$\therefore k=6$
Therefore, we found the value of k to be 6.
Note: We normally use the constant ‘k’ to denote $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ in majority of the formulas related to electrodynamics. So one shouldn’t confuse it with the one mentioned in the question. We have made minor modifications according to the question in the standard equations for the electric field due to the sphere and infinite cylinder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




